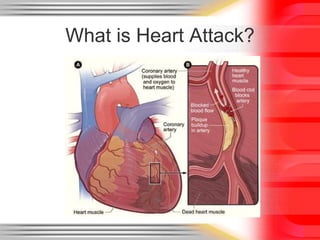
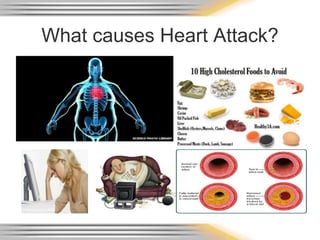
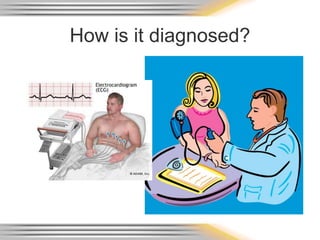
A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, damaging the heart muscle. It is typically caused by coronary heart disease, which is related to risk factors like smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and physical inactivity. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort. Diagnosis involves electrocardiograms, blood tests for cardiac enzymes, echocardiograms, and sometimes cardiac catheterization. Prevention focuses on not smoking, regular exercise, a healthy diet, weight control, and managing conditions like high blood pressure and cholesterol.