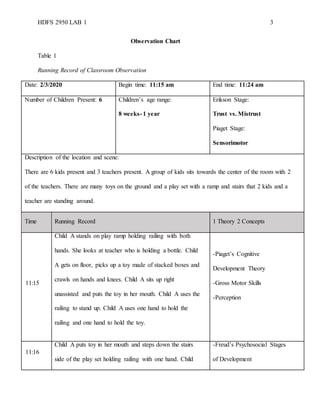
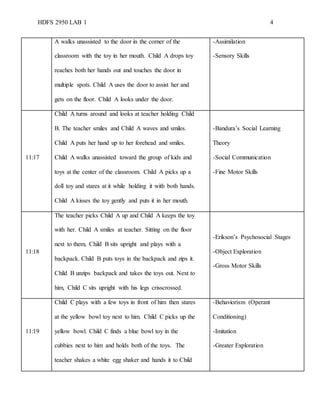
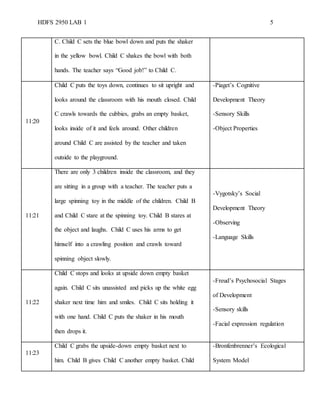
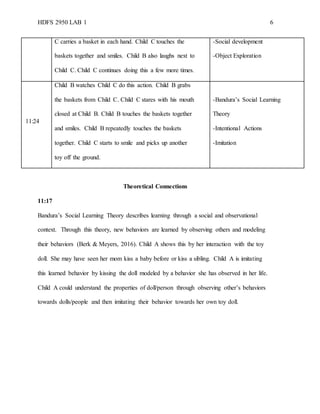
The document is a detailed running record of a classroom observation conducted on February 3, 2020, focusing on the interactions of infants with their environment and teachers. It highlights developmental theories including Piaget’s cognitive development theory, Bandura’s social learning theory, and Freud’s psychosocial stages, showcasing children's behaviors and learning processes during playtime. Specific instances of children (labeled A, B, and C) demonstrate the application of these theories through their actions and interactions with toys and teachers.



![HDFS 2950 LAB 1 8
References
Berk, L.E., & Adena B.M, (2016). History, Theory, and Research Strategies. In T. Paulken &
J. Ashkenaz (Eds.), Infants, Children, and Adolescents(pp. 2-49). Boston: Pearson.
Leigh, K. (2020). Lab 1- Theory Review [PowerPoint slides].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfslab1-delaneysmith-210415131833/85/HDFS-2950-Lab-1-8-320.jpg)