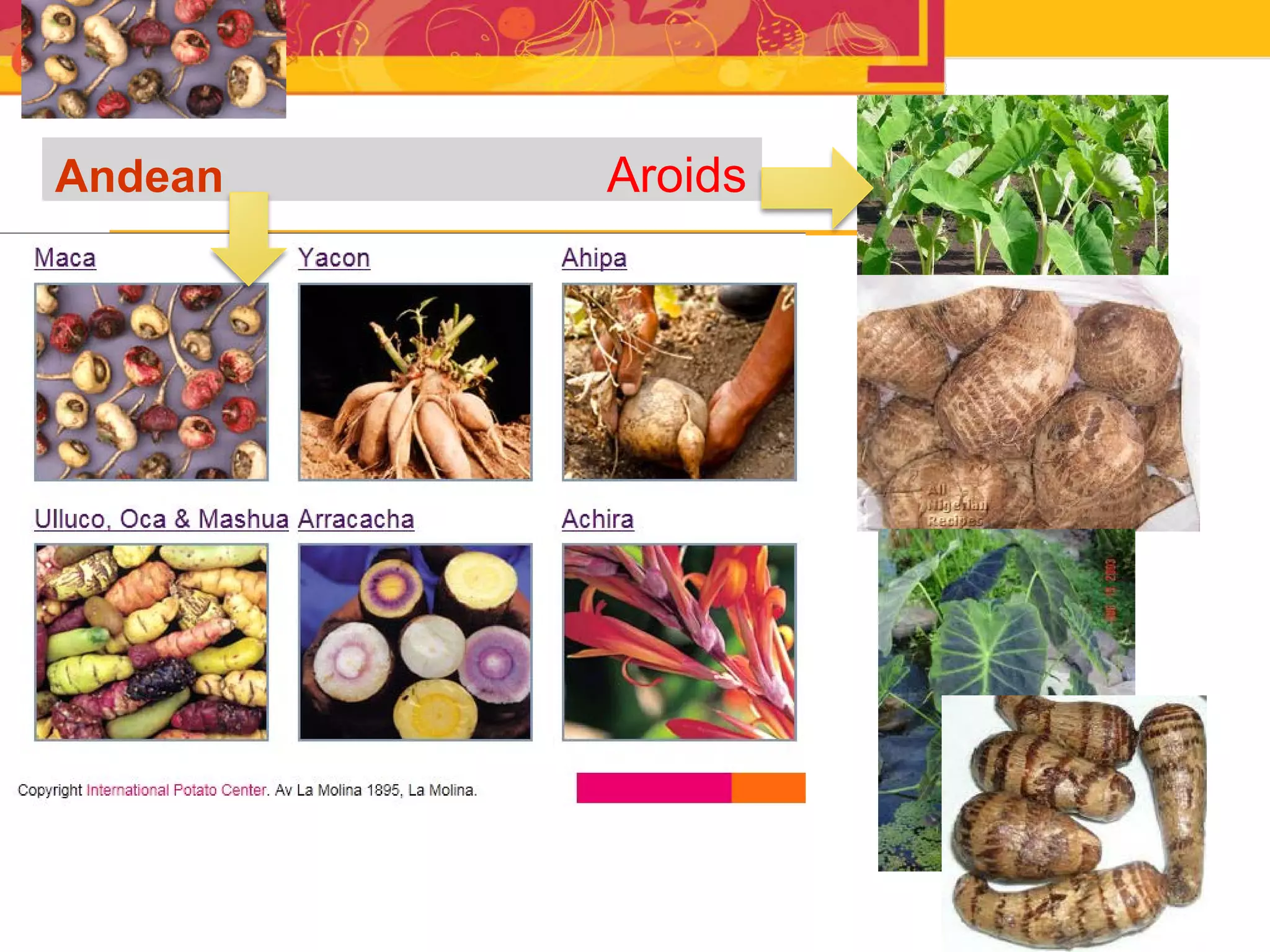
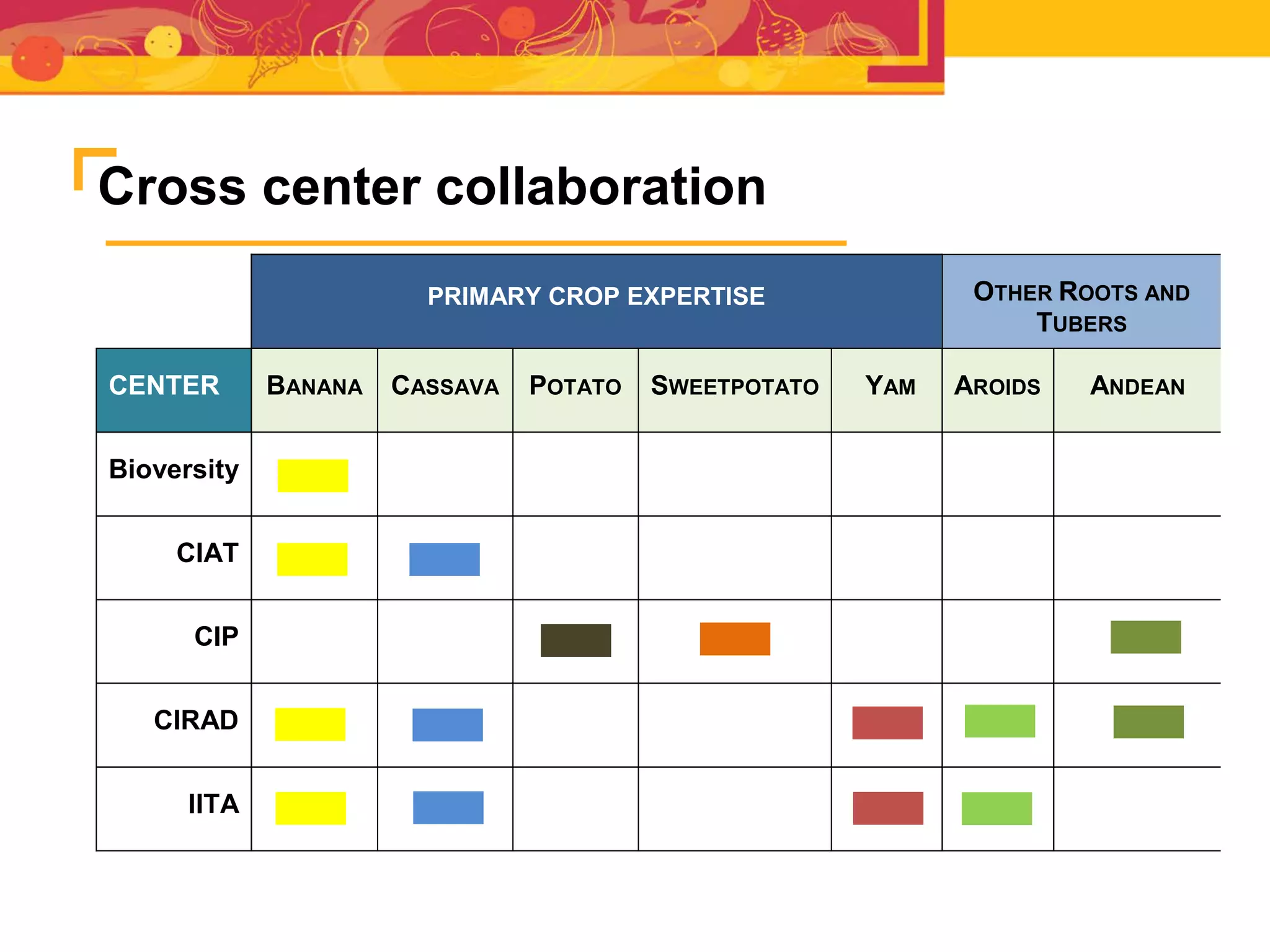
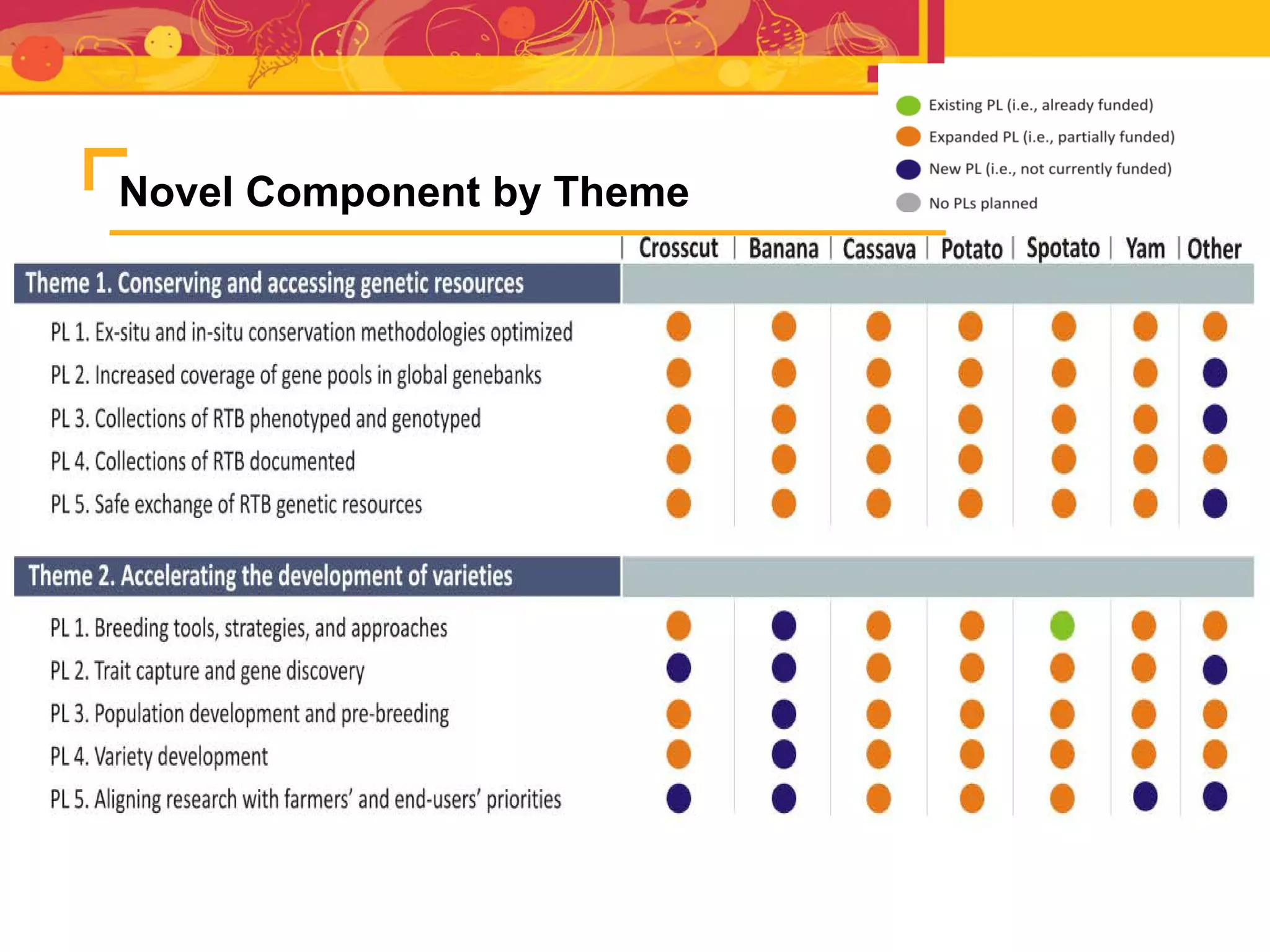
