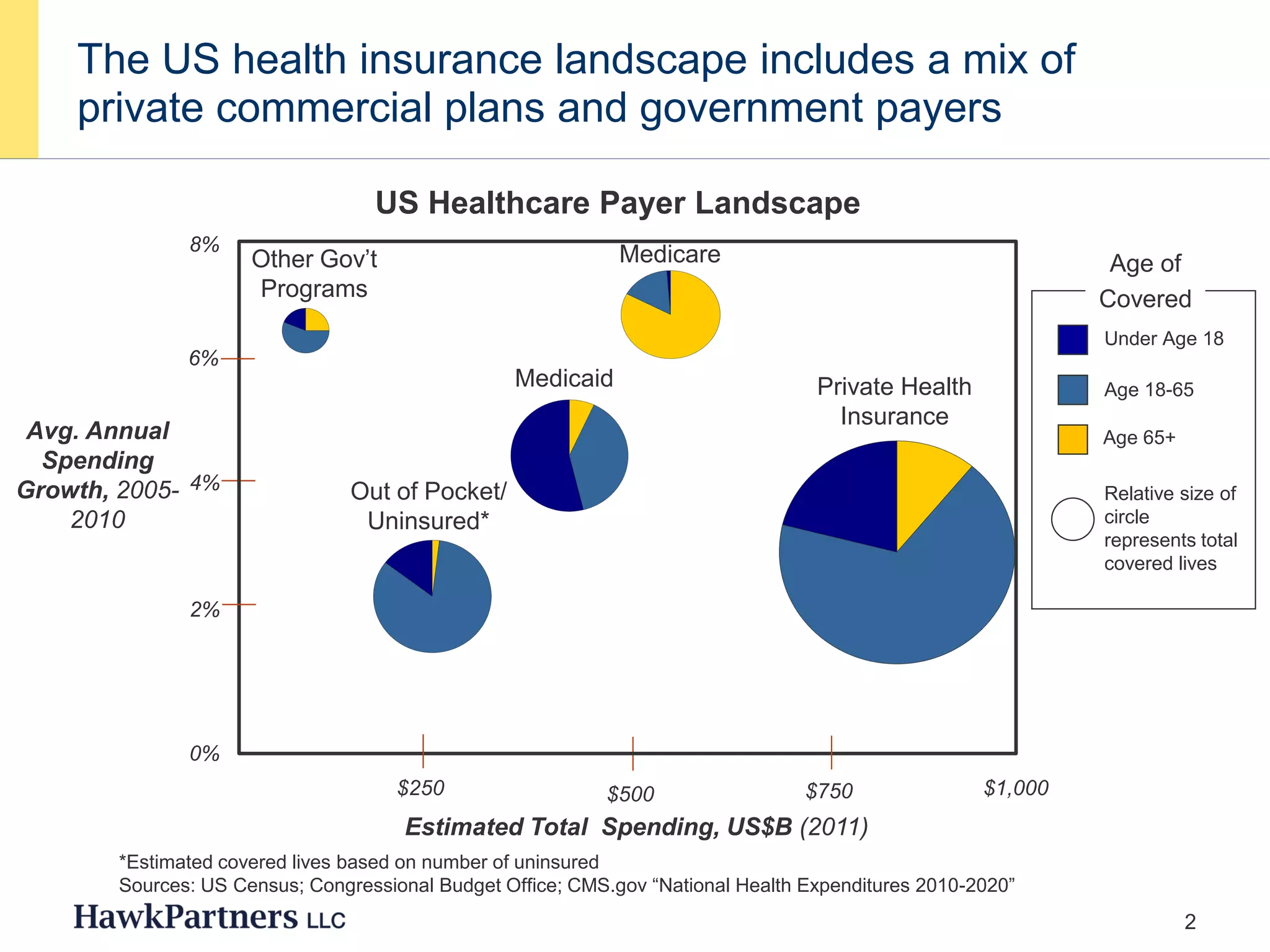
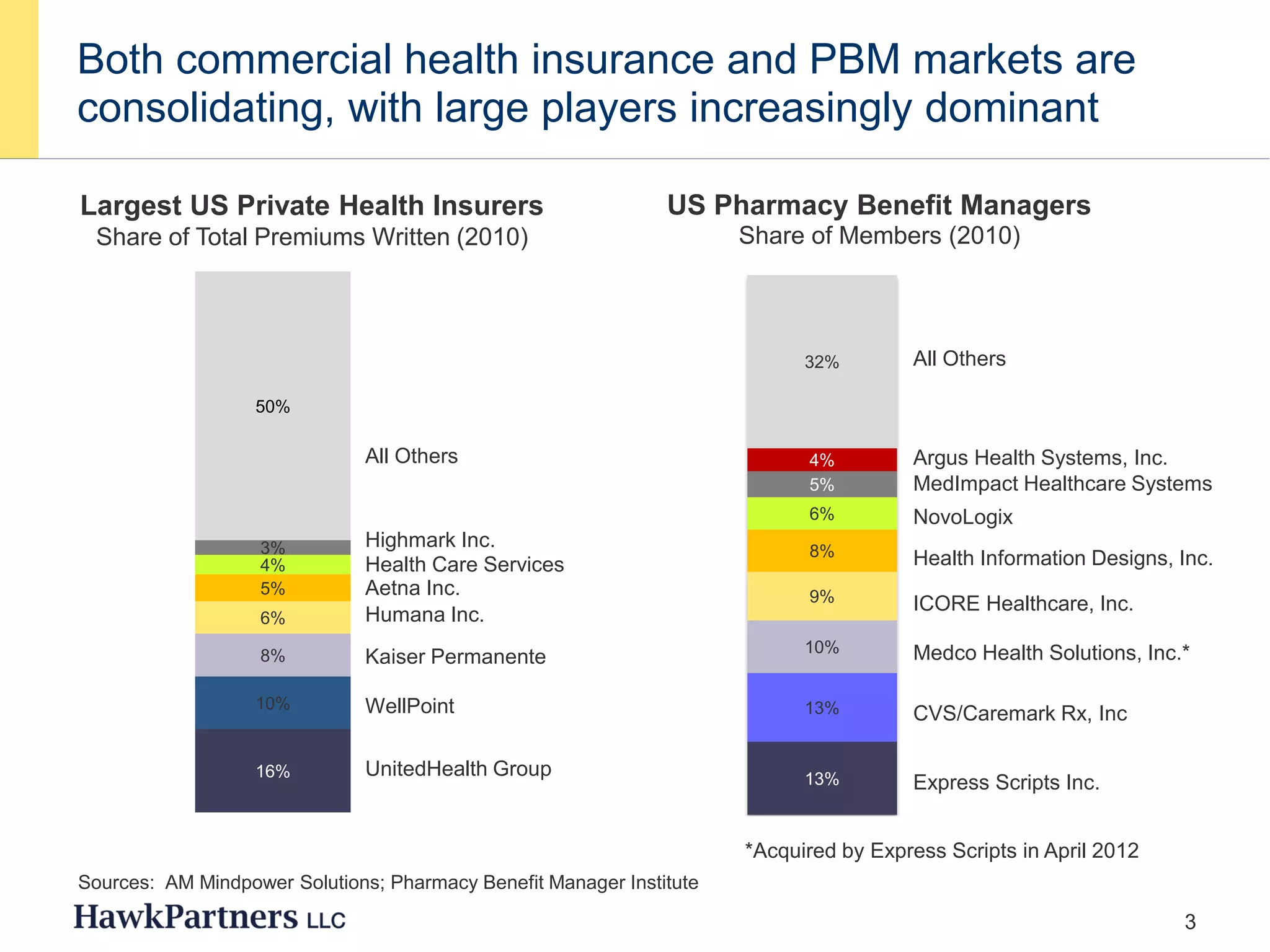
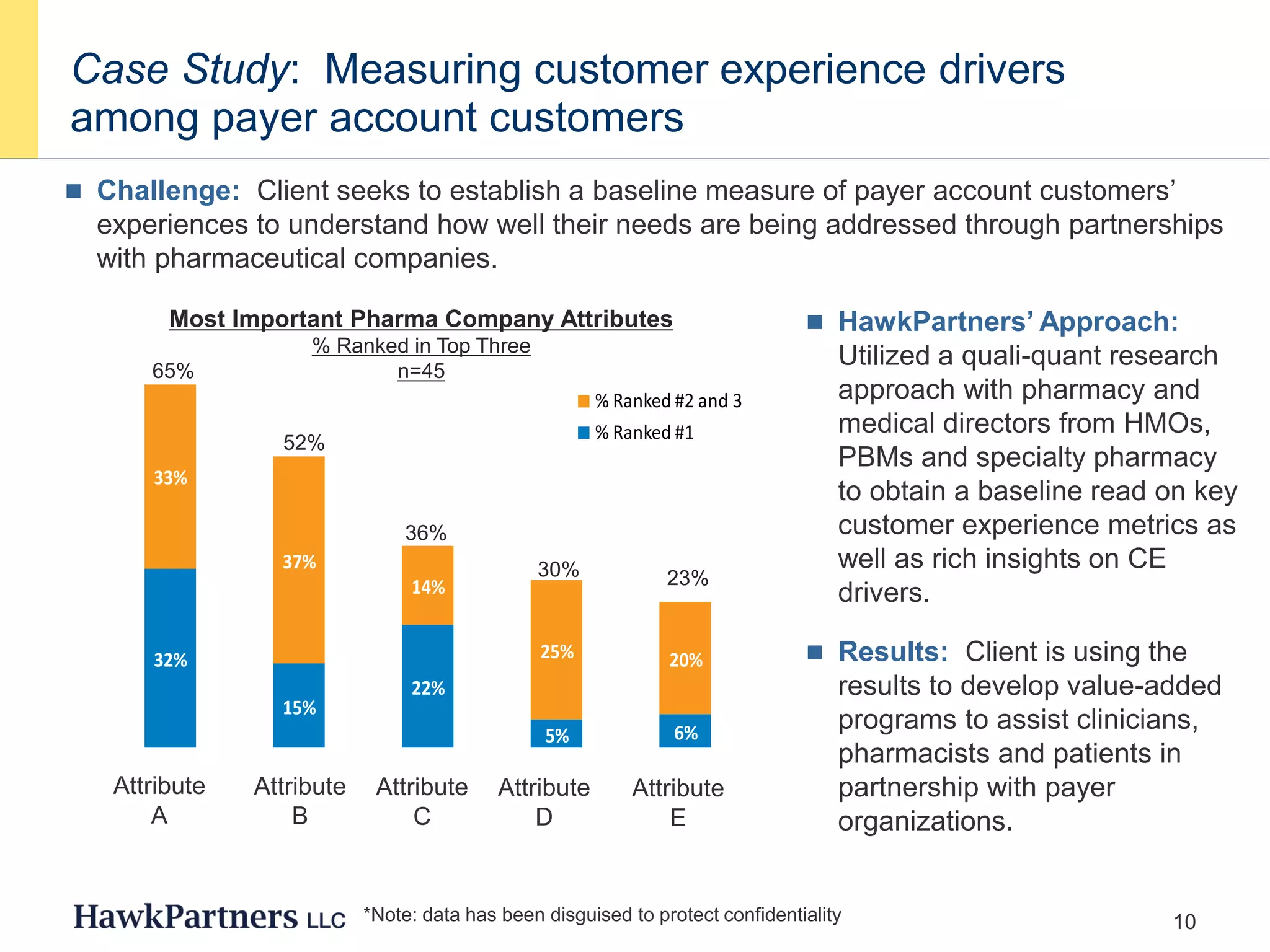
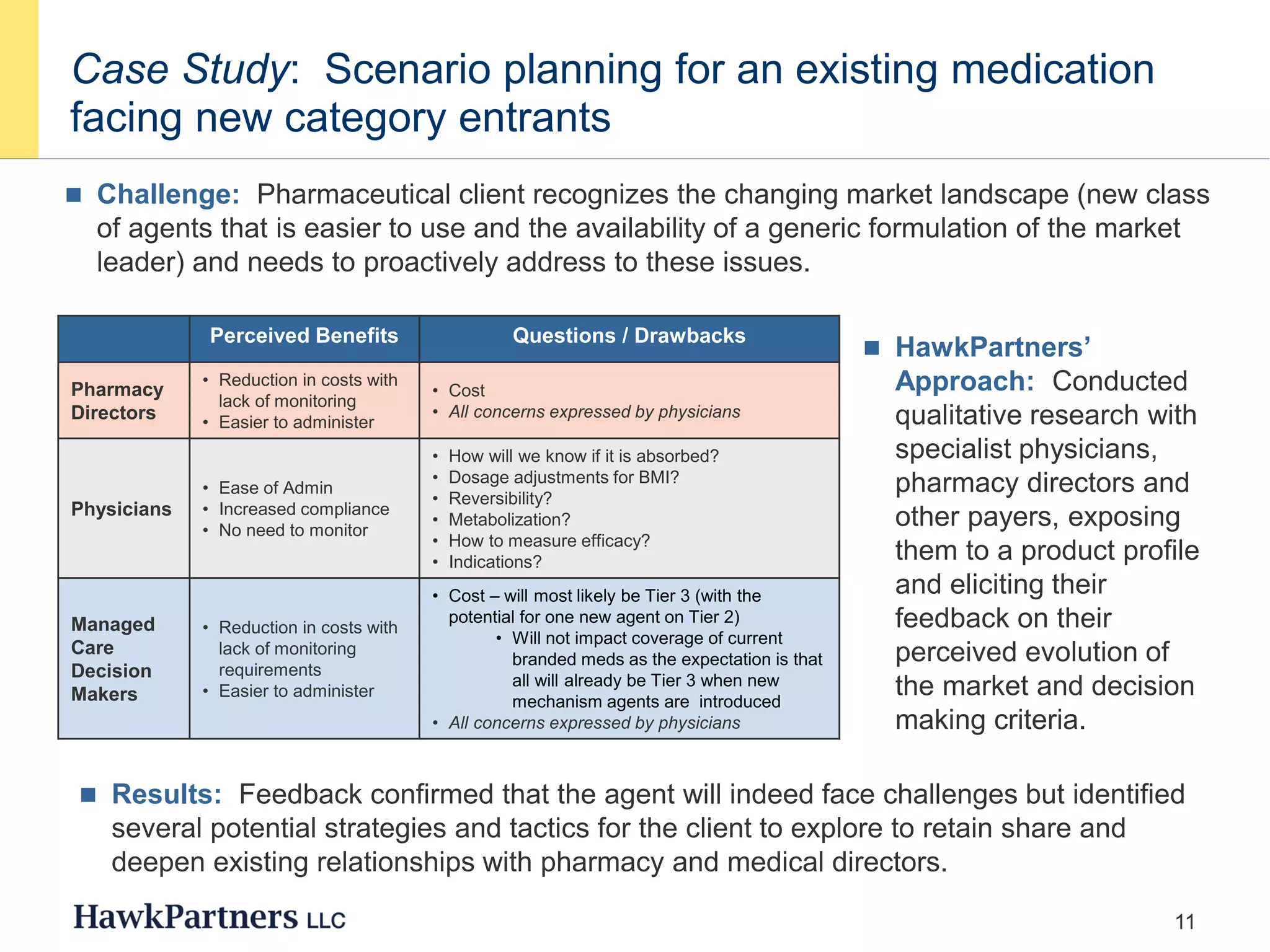
