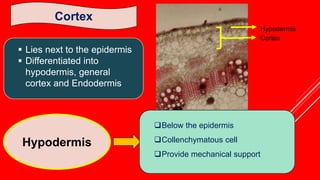
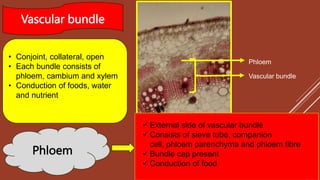
This document discusses the anatomical structures of the groundnut stem. It begins with an outline and background on studying groundnut anatomy. It then details the various tissues that make up the stem's structure, including the epidermis, hypodermis, cortex, endodermis, vascular bundles, cambium, xylem, and pith. Diagrams are included labeling each tissue. The purpose and field applications of studying plant anatomy are also mentioned.