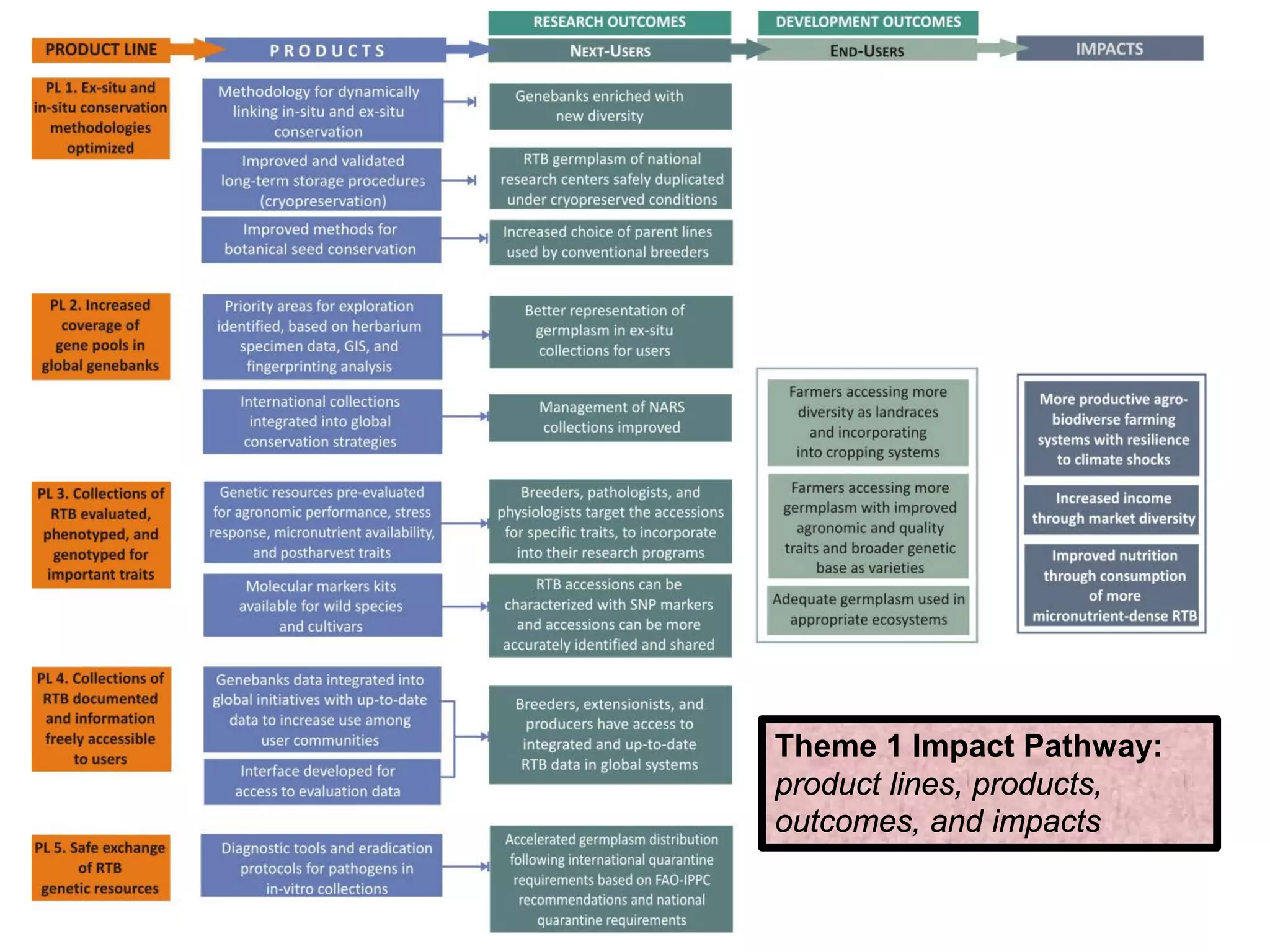
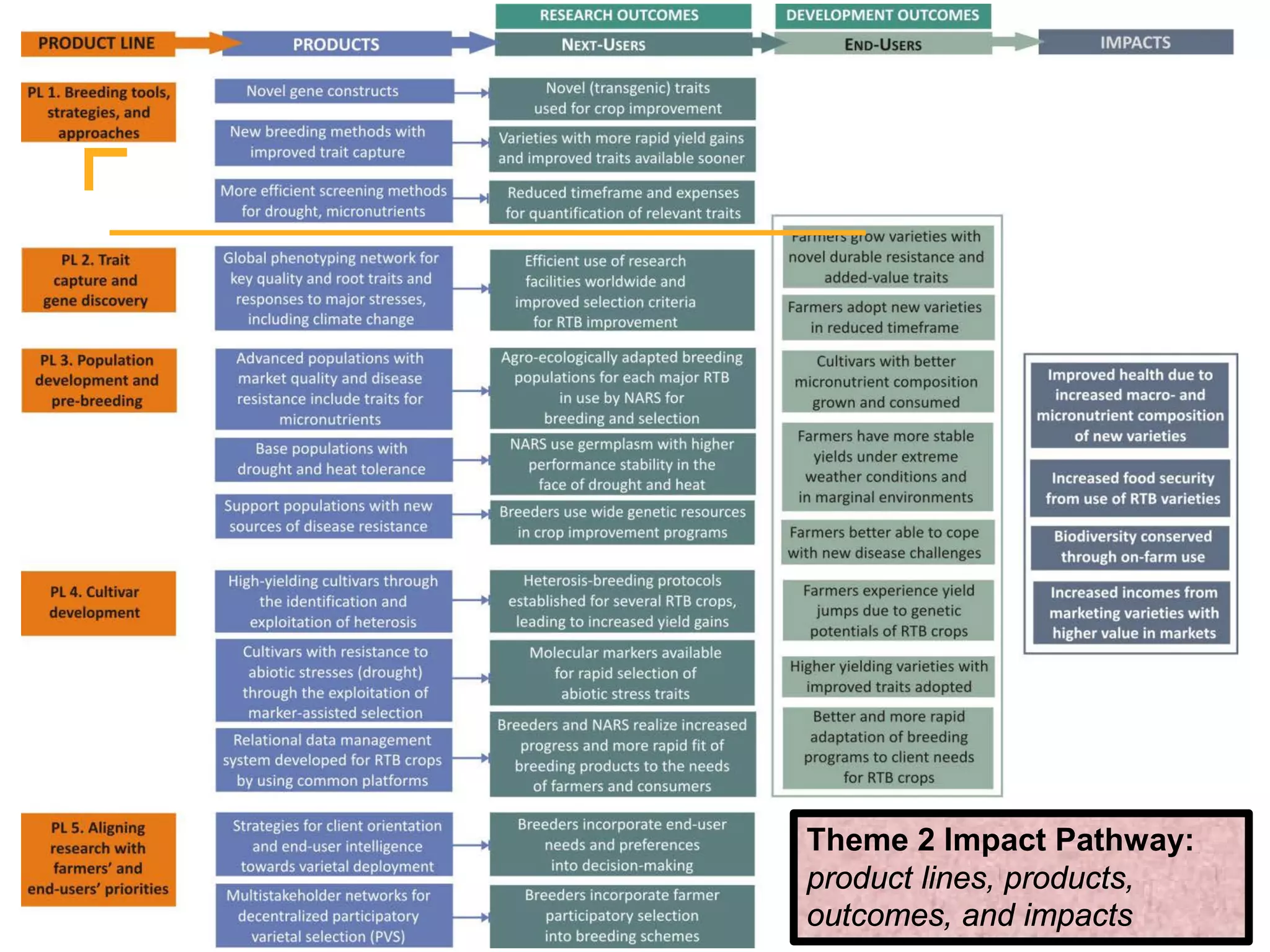
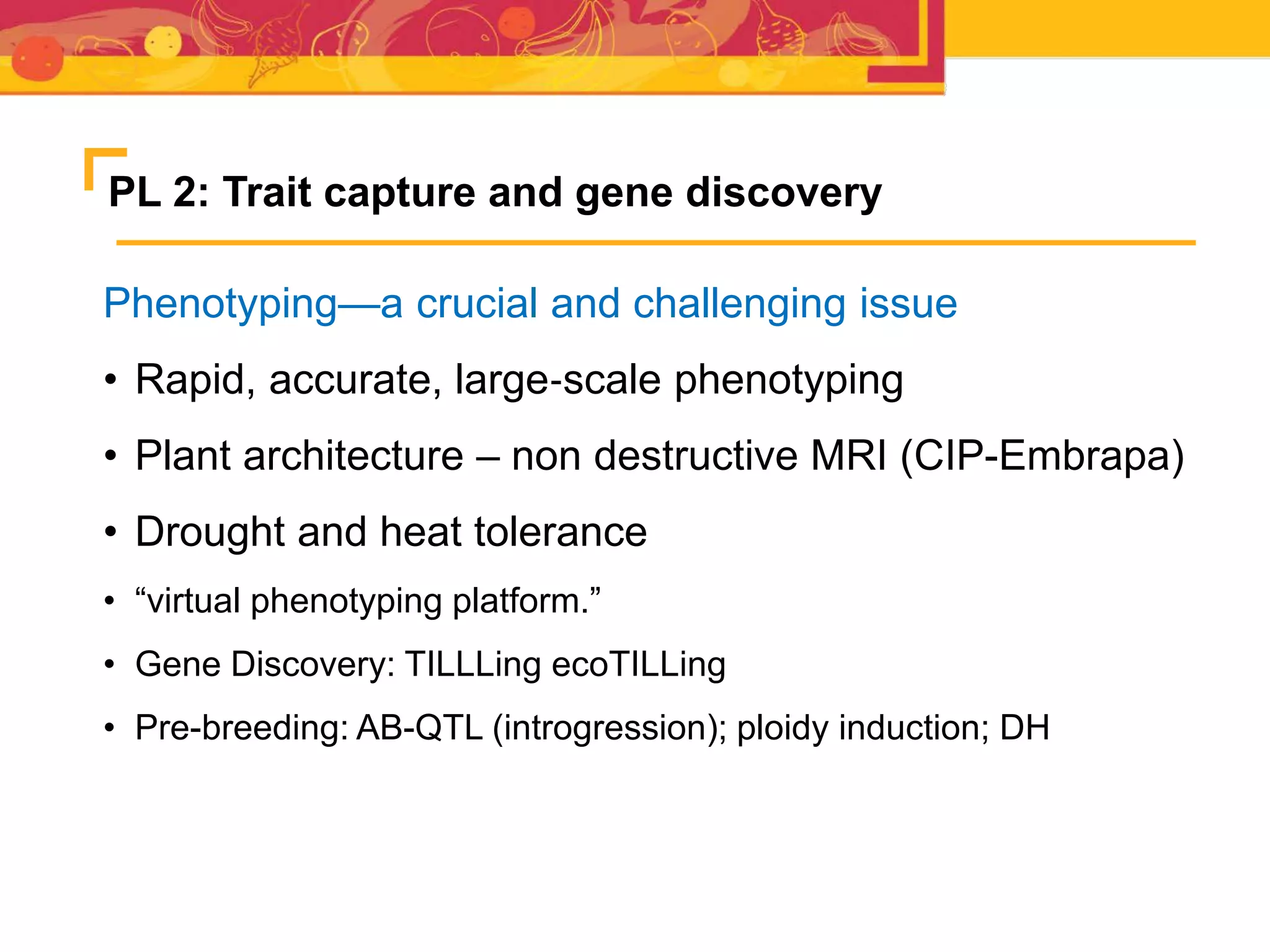
