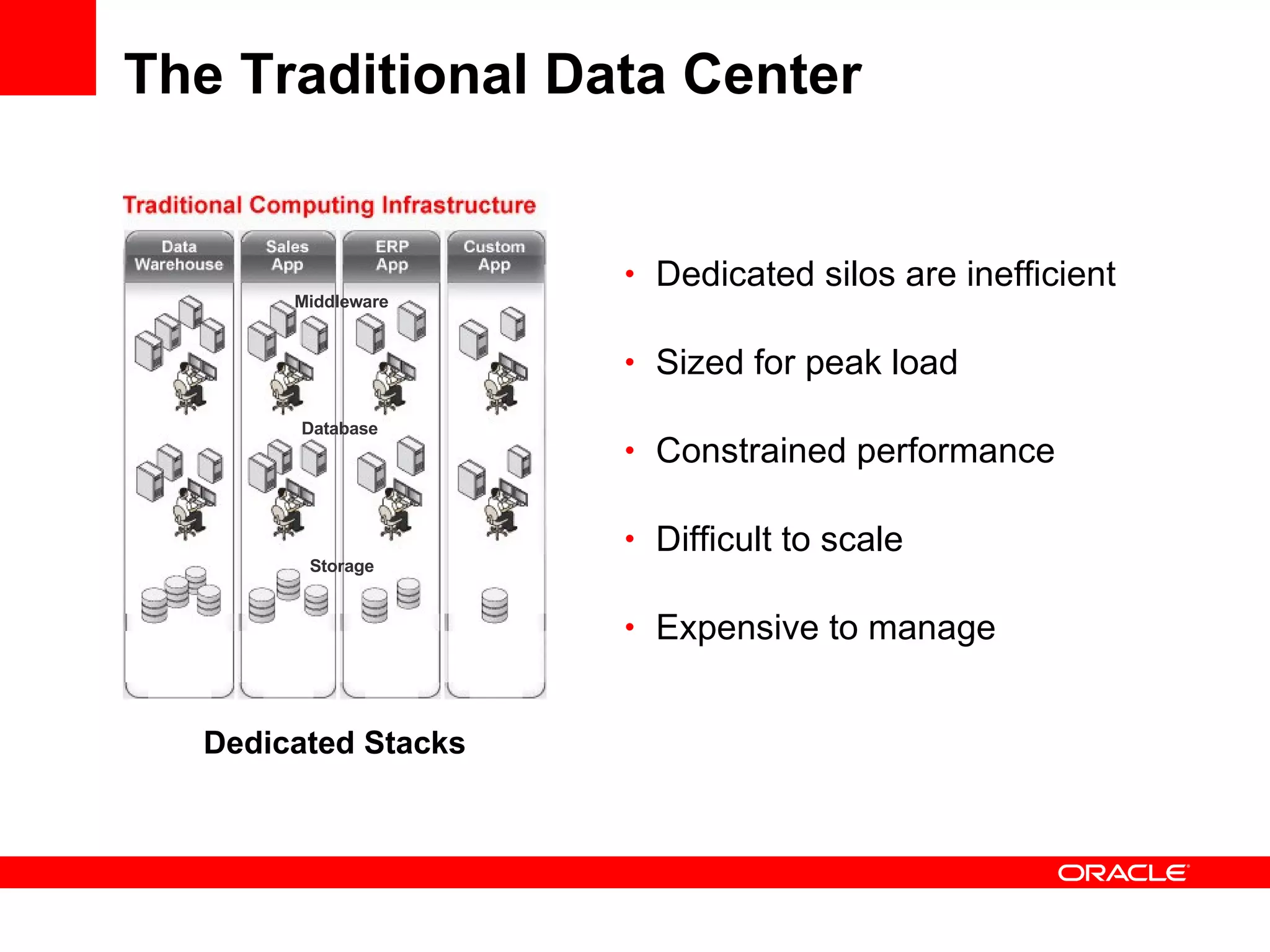
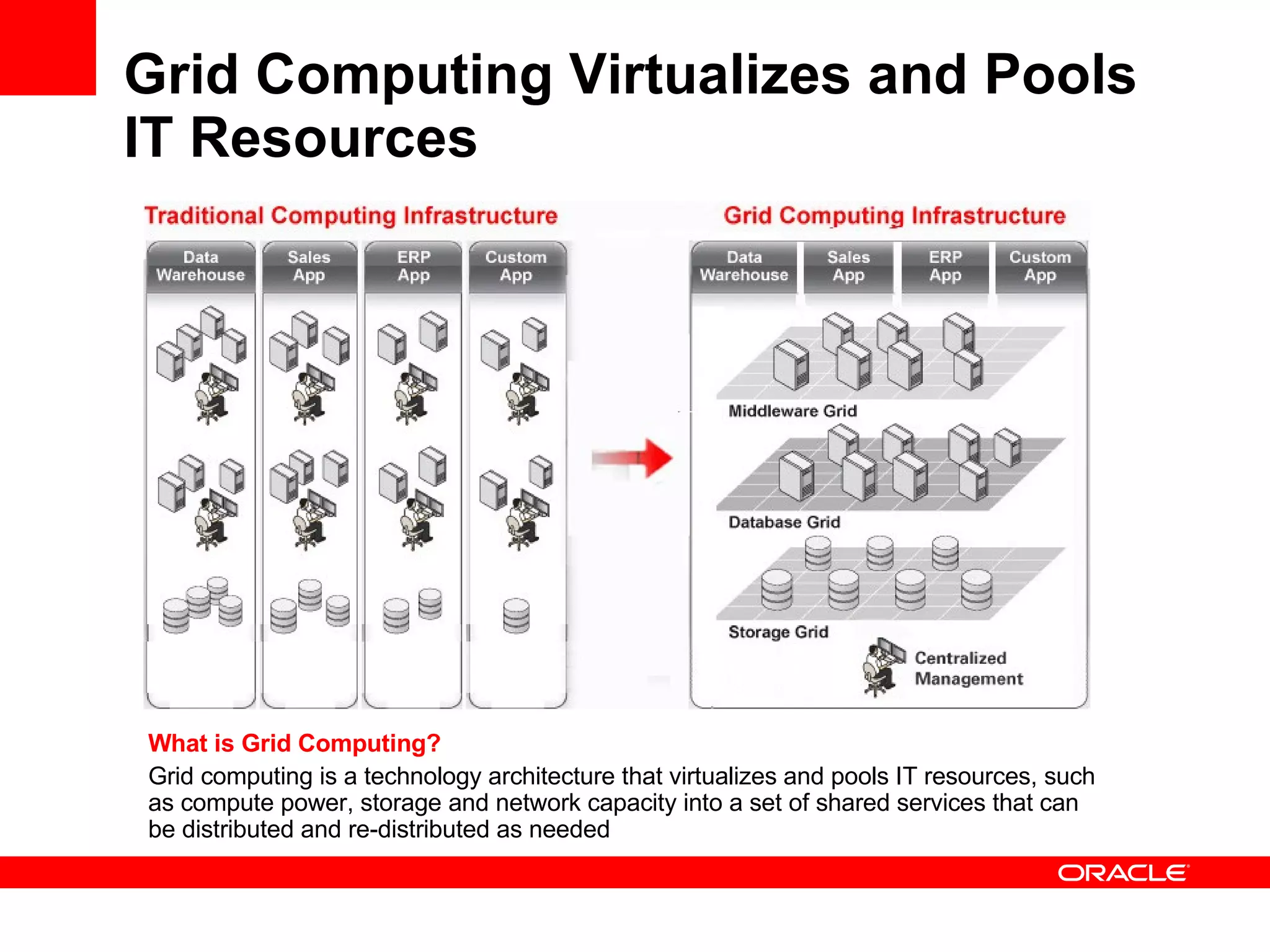
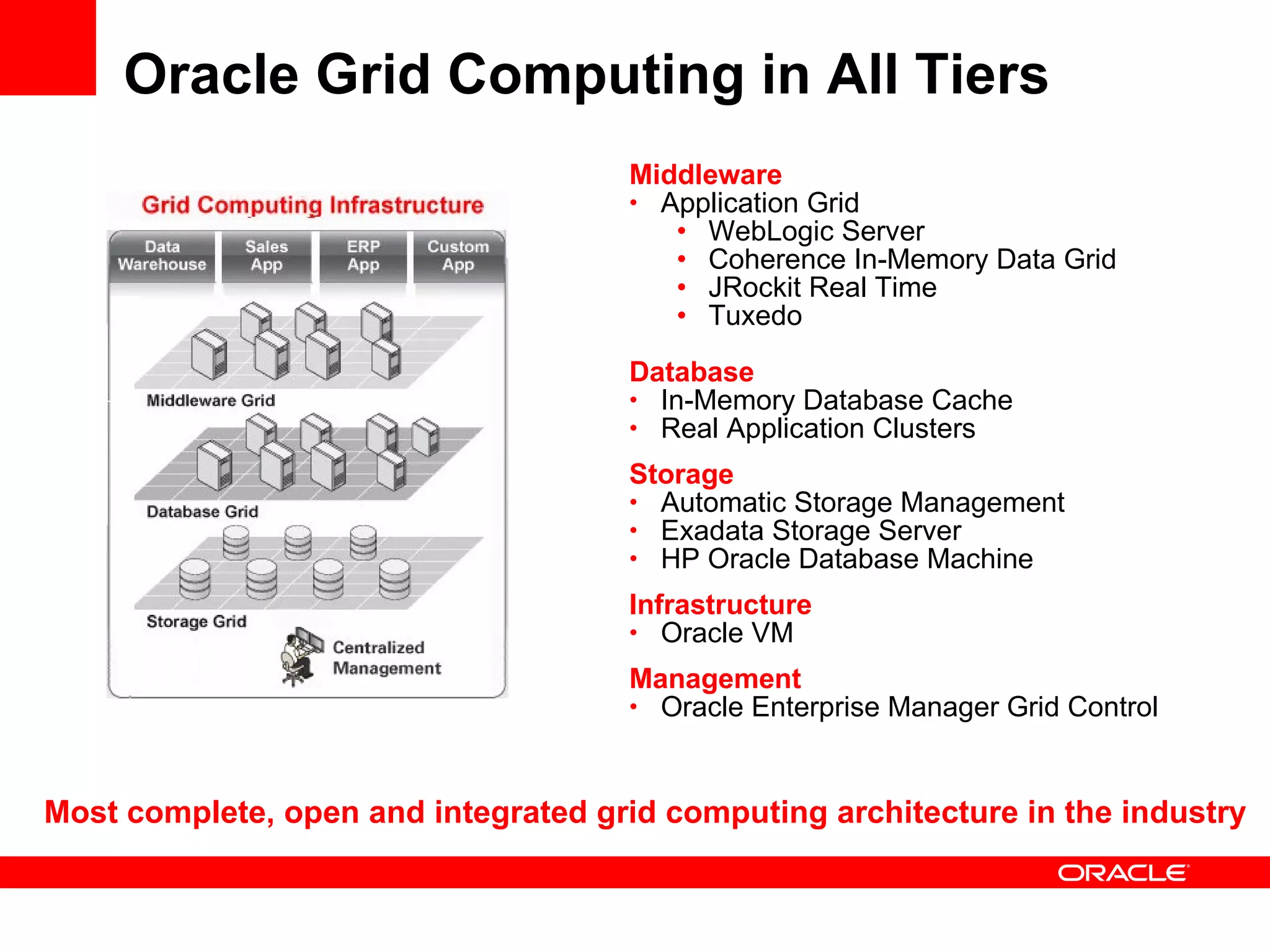
