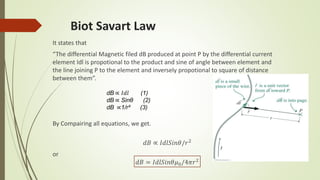
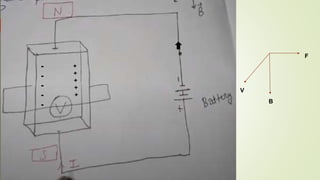
The document presents information about solid state physics concepts including Biot Savart's law, the Hall effect, and applications. Biot Savart's law states that the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying element is proportional to the current and inversely proportional to the square of the distance. The Hall effect occurs when a current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field, producing a voltage perpendicular to both. Applications of the Hall effect include determining semiconductor type, measuring magnetic fields and power in electromagnetic waves, and determining carrier mobility.