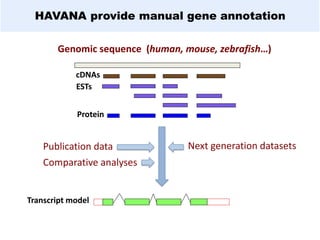
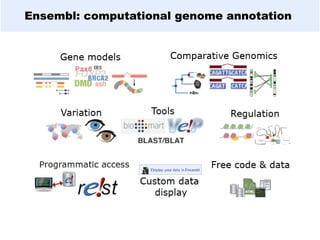
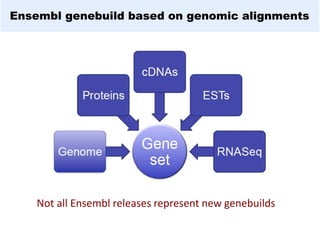
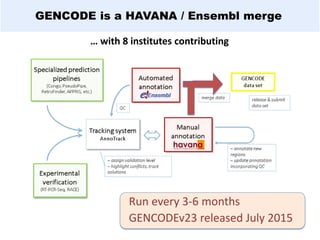
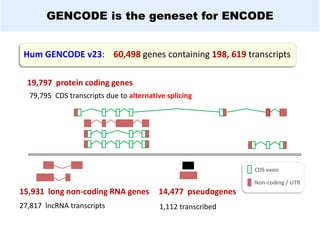
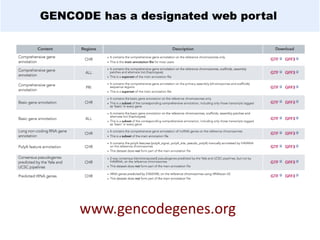
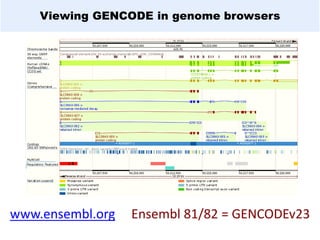
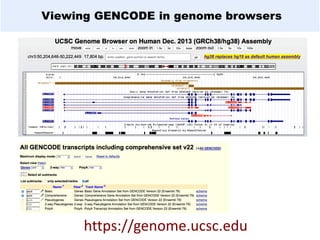
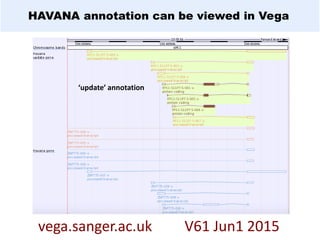
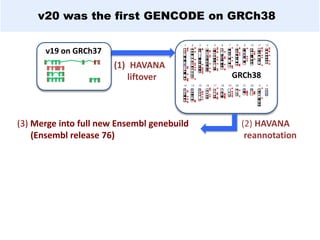
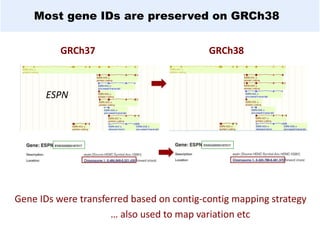
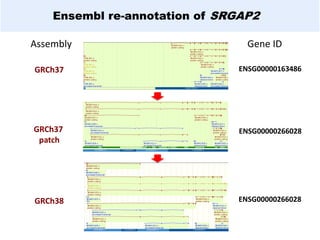
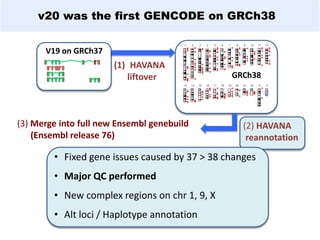
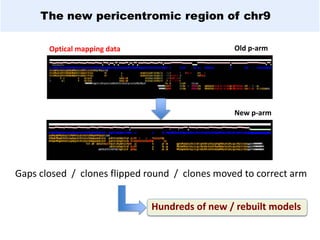
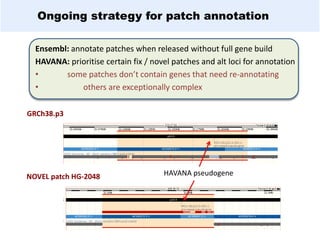
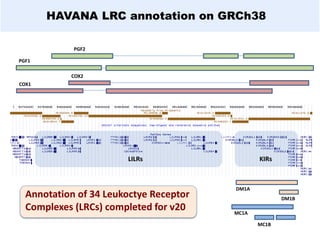
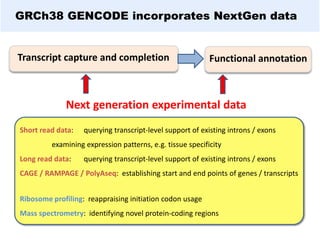
GENCODE provides manual gene annotation of the human genome based on cDNA, EST, genomic and protein sequences, as well as publication and comparative analysis data. It is a merge of annotation from HAVANA and Ensembl. GENCODE v23 contains over 60,000 genes made up of protein coding, long non-coding RNA and pseudogenes. It is the reference gene set for the ENCODE project and can be viewed on the UCSC genome browser and Ensembl. HAVANA annotation of new patches and alternative loci is ongoing to improve GENCODE.