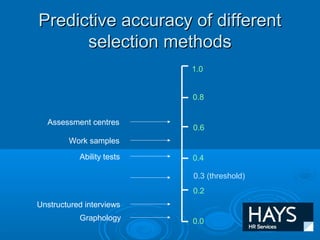
The document discusses assessment centres, which are used by 40% of employers and 75% of FTSE 100 companies to evaluate job candidates. Assessment centres assess competencies determined important for a job through multiple assessment techniques, exercises, and trained assessors. They have been shown to highly accurately predict job performance. The document provides details on common competencies, exercises in assessment centres, how to prepare, and why companies use assessment centres.