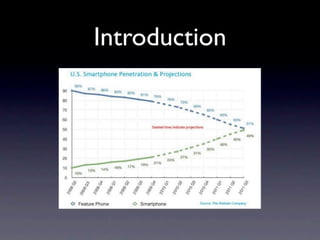
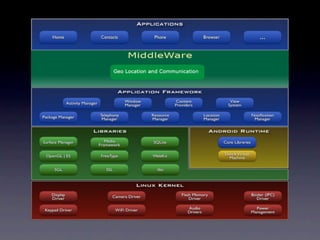
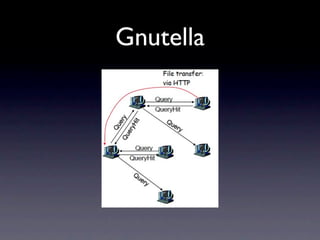
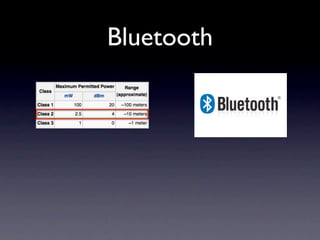
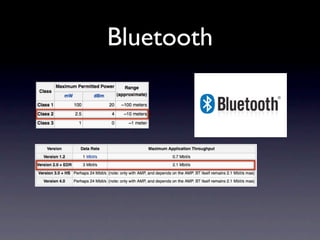
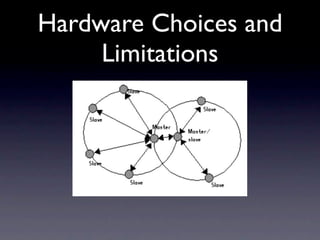
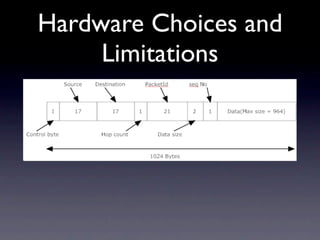
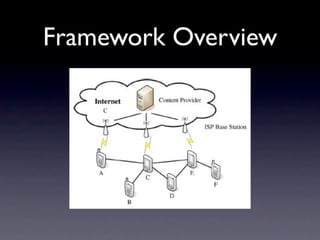
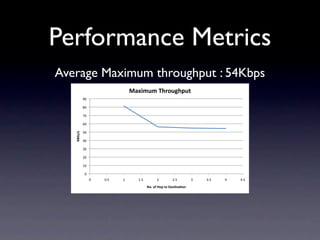
This document outlines a peer-to-peer (P2P) communication framework developed for the Android platform as an alternative to traditional mobile networks. It discusses the motivation to lower infrastructure costs, proposes a solution using an open-source P2P framework, and recaps the work done including server implementation and literature reviews. The document then covers design decisions around using the Android platform, hardware limitations, and a modified Gnutella network design. It presents implementation results and performance metrics and demonstrates the framework through a demo. Limitations discussed include Bluetooth capabilities and dependency on a geo-location server, with future work proposed around Wi-Fi support, optimization, and security.