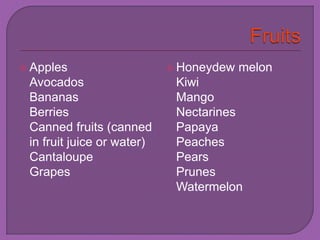
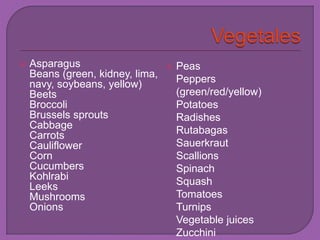
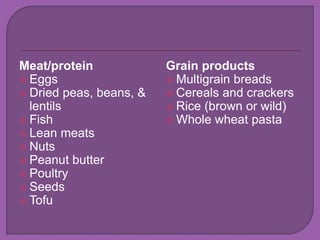
The document discusses fiber and its effects on digestion. It explains that there are two types of fiber - soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and helps slow digestion, while insoluble fiber speeds up digestion. Getting enough fiber is important for digestive health as it can help with conditions like IBS, acid reflux, constipation, and can lower cholesterol. The document provides recommendations for increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, whole grains and supplements.