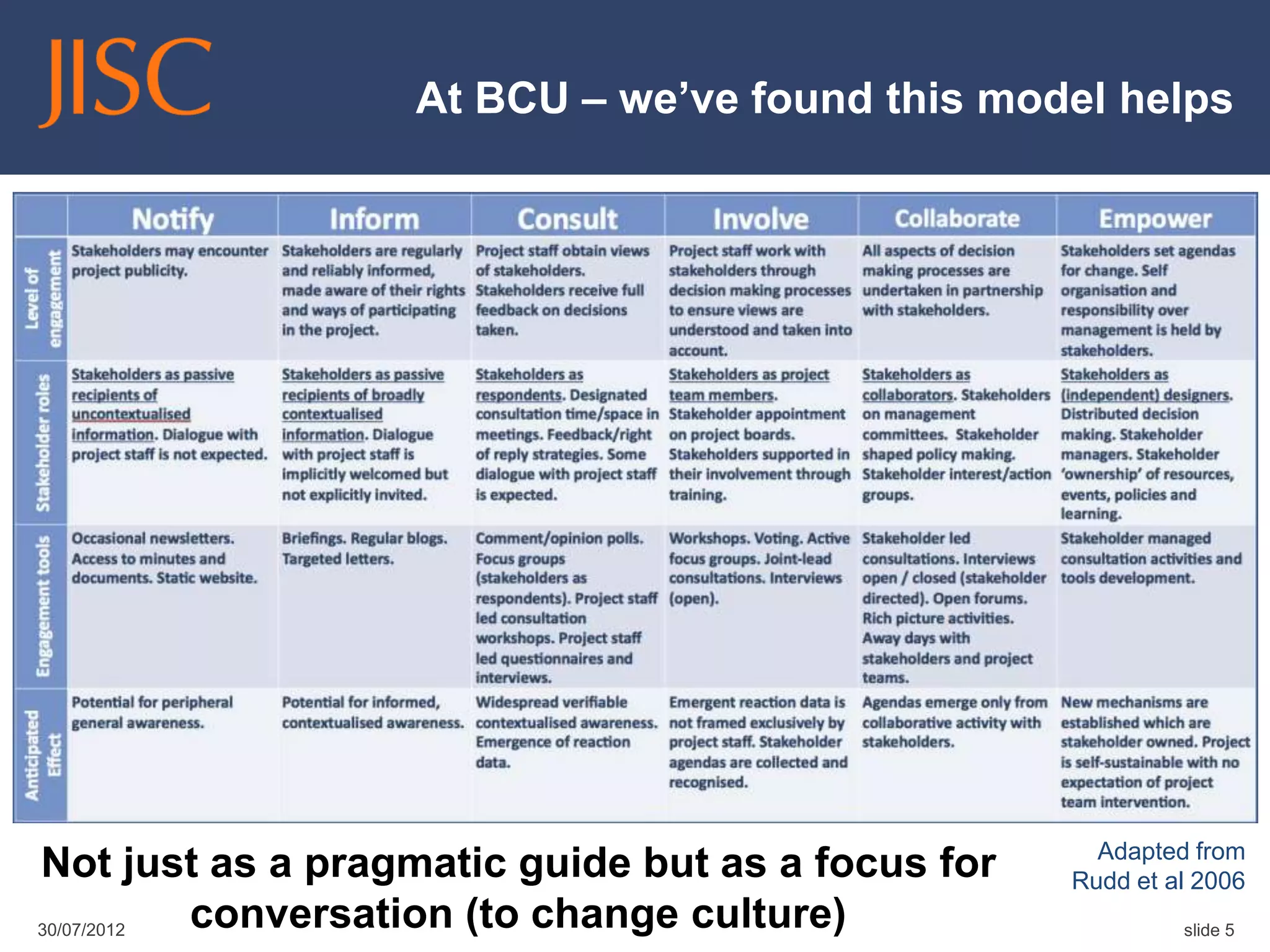
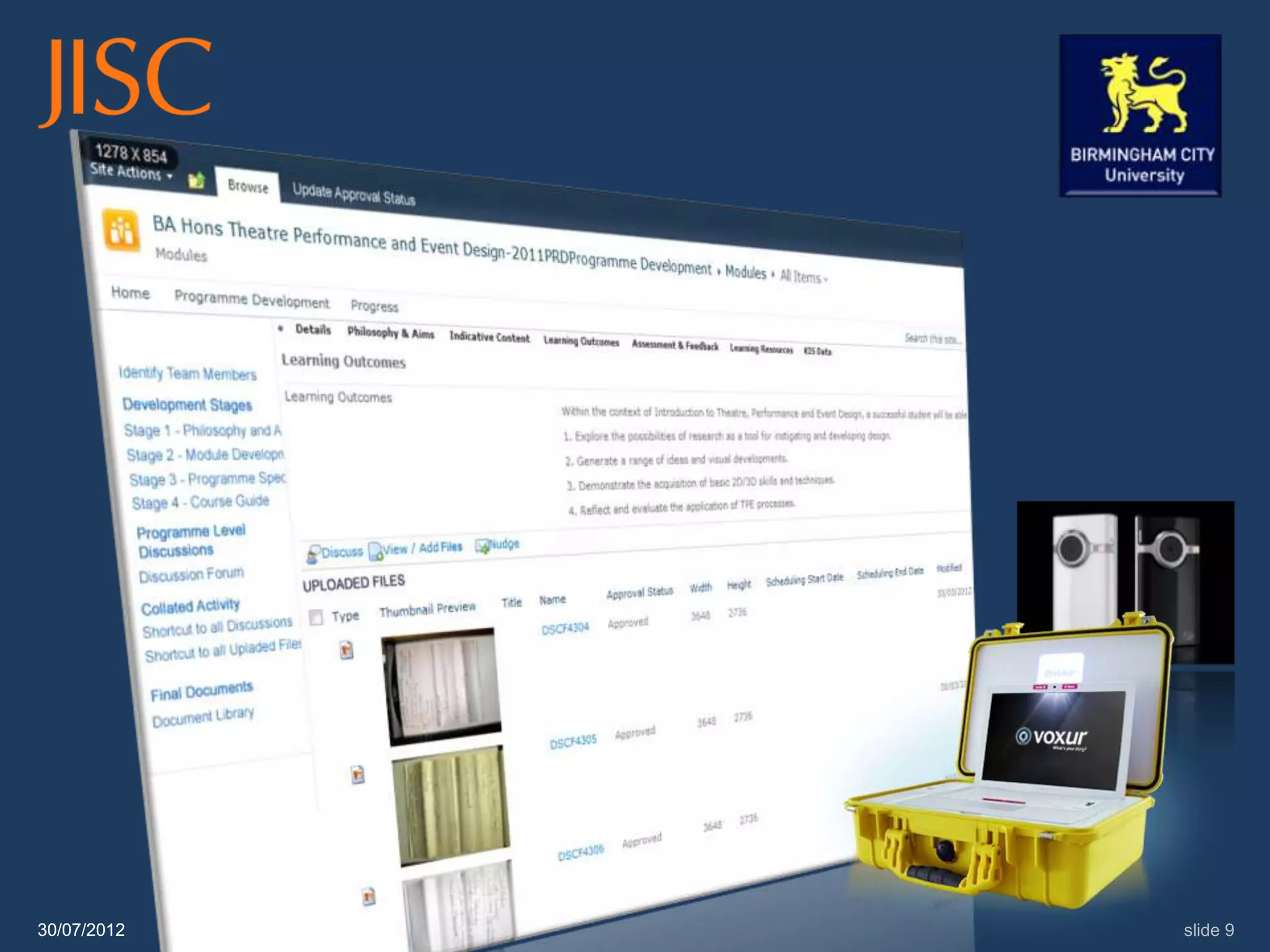
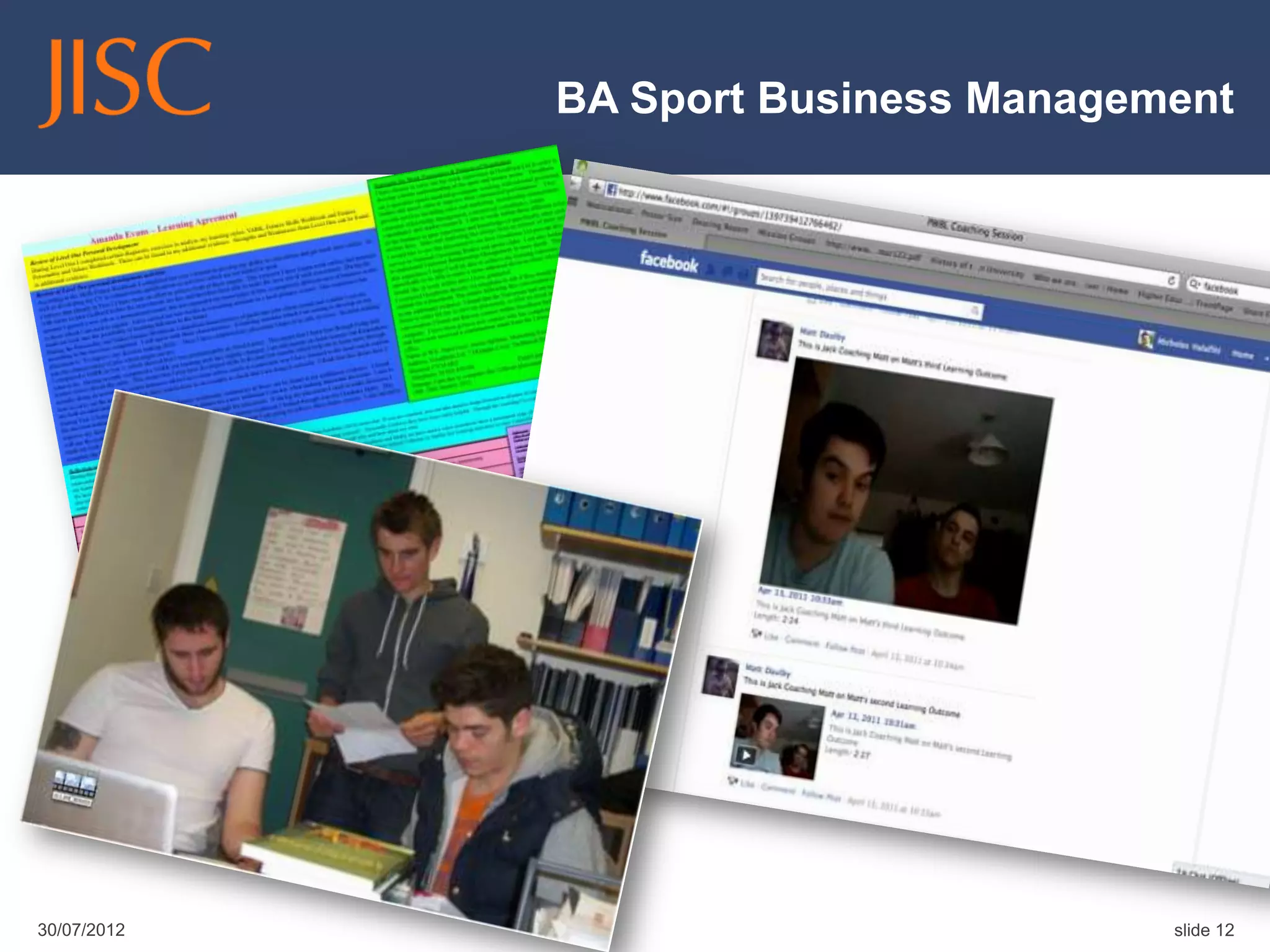
The document discusses the concept of students as co-creators of the curriculum, emphasizing the importance of a broader definition of 'curriculum' that includes the entire academic experience. It outlines various initiatives at institutions like BCU and Leeds Met that engage students in curriculum design and development, fostering a collaborative educational environment. The presentation also highlights the benefits of such partnerships for students, institutions, and the wider sector.