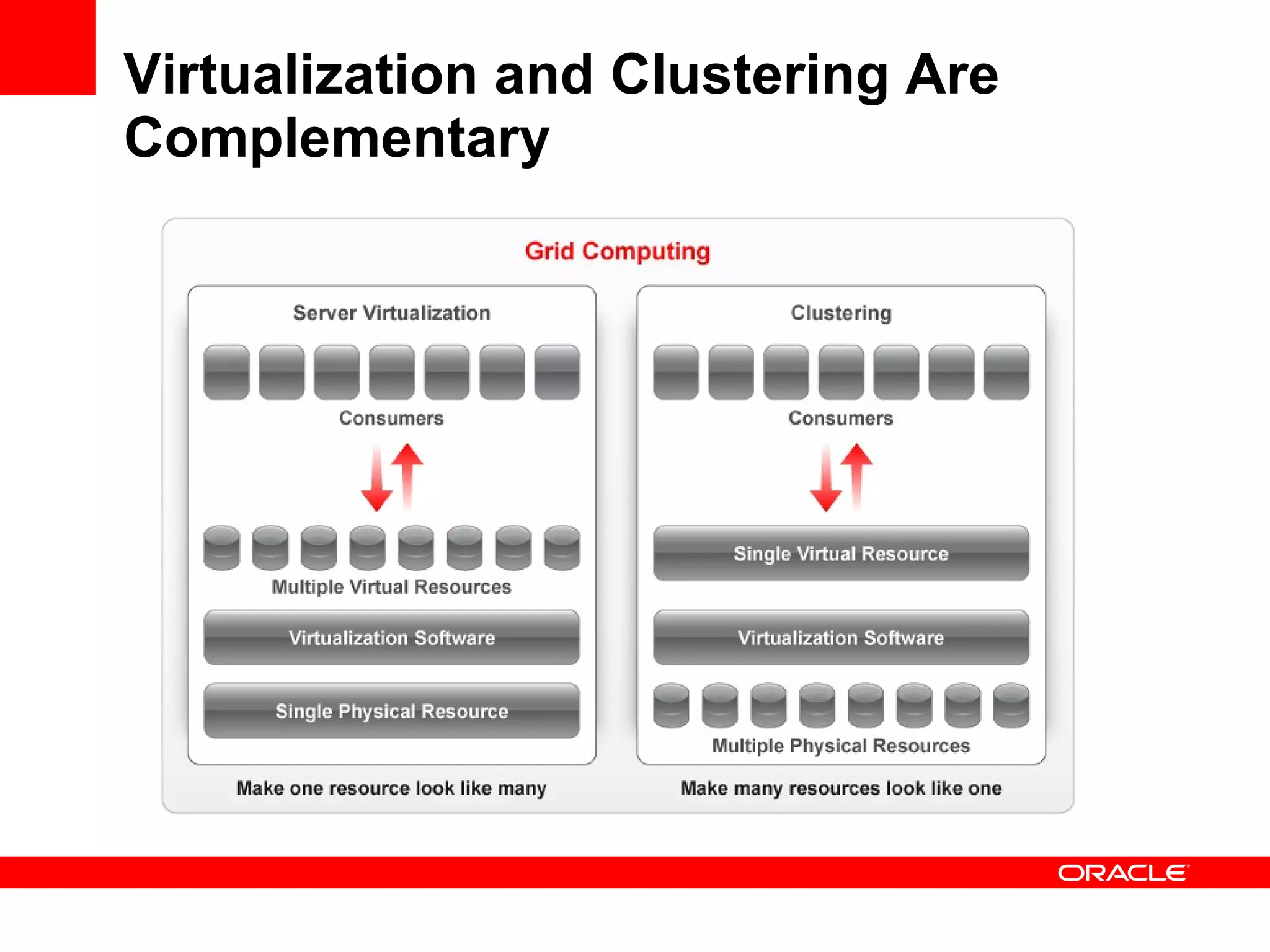
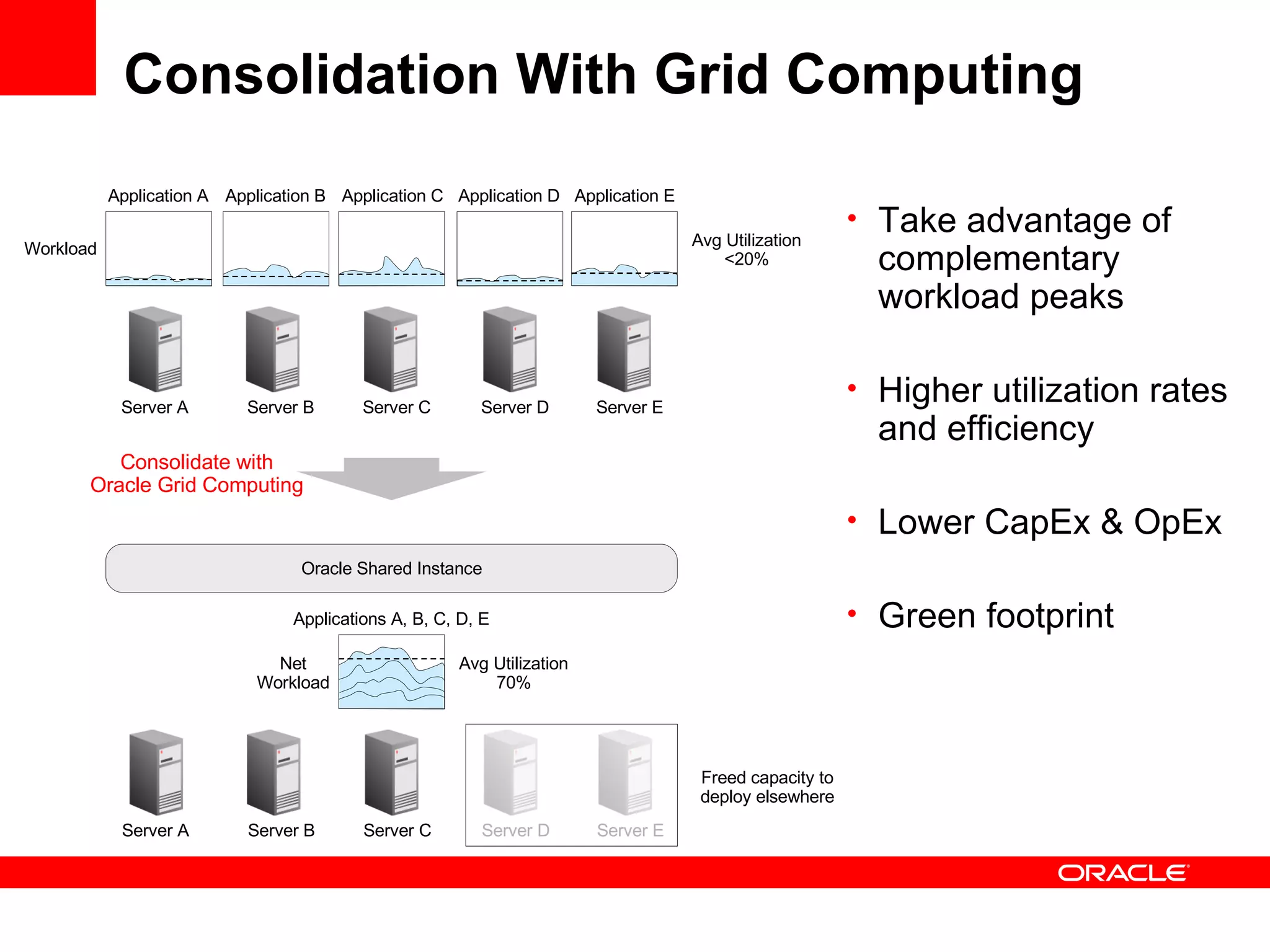
