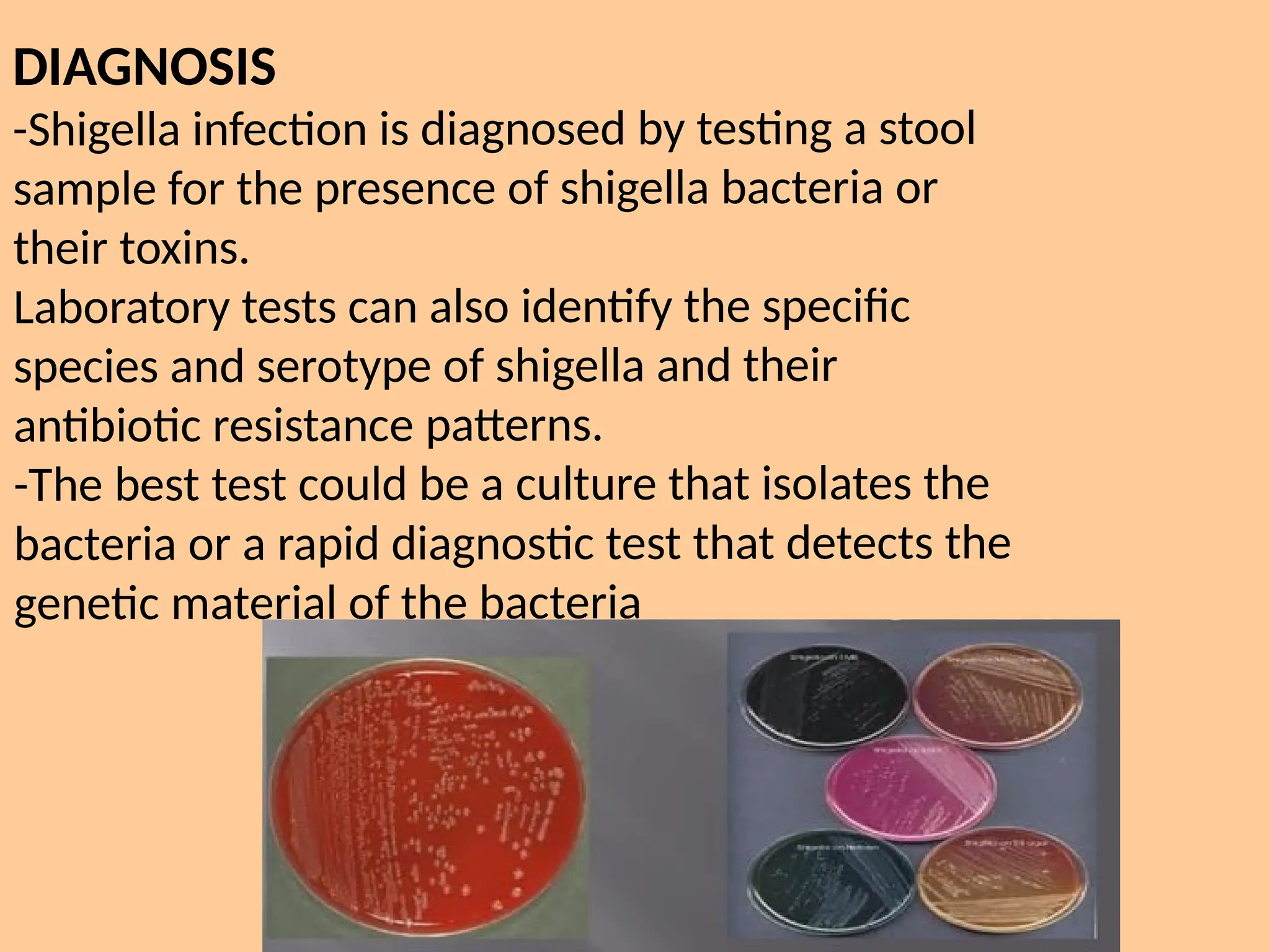
Shigella is a genus of highly contagious bacteria responsible for shigellosis, characterized by severe diarrhea predominantly affecting children in unsanitary conditions, with millions of cases and significant mortality worldwide. The infection primarily spreads through contaminated food and water or direct person-to-person contact, leading to severe inflammation of the colon and toxic symptoms such as hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Prevention focuses on hygiene practices, while treatment often emphasizes fluid replacement, with antibiotics reserved for severe cases.