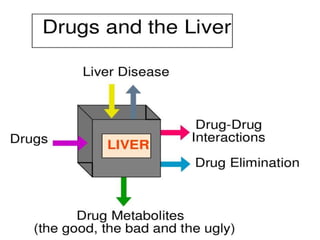
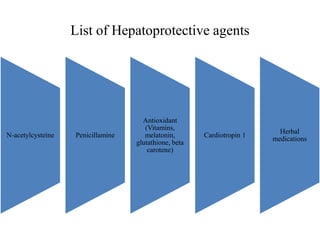
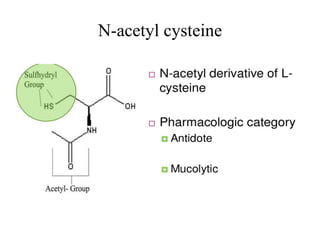
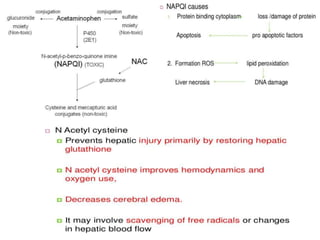
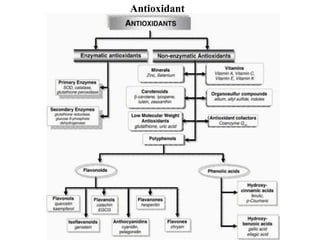
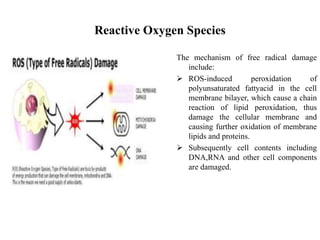
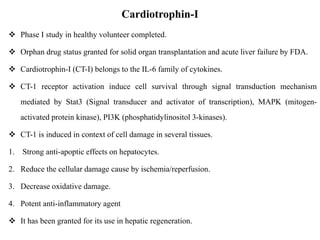
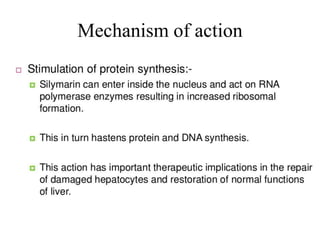
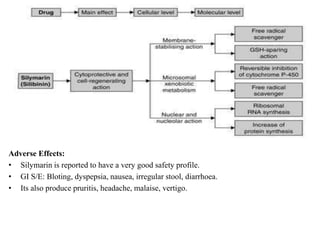
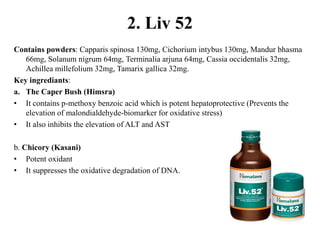
The document discusses hepatoprotective agents that support liver health and prevent liver damage caused by toxins, drugs, and diseases. It categorizes these agents into hepatotropic and hepatoprotective types, detailing their mechanisms of action, including antioxidant effects and cellular regeneration. Notable agents mentioned include N-acetylcysteine, penicillamine, and herbal medications like silymarin, along with future directions for addressing increasing hepatotoxicity issues.