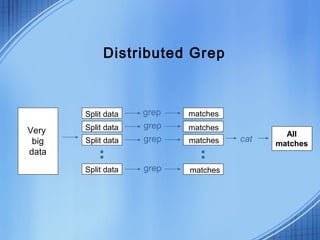
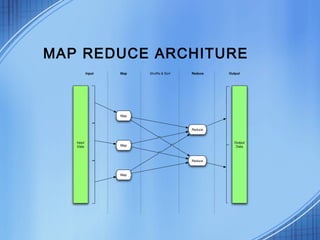
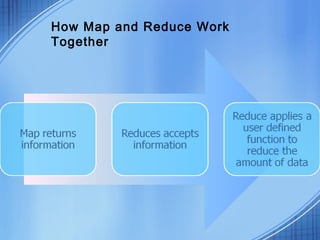
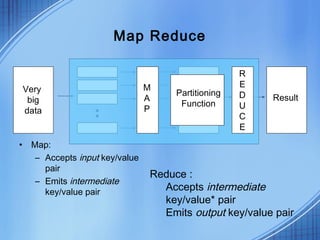
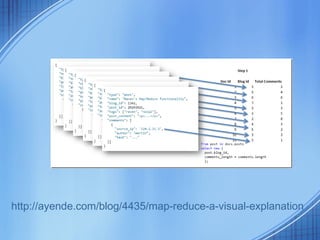
This document discusses the growth of data and challenges in storing and analyzing large datasets. It introduces Hadoop as a solution for processing large datasets in parallel across commodity servers. Key aspects of Hadoop covered include its core components HDFS for storage and MapReduce for distributed processing. Example uses by large companies like Amazon and Facebook are listed. The document contrasts Hadoop with RDBMS and explains when Hadoop is preferable to use.





![Hadoop History
• Hadoop was created by Doug Cutting, who named it
after his son's toy elephant .
• 2002-2004 Nutch Open Source web-scale, crawler-
based search
• 2004-2006 Google File System & MapReduce papers
published.Added DFS & MapReduce impl to Nutch
• 2006-2008 Yahoo hired Doug Cutting
• On February 19, 2008, Yahoo! Inc. launched what it
claimed was the world's largest Hadoop production
application
• The Yahoo! Search Webmap is a Hadoop application
that runs on more than 10,000 core Linux cluster and
produces data that is now used in every Yahoo! Web
search query.[22]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoopbysunitha-120826205259-phpapp01/85/Hadoop-by-sunitha-7-320.jpg)