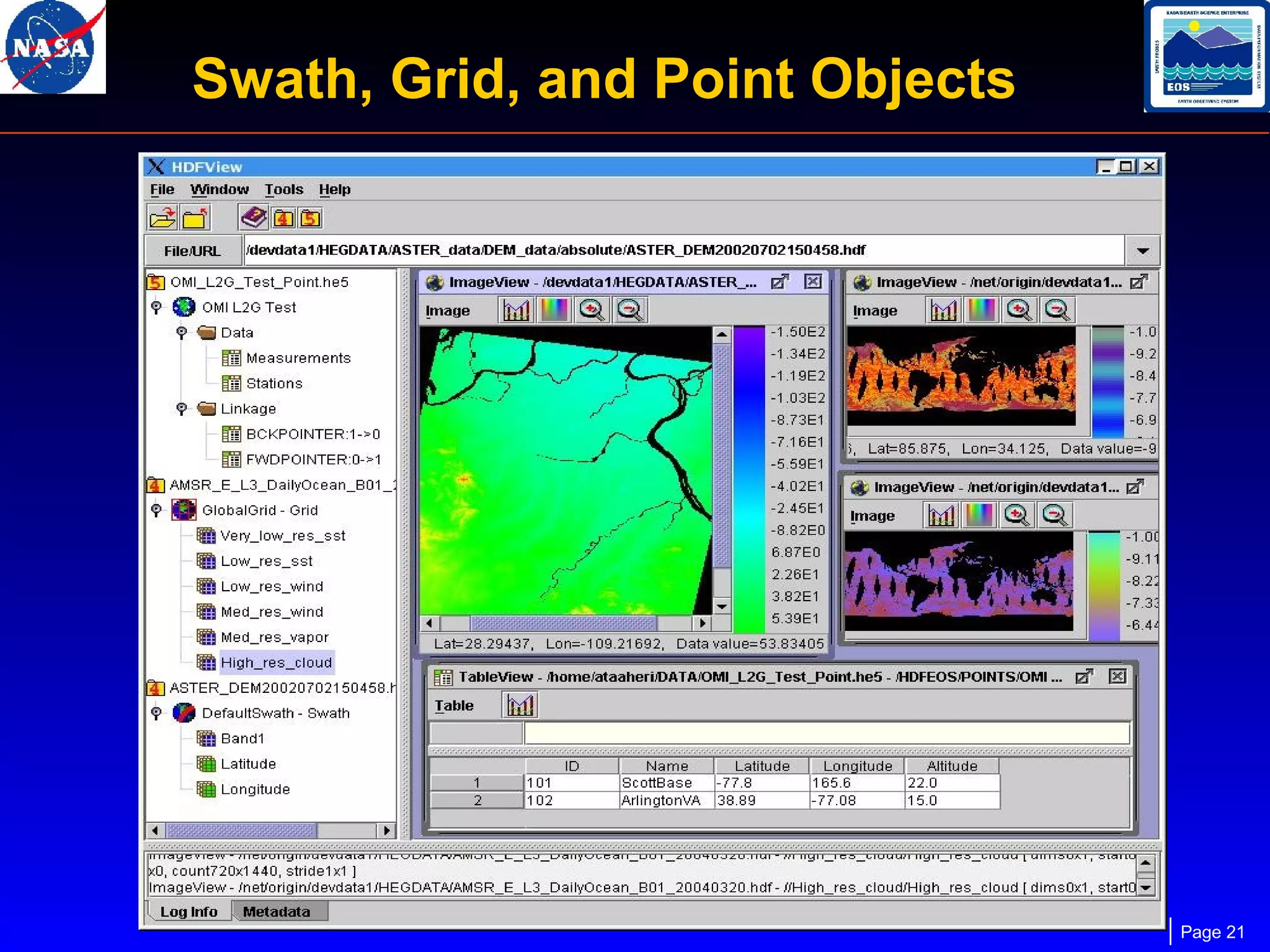
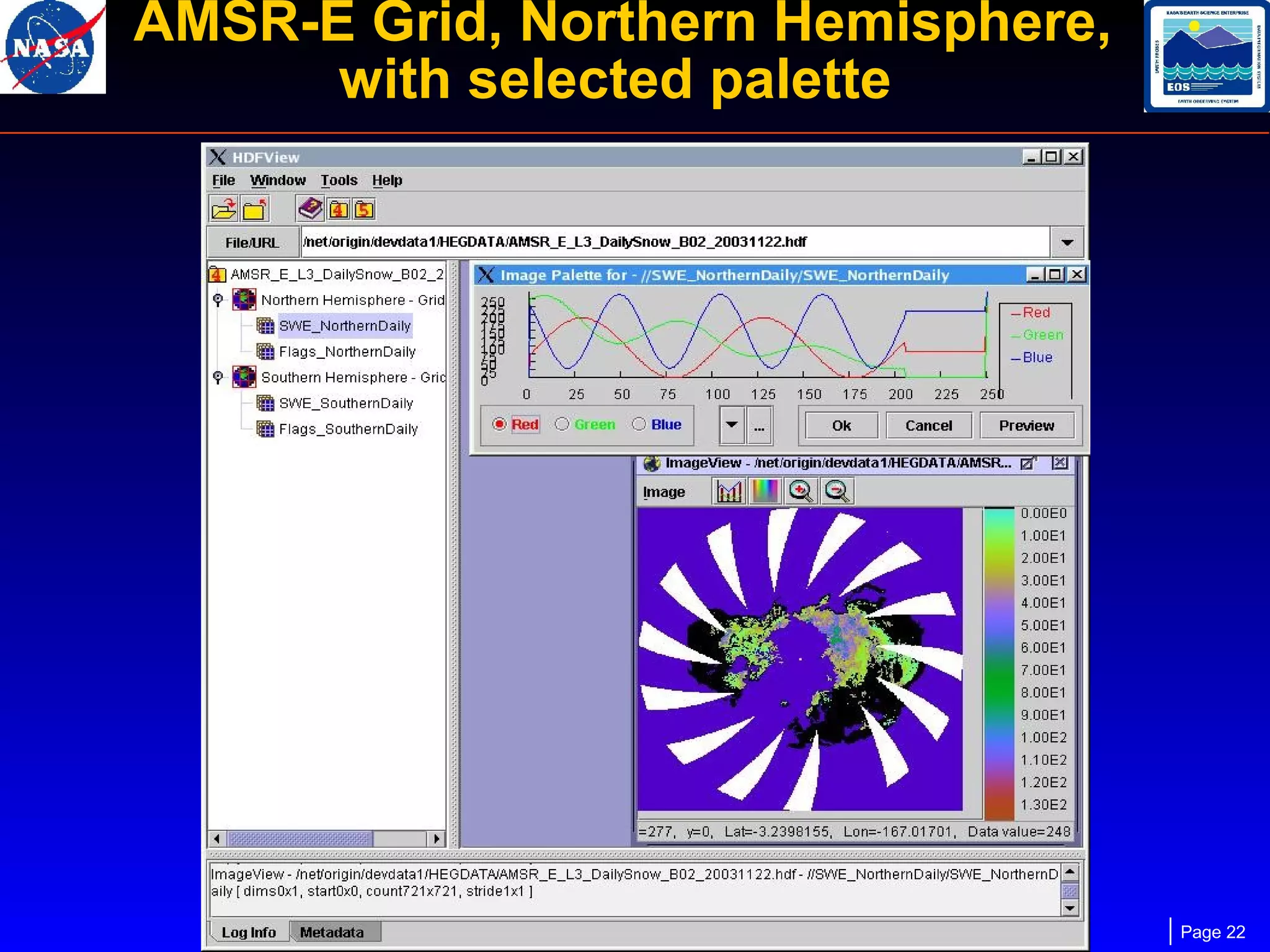
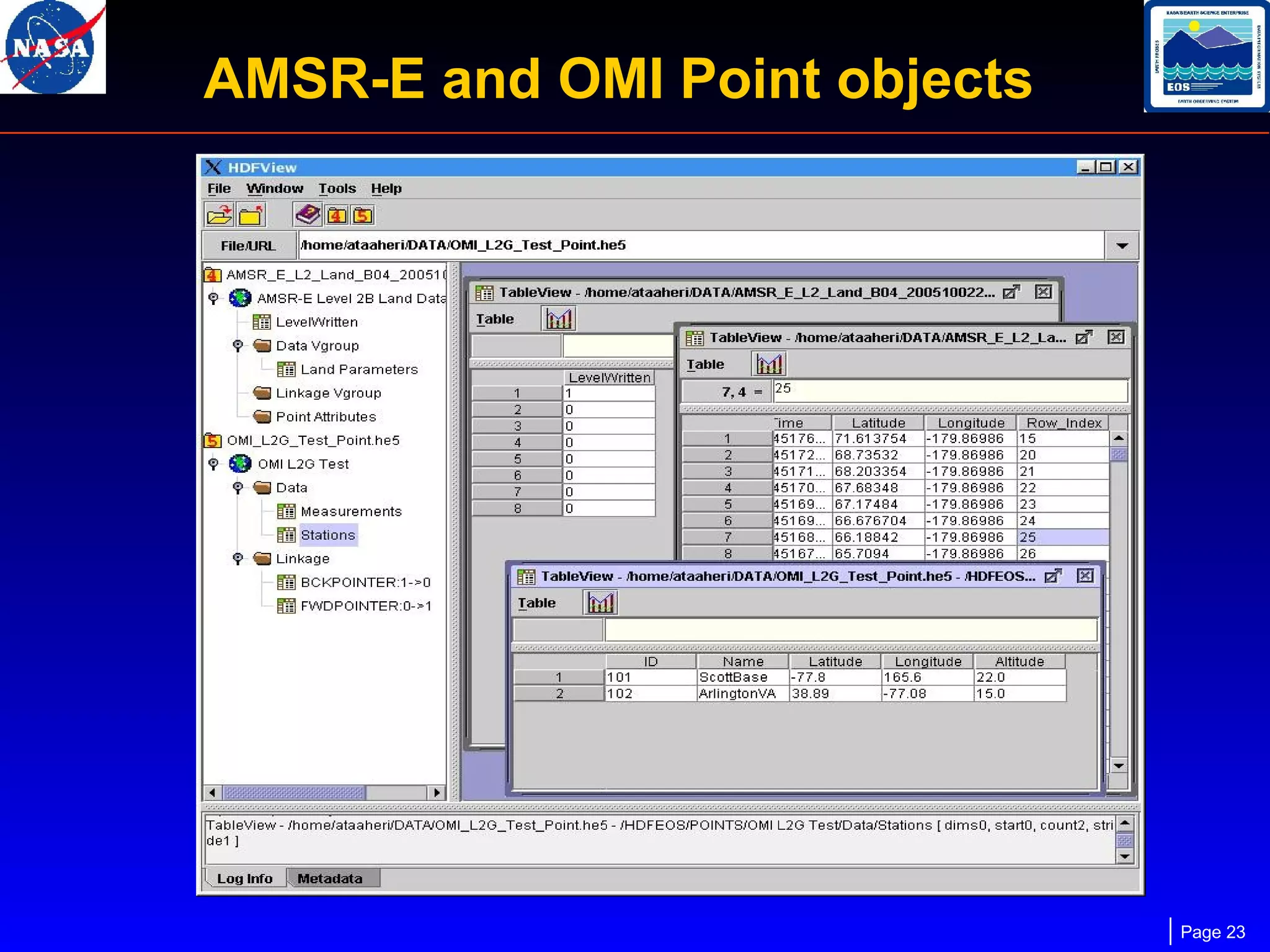