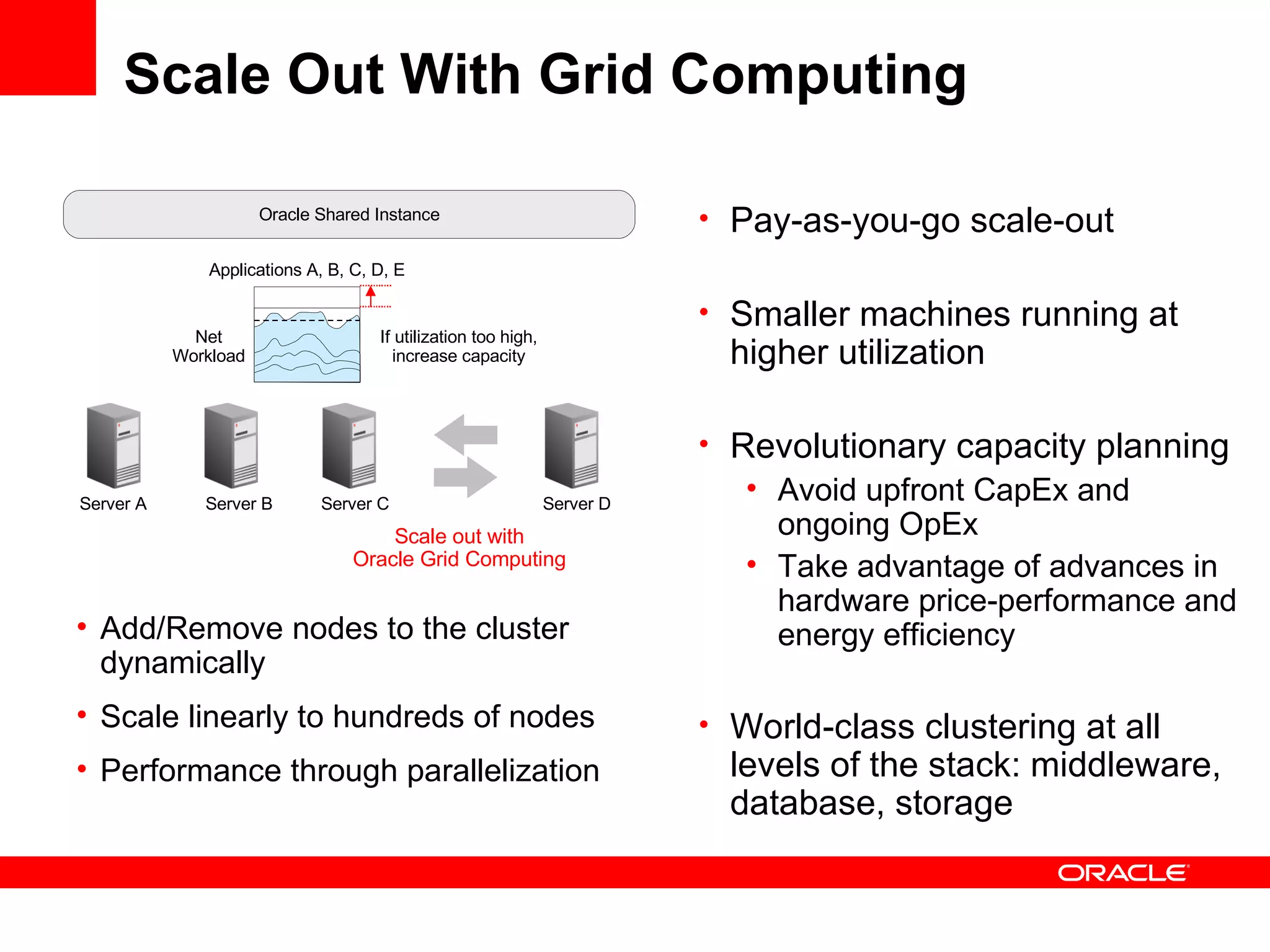
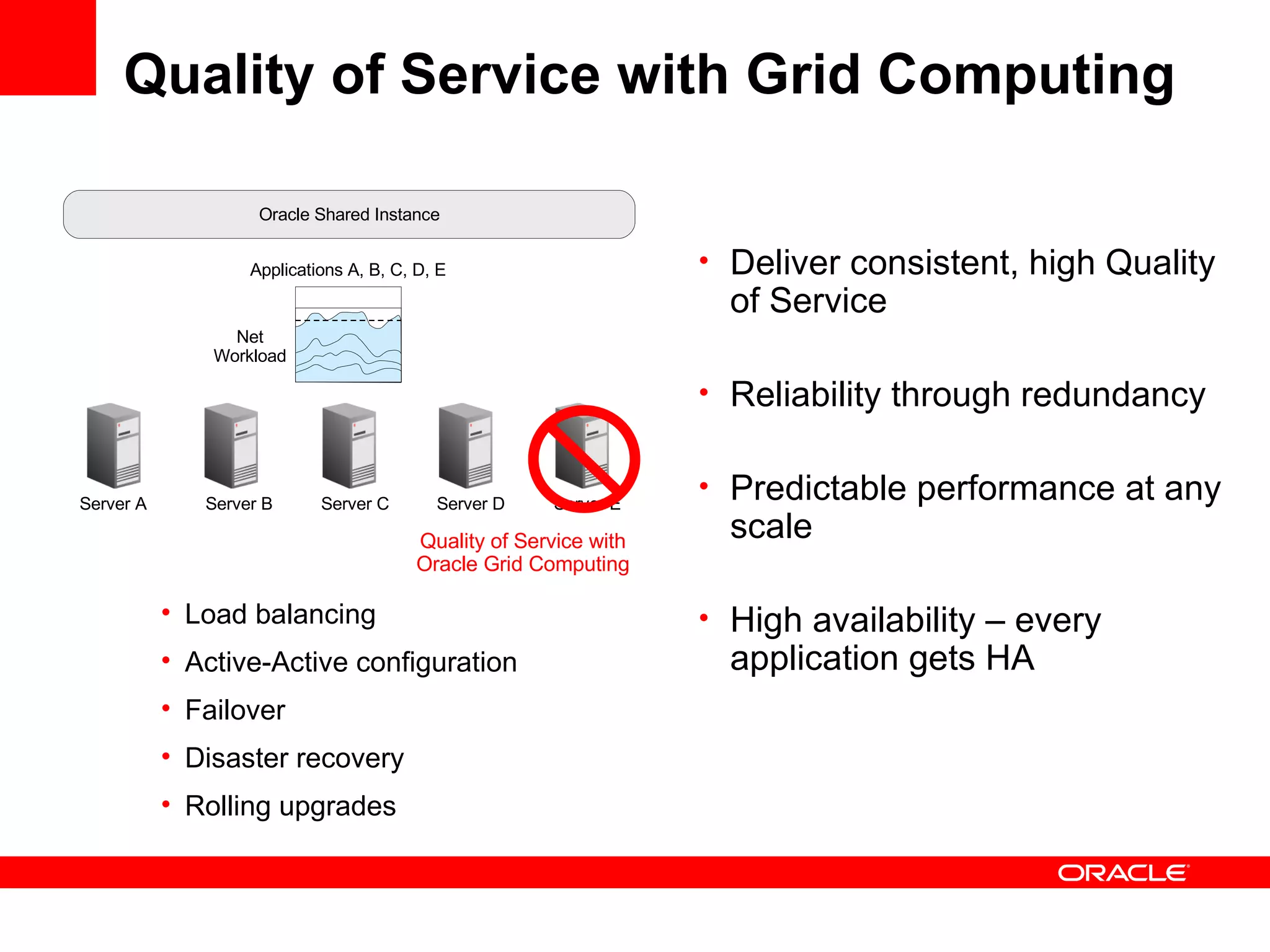
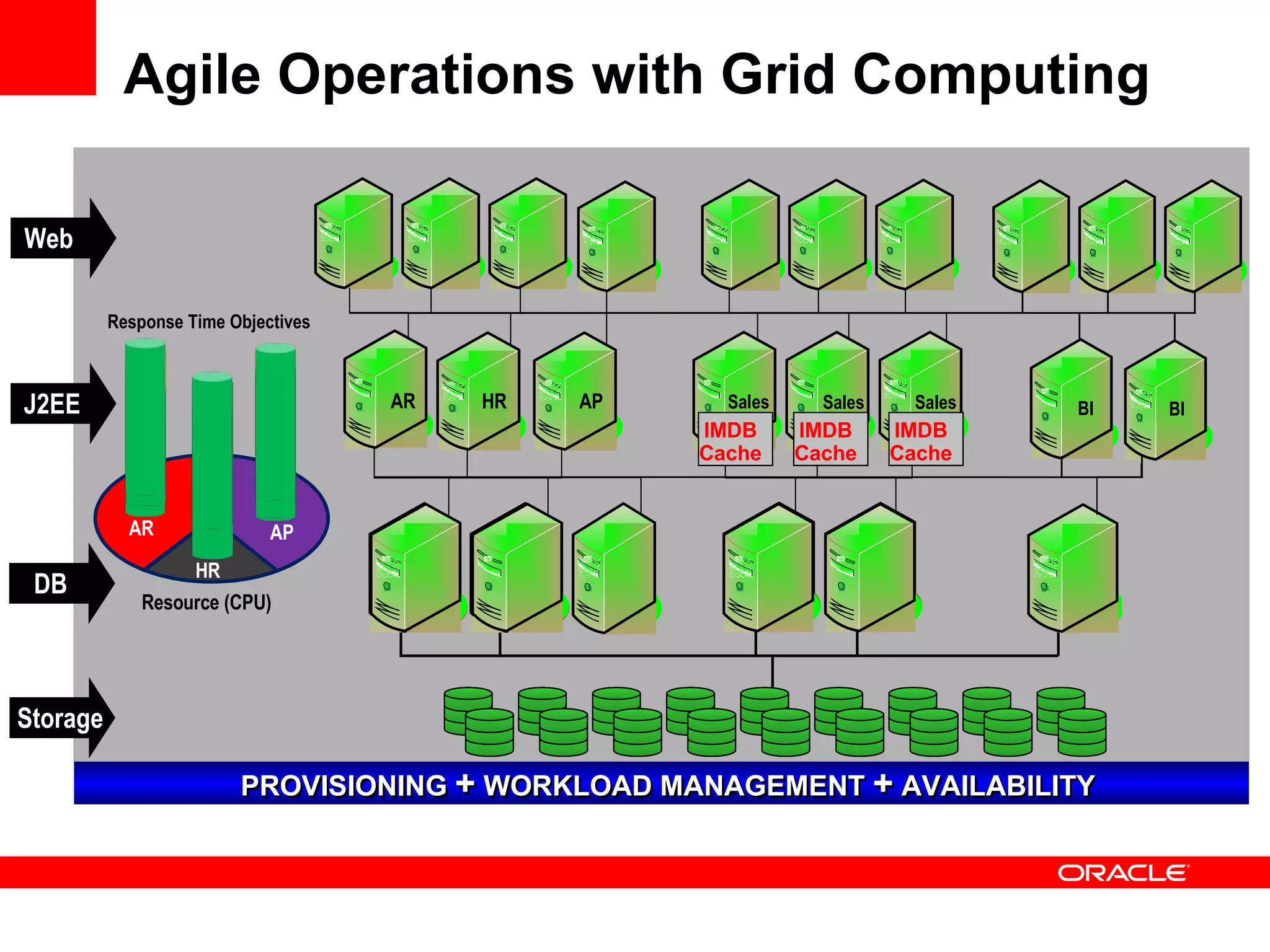