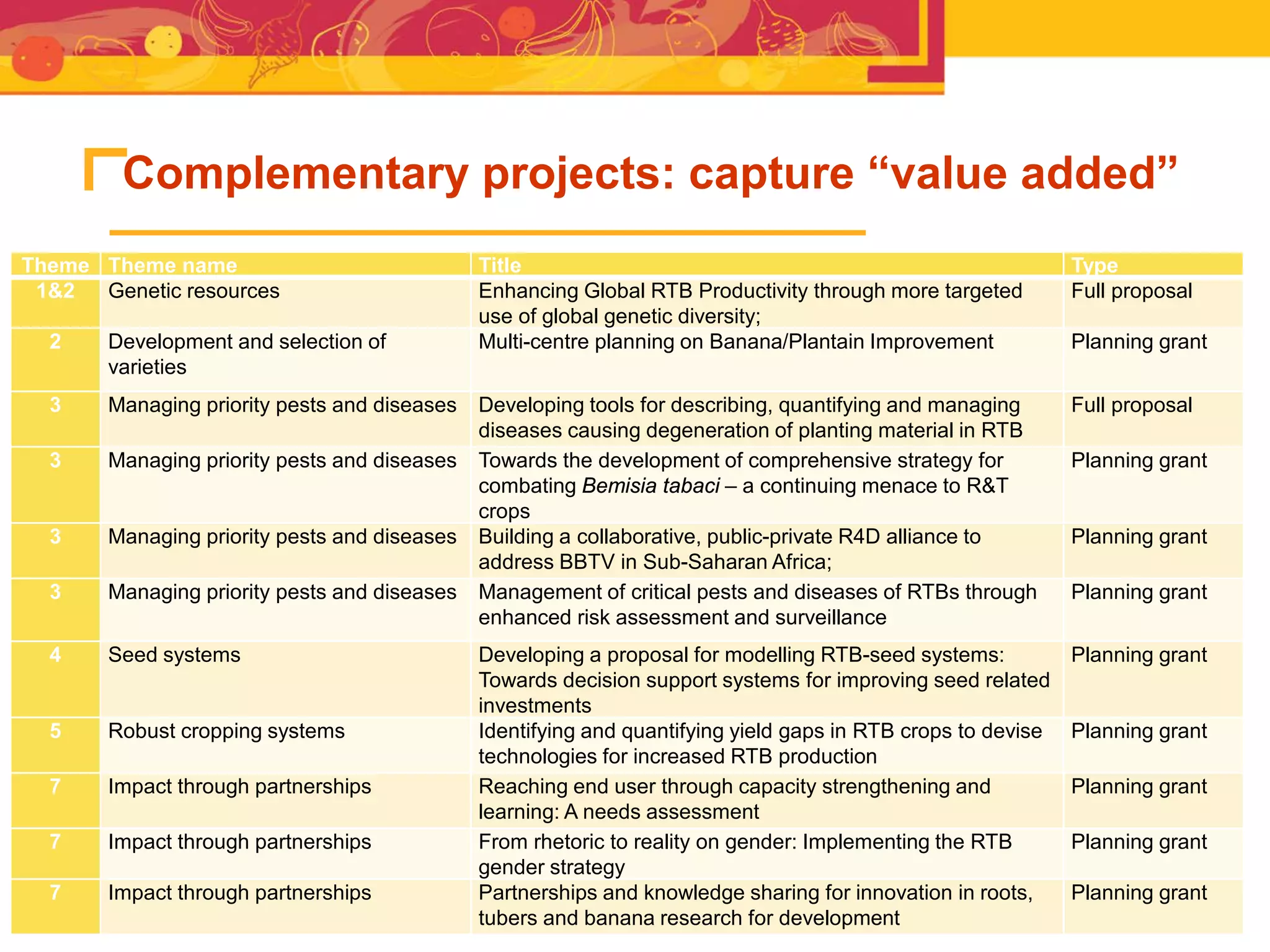
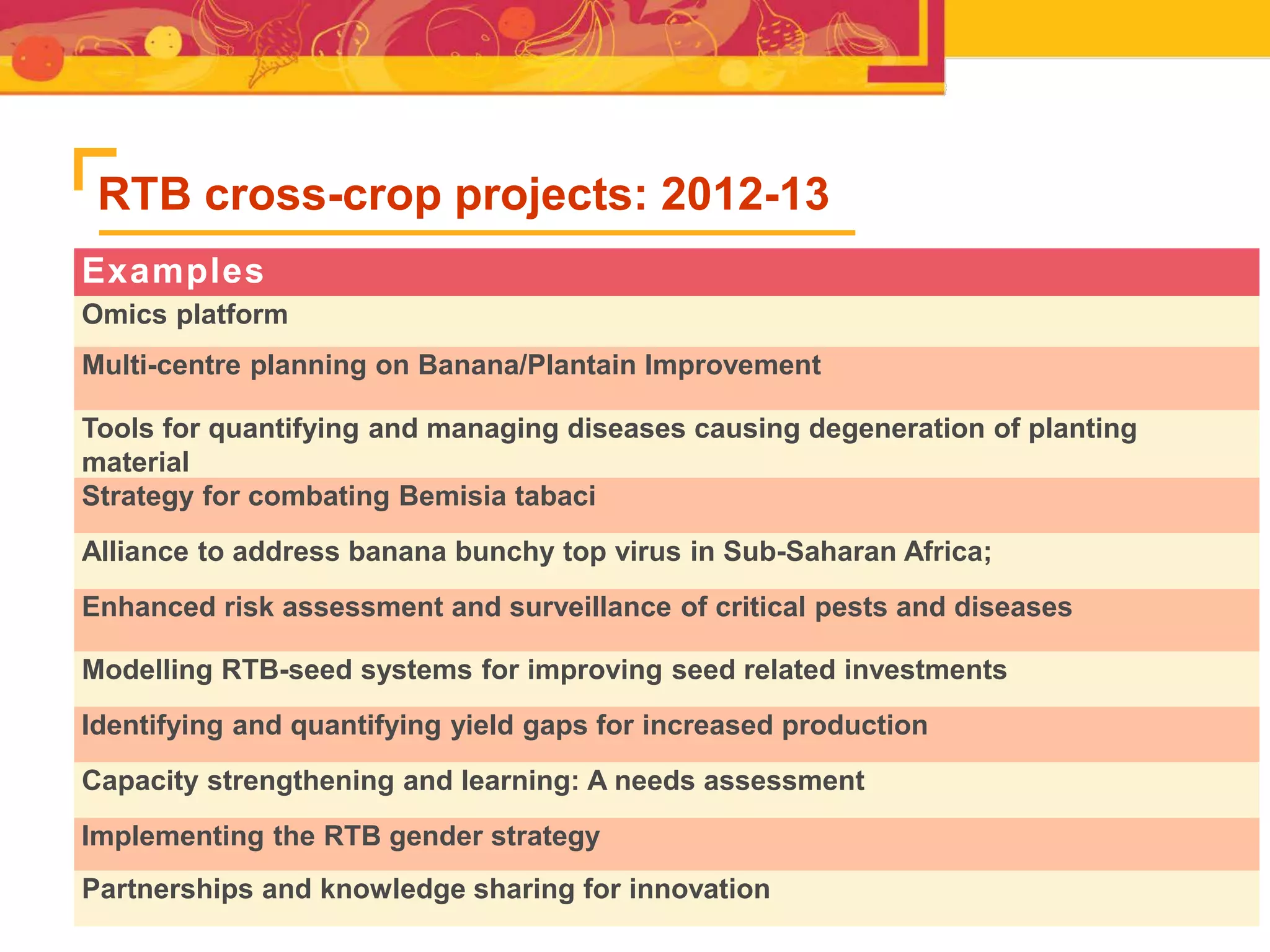
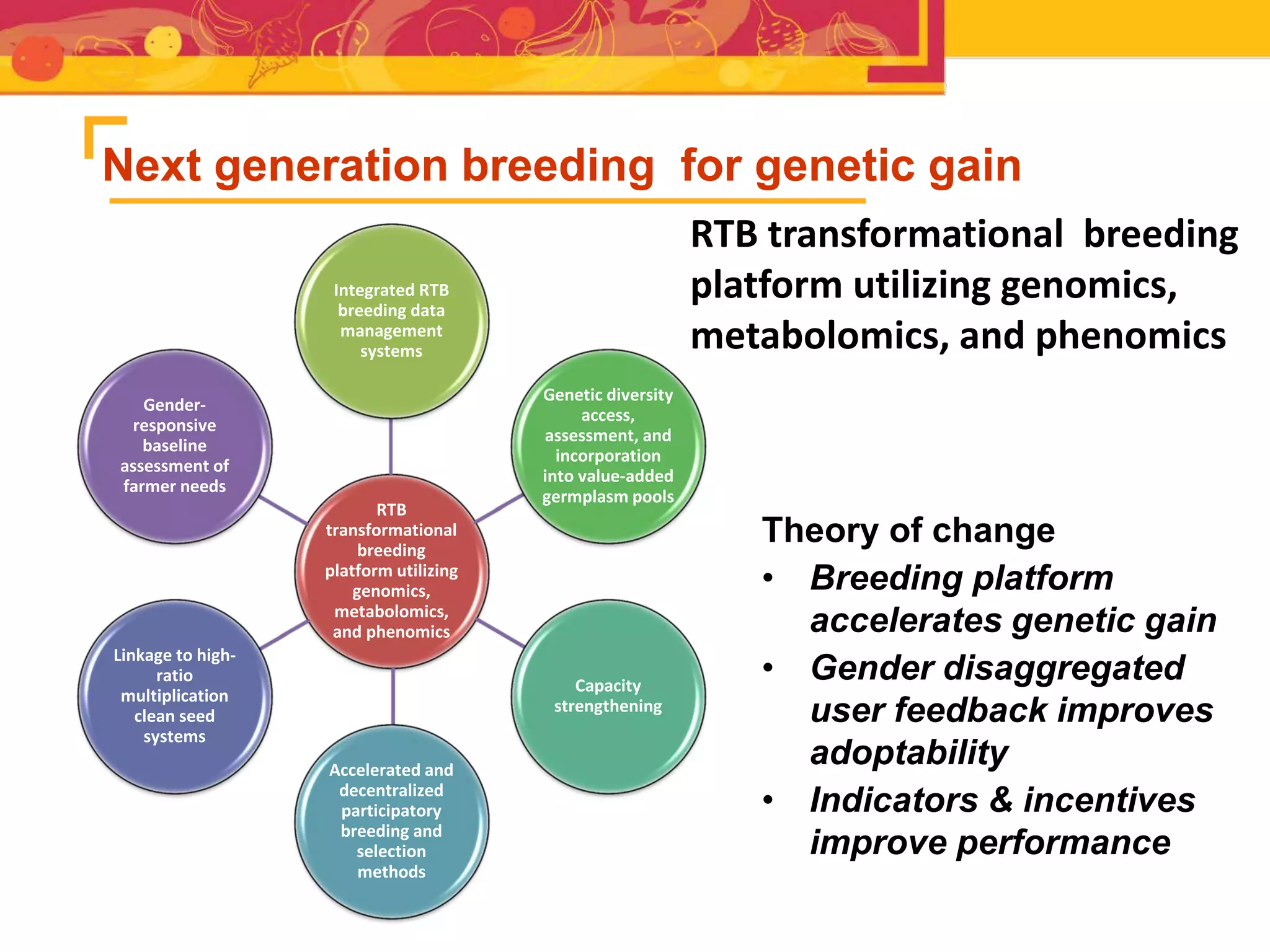
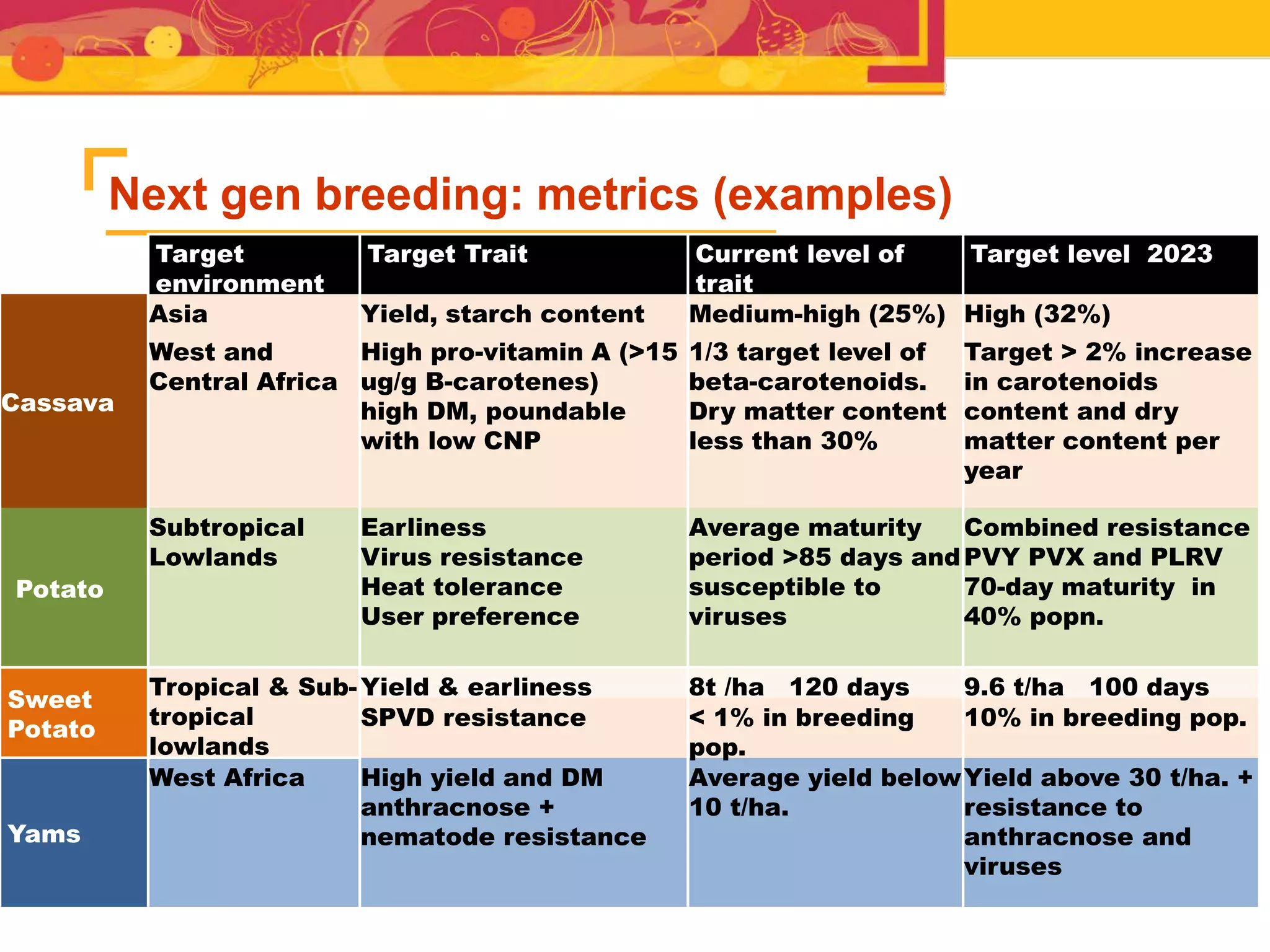
The document outlines the CGIAR Research Program on Roots, Tubers, and Bananas (RTB), emphasizing its collaboration with various stakeholders to improve production and utilization of RTB crops that are essential for 200 million farmers. Key challenges include genetic improvement, pest management, and post-harvest technology, with the program structured around seven thematic areas aimed at enhancing genetic resources, crop yield, and market opportunities. The initiative aims to accelerate breeding and selection processes through innovative tools and partnerships, ultimately increasing productivity and sustainability in RTB crops.