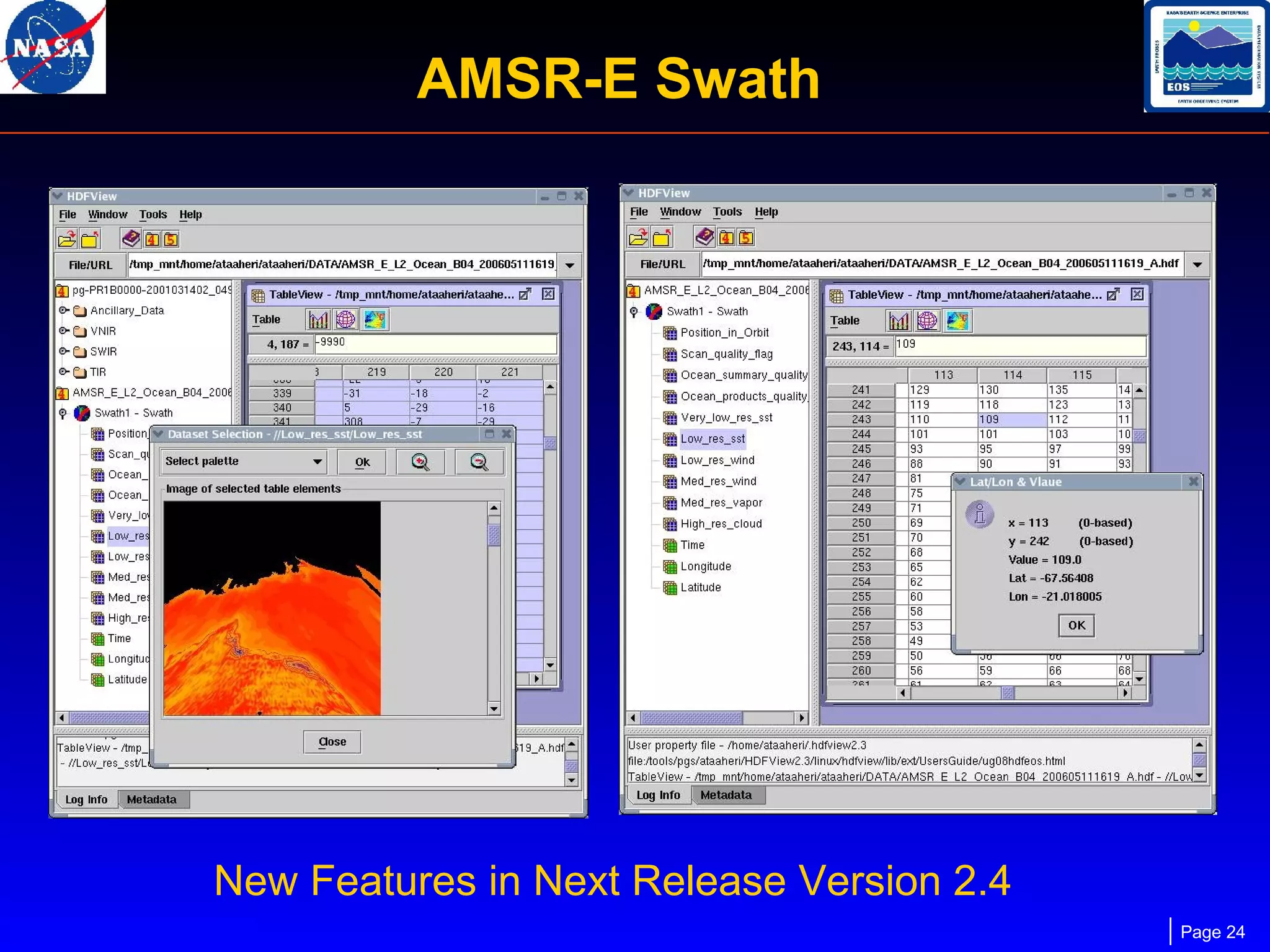
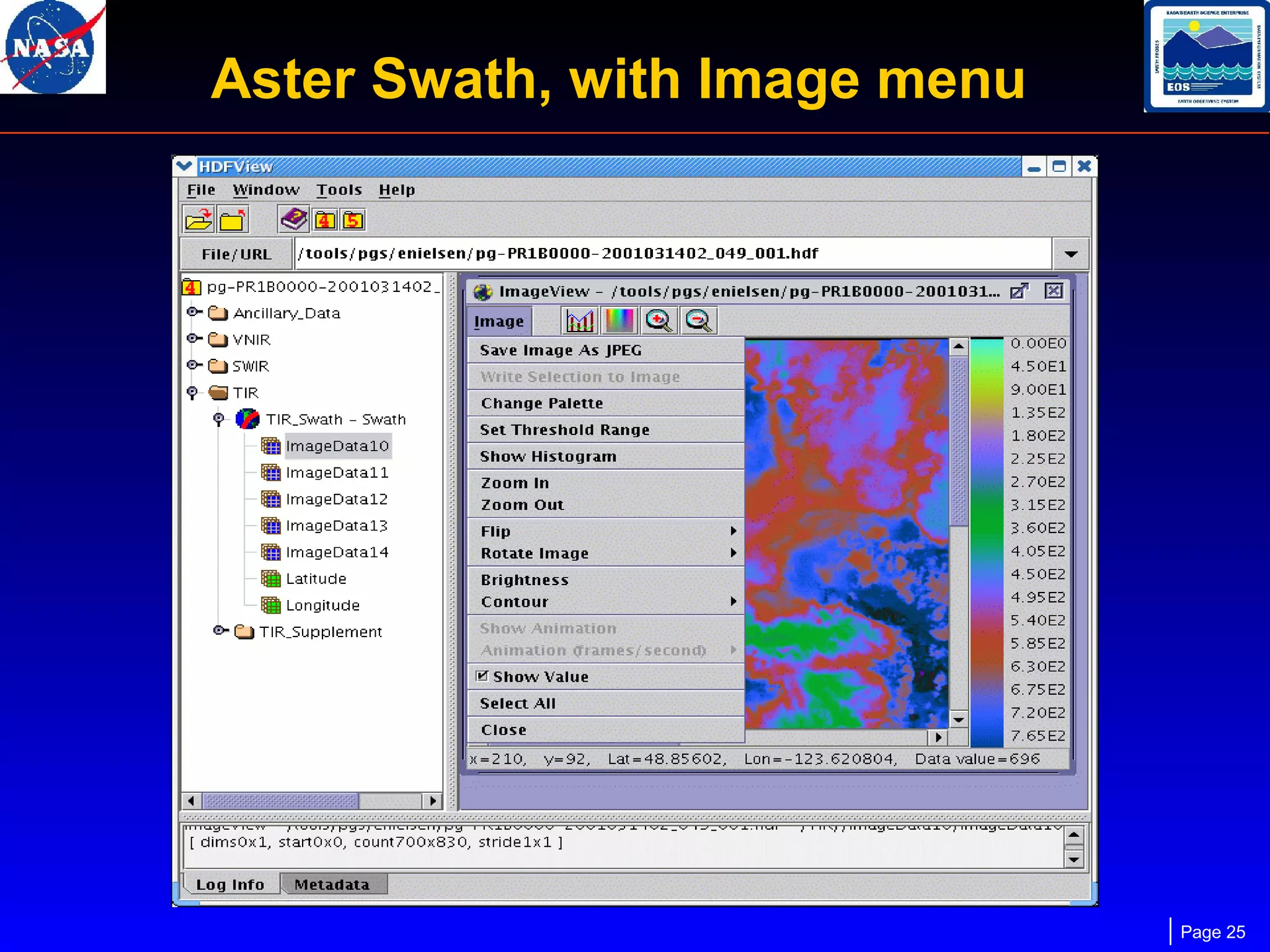
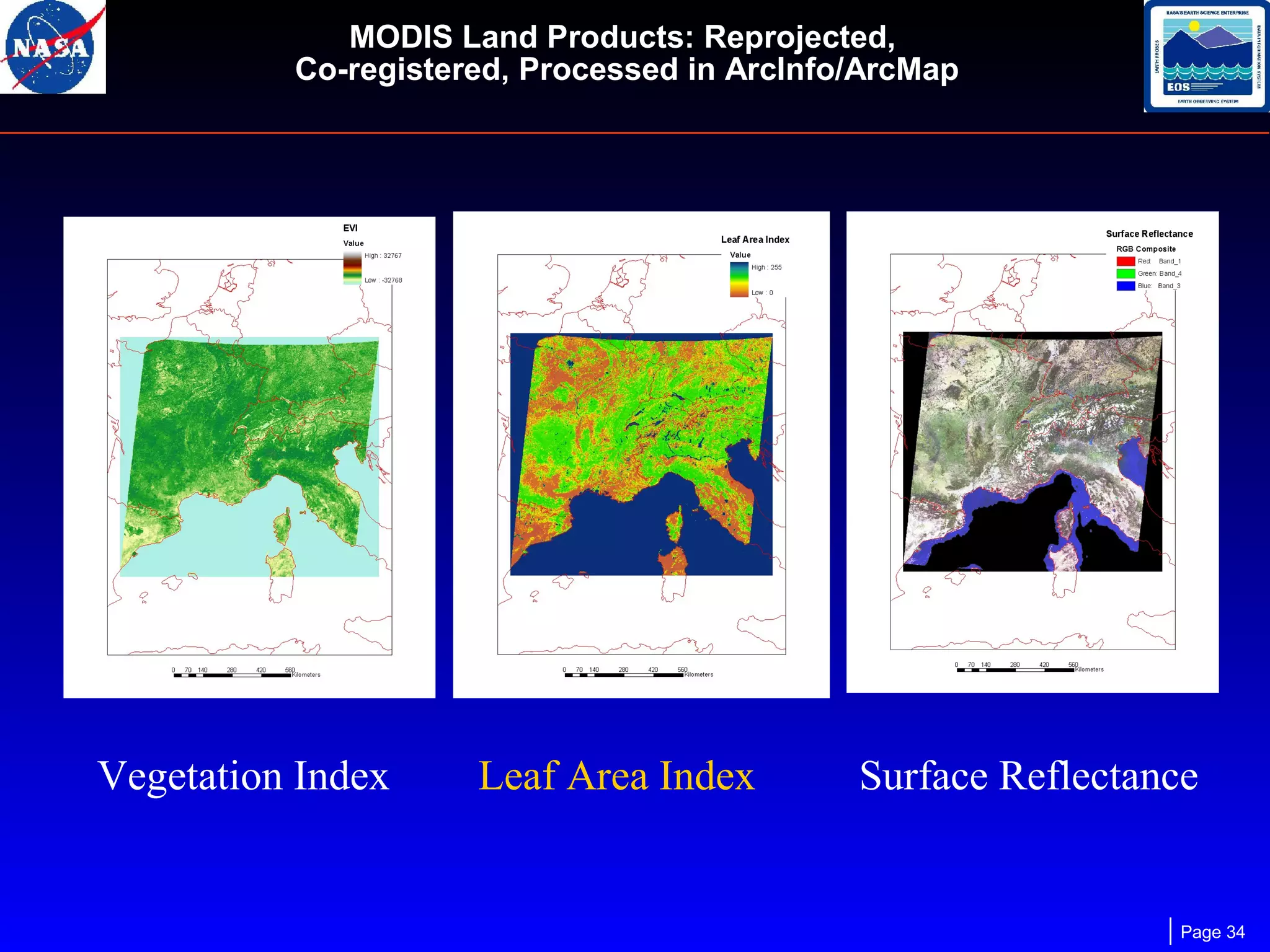
The document outlines the maintenance and support of HDF-EOS tools and software, detailing staff roles, current and upcoming releases, and software features. It highlights the functionality of various applications like the science data production toolkit, HDF-EOS, and HEG for converting HDF-EOS data into GIS-compatible formats. Future development plans include enhancements for compatibility and performance improvements, particularly in support of new HDF versions and systems.