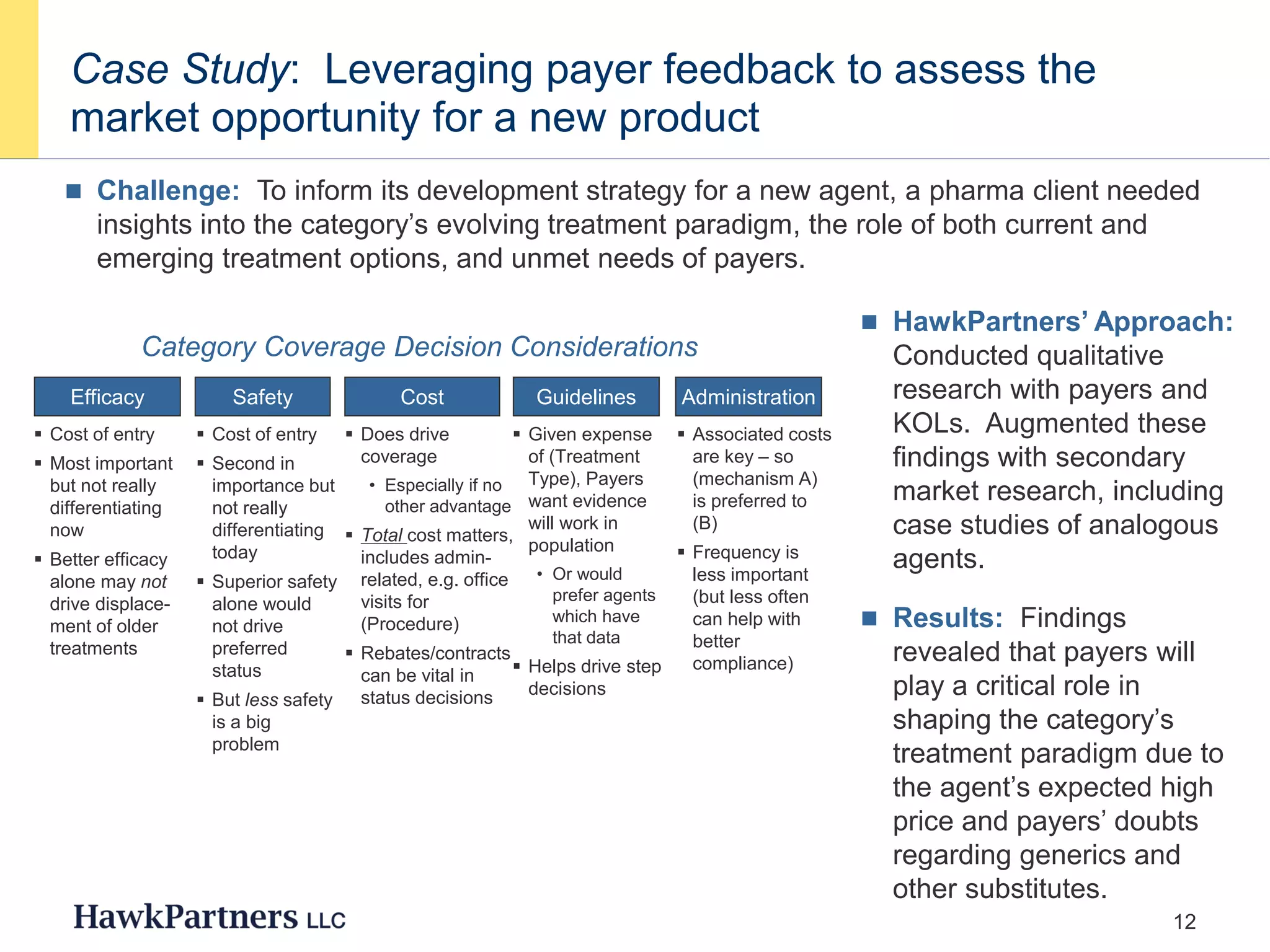
The document discusses the evolving landscape of healthcare payers in the U.S., highlighting the increasing influence of payers in the pharmaceutical marketplace and the need for strategic partnerships between pharma companies and payers. It emphasizes the importance of market research to understand payer needs and includes various case studies demonstrating successful payer research conducted by HawkPartners. The document outlines key success factors for effective payer research, including respondent recruitment, insight maximization, and results integration.