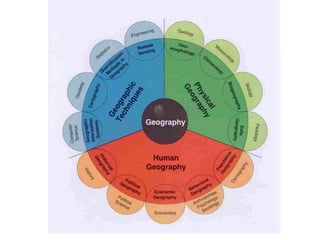
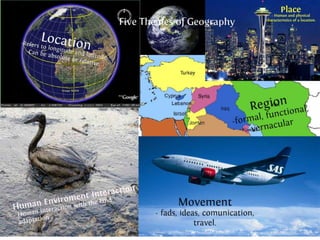
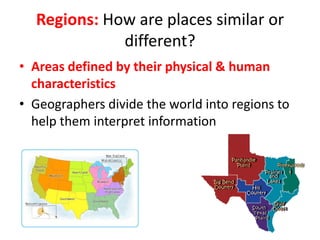
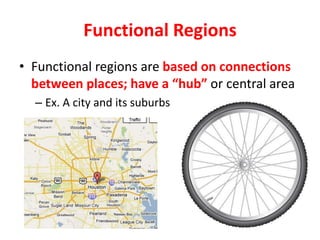
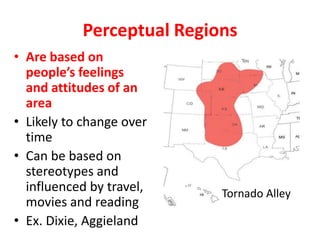
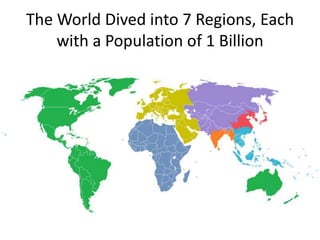
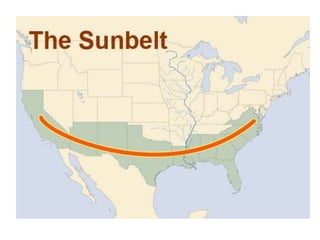
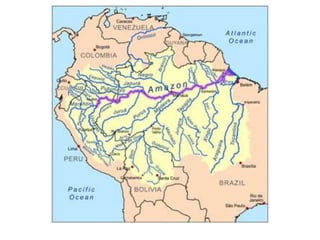
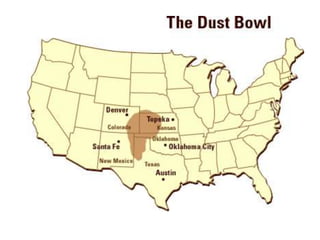
The document provides an agenda for a geography class that will cover the key concepts of geography including the five themes: location, place, region, human-environment interaction, and movement. It defines each theme and provides examples to help students understand and identify the themes. It also includes warm-up questions, an activity using pictionary to practice identifying themes, and a closure for the class.