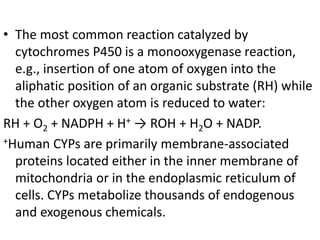
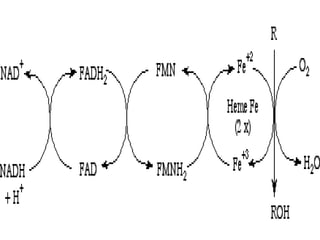
The cytochrome P450 system is a group of enzymes found mainly in the liver and gut that control the concentrations of endogenous substances and drugs. It is comprised of about 40-50 isoenzymes encoded by individual genes. The system was originally identified by a characteristic pigment seen in hepatic microsomes under spectrophotometric analysis with a peak absorption at 450nm. A few specific cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, such as CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, are responsible for metabolizing commonly used drugs by catalyzing oxidation reactions that make the substrates more water-soluble and excretable. The metabolism of drugs can be altered by substances that induce or inhibit these cytochrome P450