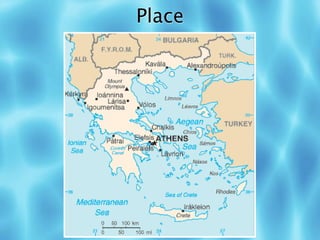
The Greek mainland is located on the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula and is bordered by the Aegean Sea and Ionian Sea. There are over 2,000 islands around the mainland, though only about 170 are inhabited, with Crete being the largest. Ancient Greece flourished from 800-400 BC, with Athens being the birthplace of democracy. Greece has a mountainous landscape with poor soil, though no part is further than 85 miles from the sea. The economy relies on agriculture including olive and grape crops as well as shipping and tourism, as Greece imports most goods. The majority of Greeks are Greek Orthodox and live in urban areas.