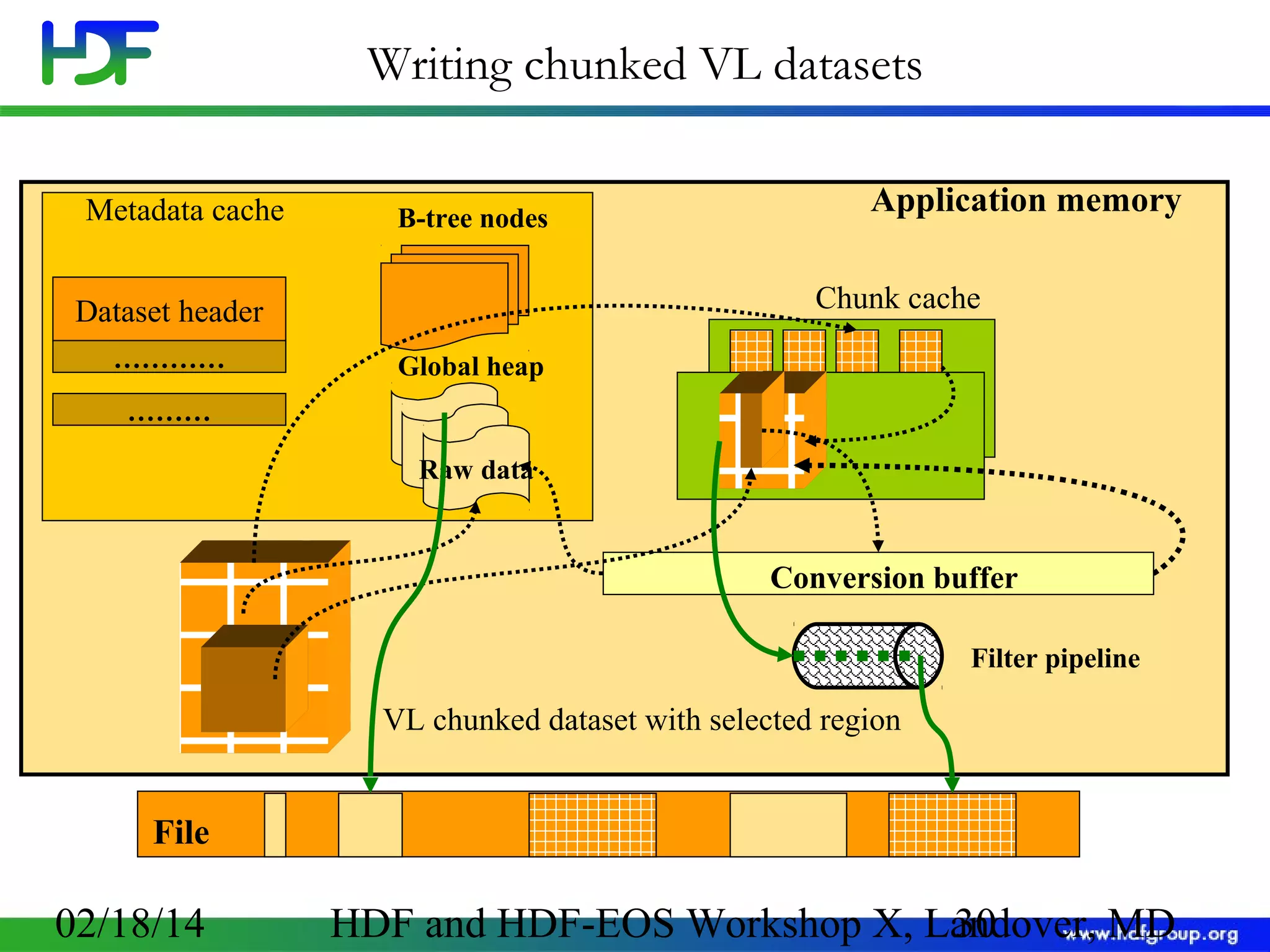
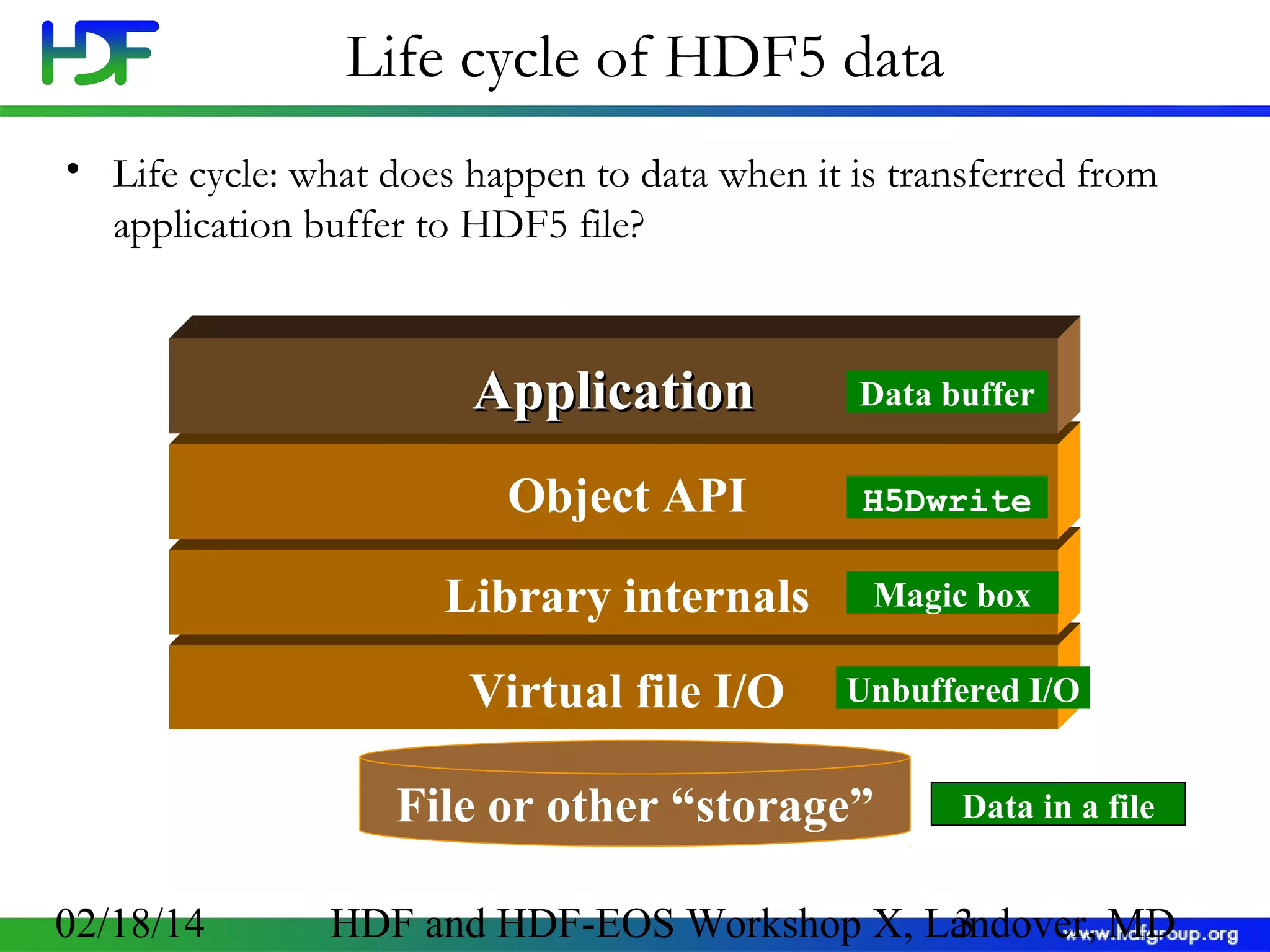
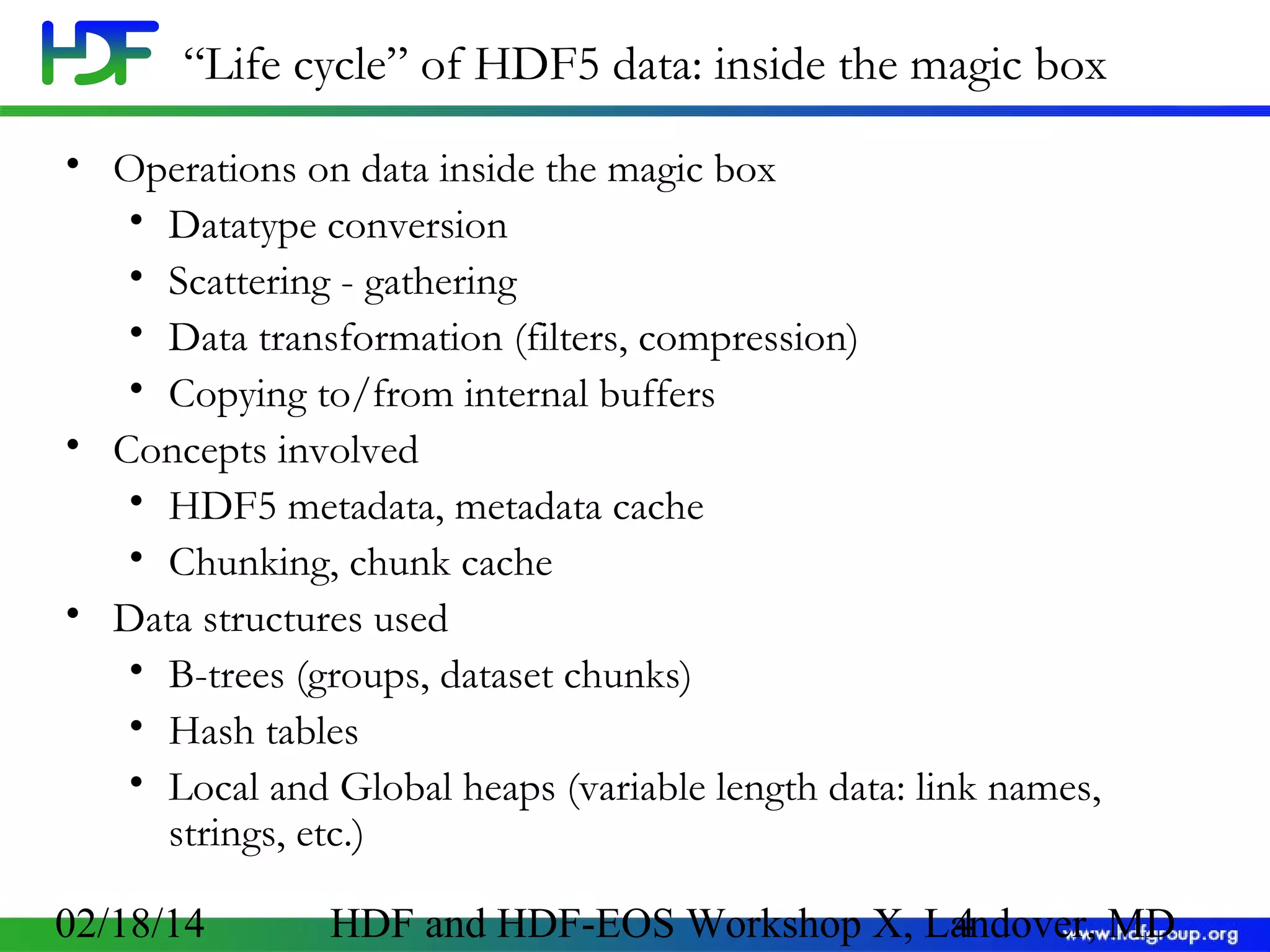
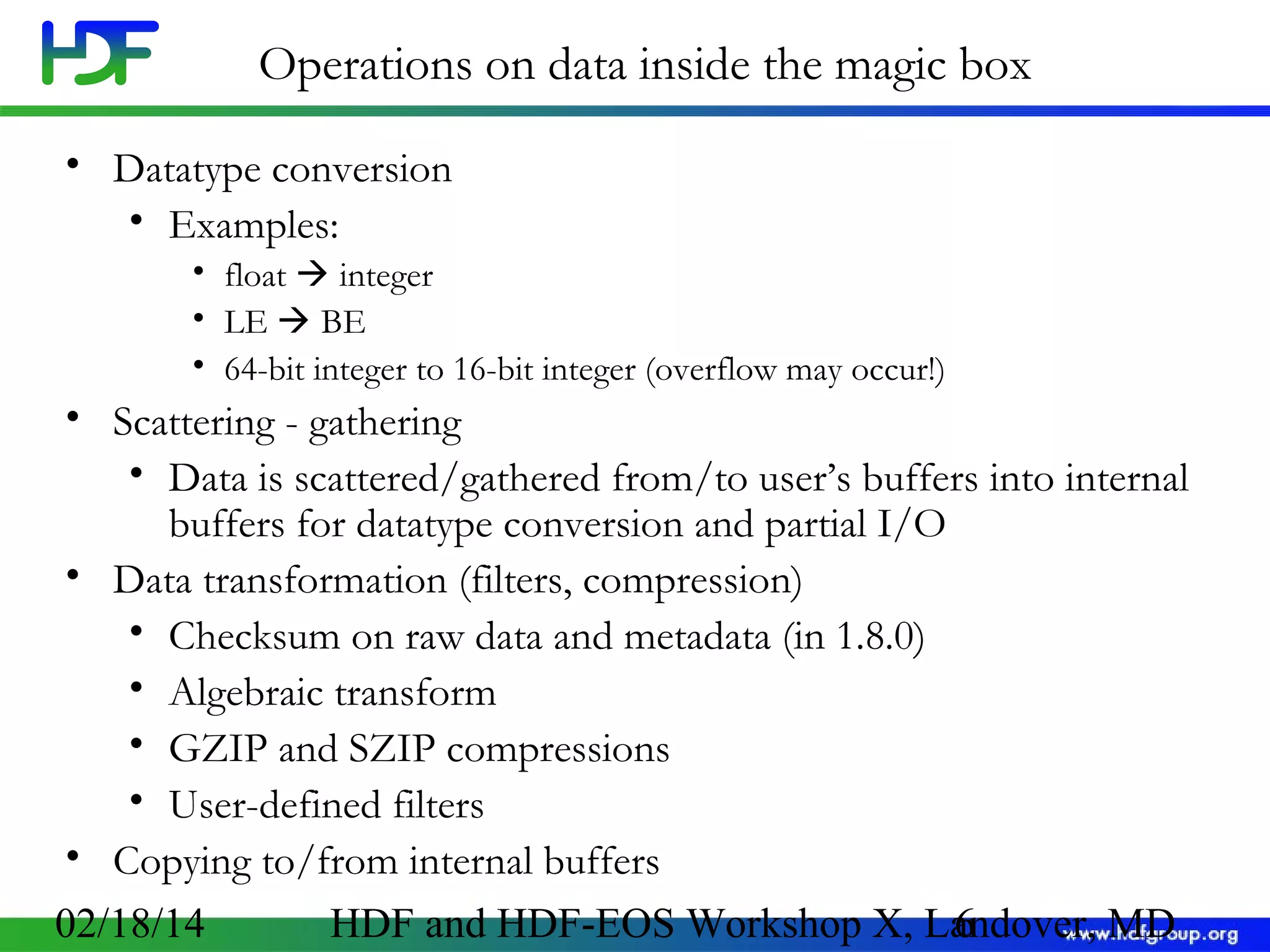
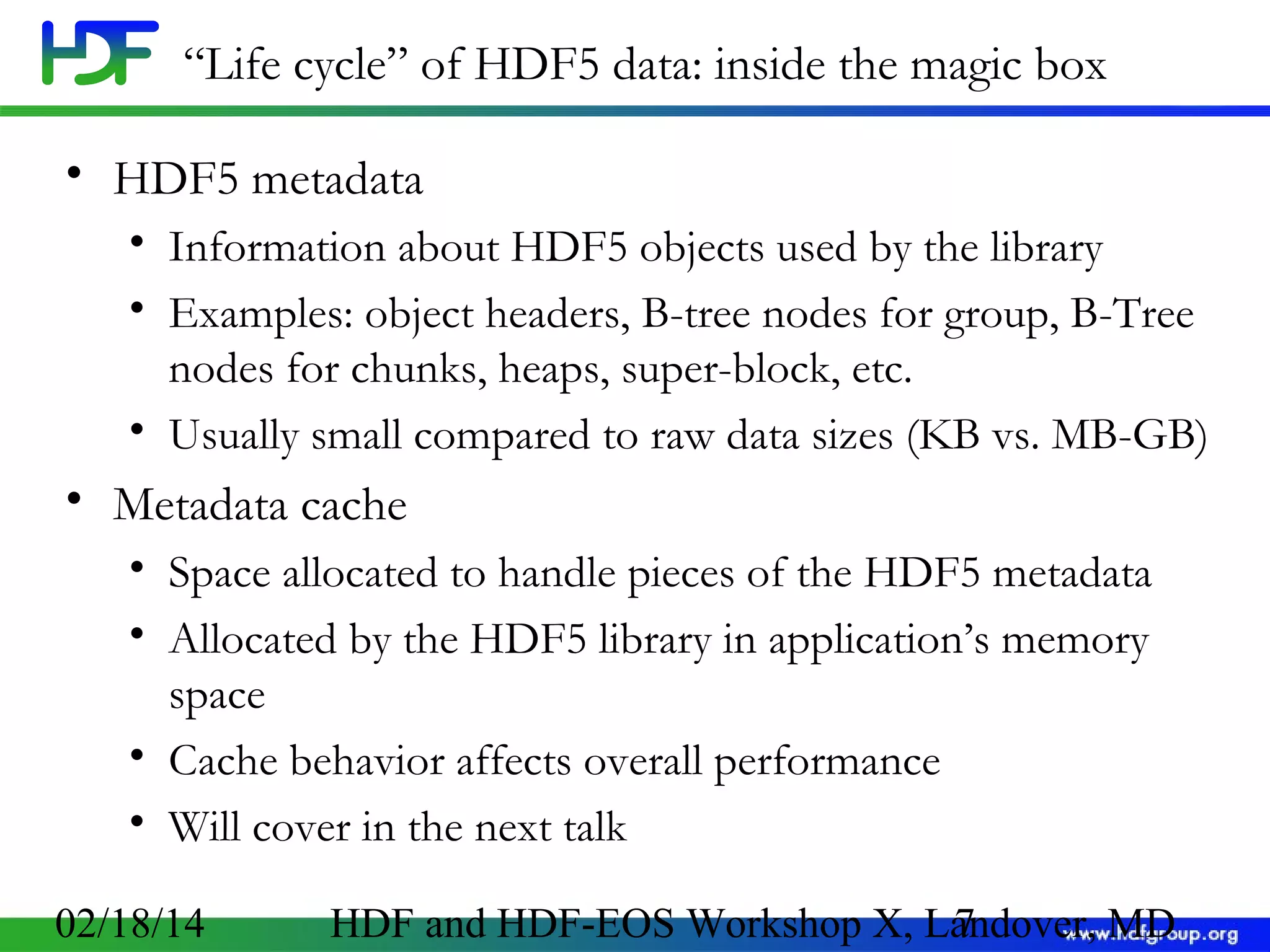
