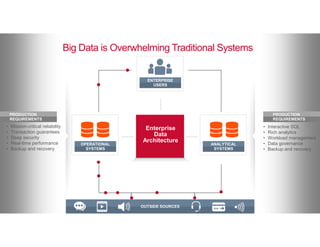
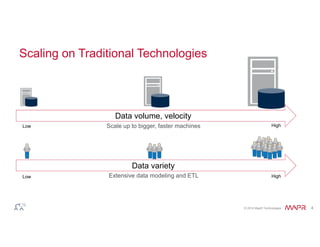
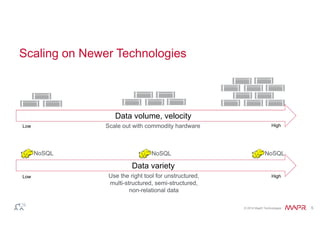
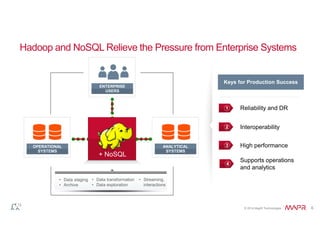
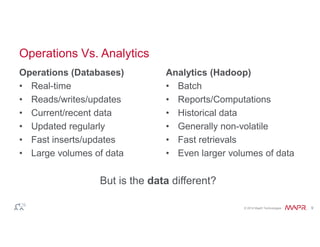
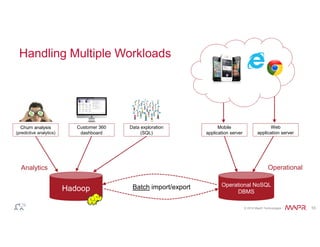
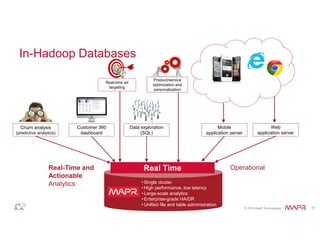
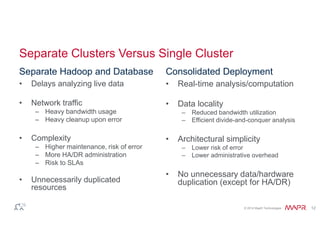
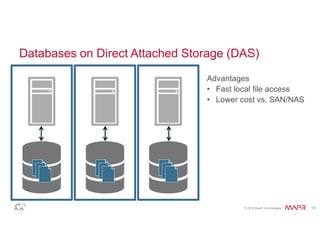
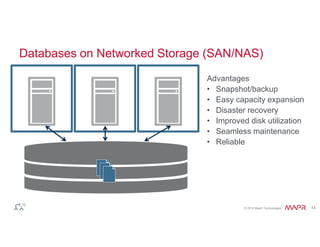
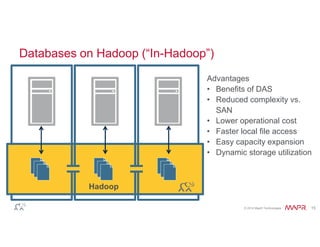
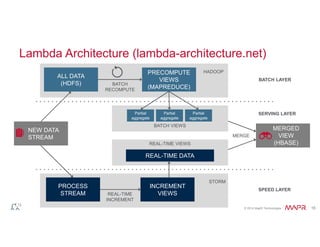
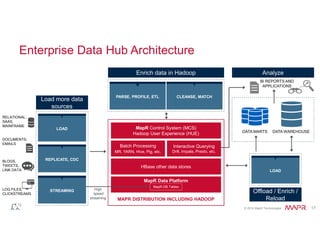
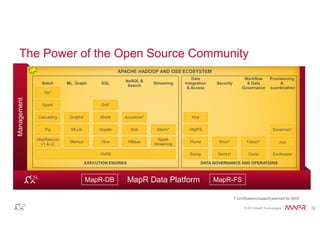
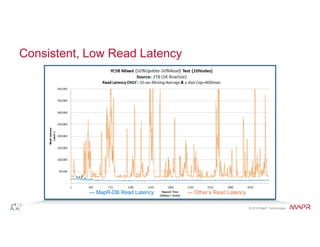
The document discusses the integration of Hadoop and NoSQL technologies for big data solutions, highlighting the advantages of using these systems for mission-critical applications, real-time performance, and scalability. It details the operational and analytical capacities of both technologies, emphasizing their ability to handle various data types efficiently. Additionally, the document outlines examples, trends, and technical specifications of in-Hadoop databases and their operational benefits.