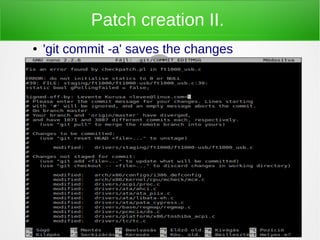
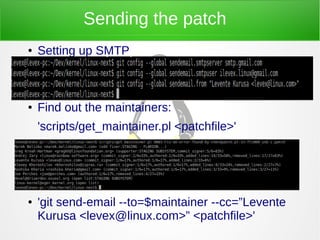
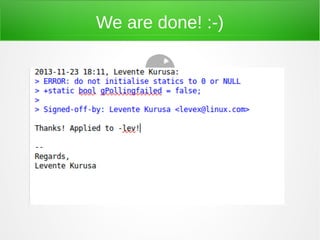
The document discusses the history and development of the Linux kernel, initiated by Linus Torvalds in 1991. It highlights Linux as a monolithic and modular free software kernel with extensive usage across various platforms, including Android devices and financial systems. Additionally, it outlines the process of contributing to the kernel through patch creation and submission, emphasizing community involvement and collaboration.