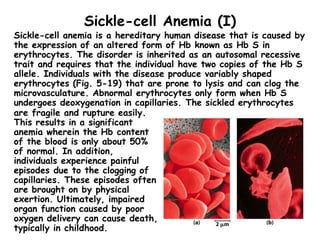
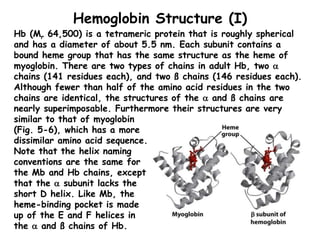
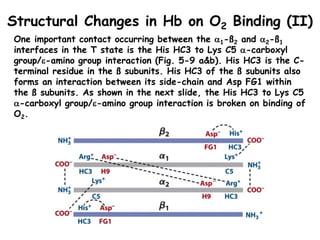
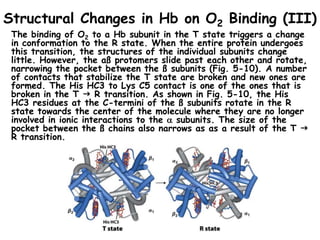
- Hemoglobin (Hb) is an oxygen-transport protein found in red blood cells. It has a tetrameric structure composed of two alpha and two beta subunits, each containing an iron-containing heme group that reversibly binds oxygen.
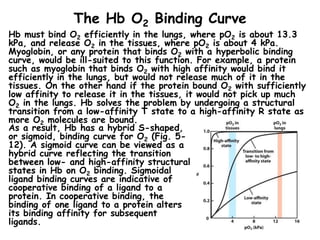
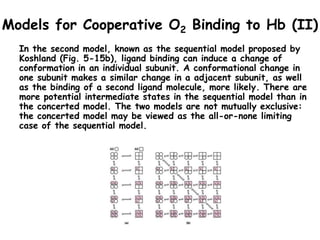
- Hb binds oxygen cooperatively, meaning that the binding of oxygen to one subunit increases the affinity of the other subunits for oxygen. This allows for efficient oxygen uptake in the lungs and release in tissues.
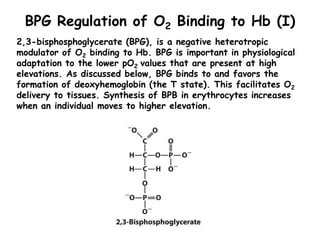
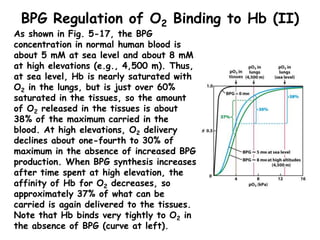
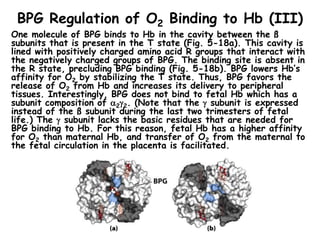
- Factors like pH, carbon dioxide levels, and 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate regulate Hb's affinity for oxygen and allow for oxygen delivery to tissues where it is needed. Sickle cell anemia results from a mutation that causes Hb to polymer







![Transport of H+ and CO2 by Hb (I)
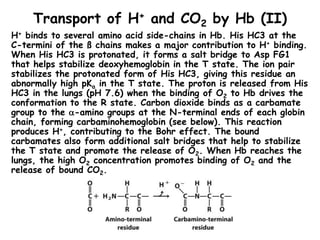
Hb binds to and transports about 40%
of the total H+ and 15% to 20% of the
CO2 formed in peripheral tissues to the
lungs and kidneys. The remainder of
the H+ is absorbed by the plasma’s
bicarbonate buffer system. The
remainder of the CO2 is transported as
dissolved HCO3
- and CO2. [Note that
the solubility of CO2 in the blood is
increased by the carbonic anhydrase
reaction (CO2 + H2O H+ + HCO3
-)
which occurs in erythrocytes.] The
binding of H+ and CO2 to Hb decreases
the affinity of
Hb for O2, favoring the release of O2 to the tissues where the
concentrations of these components are relatively high. Conversely,
in the capillaries of the lung, as CO2 is excreted and the blood pH
consequently rises, the affinity of Hb for O2 increases and the
protein binds more O2 for transport to the peripheral tissues. The
effect of pH and CO2 concentration on the binding and release of
O2 by Hb is known as the Bohr effect. The effect of pH on Hb O2
binding curves is shown in Fig. 5-16.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haemoglobinppt1-230203161736-38cebc5f/85/HAEMOGLOBIN-PPT-1-ppt-15-320.jpg)