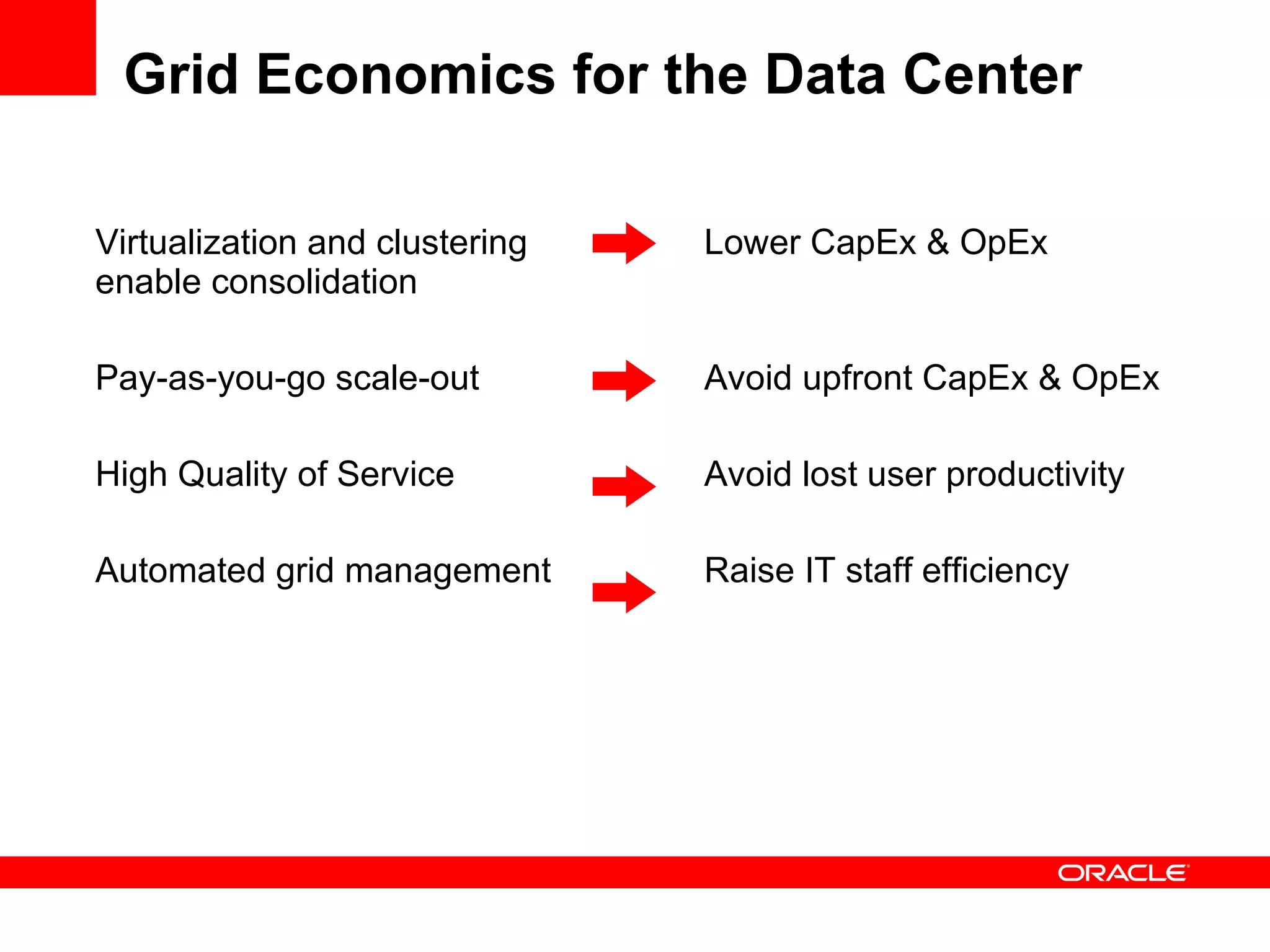
Grid computing virtualizes and pools IT resources such as compute power, storage, and network capacity into shared services that can be distributed as needed. Oracle provides a complete, open, and integrated grid computing architecture across all tiers including middleware, database, storage, and infrastructure. Grid computing allows for consolidation of servers for higher utilization, pay-as-you-go scale out to add capacity as needed, and quality of service through load balancing and failover.