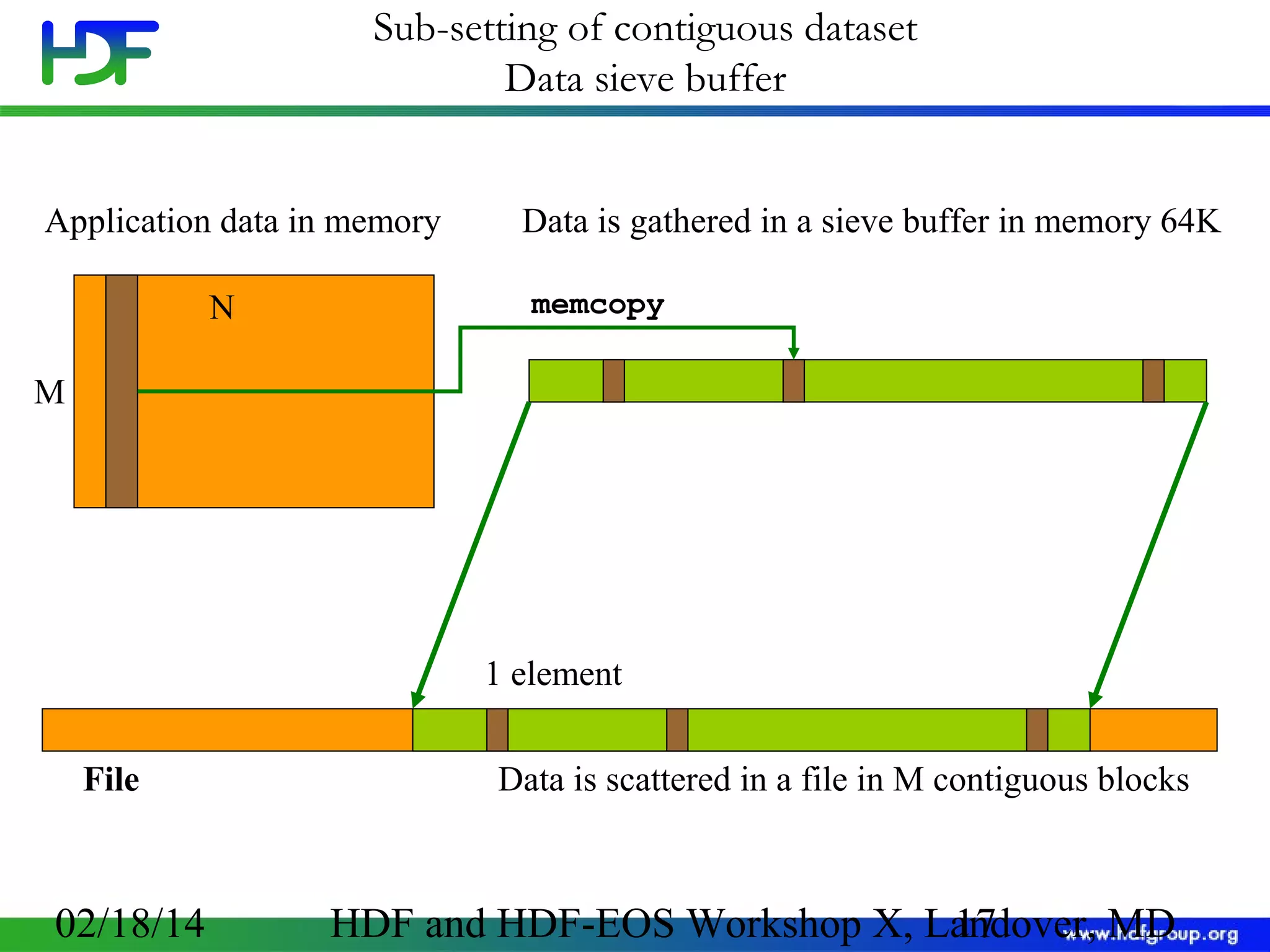
The document discusses the life cycle of HDF5 data, detailing I/O operations, storage layouts, and internal mechanics involved in data transfer from application buffers to HDF5 files. Key topics include datatype conversion, chunking mechanisms, and performance tuning strategies for datasets. It aims to enhance understanding of HDF5 structure to improve application efficiency and performance.



















![Variable length datasets and I/O
• Examples of variable-length data
• String
A[0] “the first string we want to write”
…………………………………
A[N-1] “the N-th string we want to write”
• Each element is a record of variable-length
A[0] (1,1,0,0,0,5,6,7,8,9) length of the first record is 10
A[1] (0,0,110,2005)
………………………..
A[N] (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,….,M) length of the N+1
record is M
02/18/14
HDF and HDF-EOS Workshop X, Landover, MD
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-life-cycle-140218104529-phpapp02/75/HDF5-Life-cycle-of-data-27-2048.jpg)