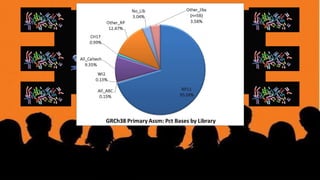
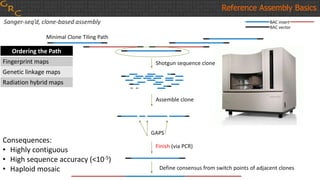
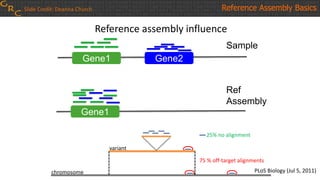
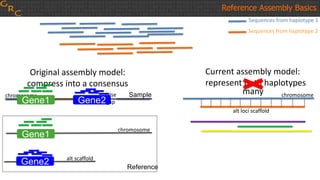
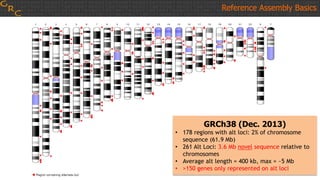
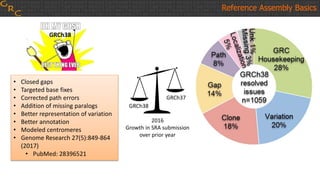
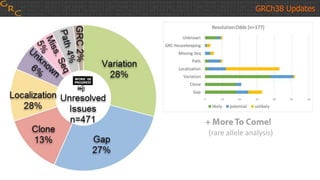
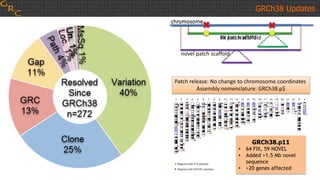
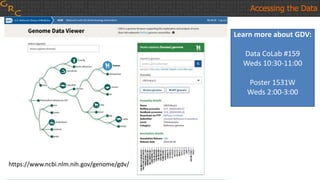
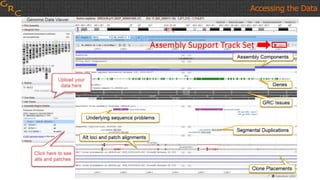
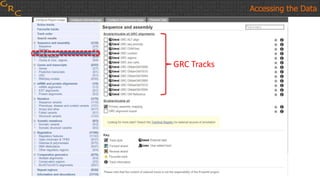
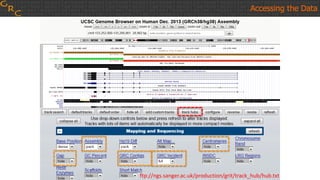
The document outlines a workshop on utilizing reference assemblies and materials, featuring presentations on GRCh38 assembly updates, variation graphs, and benchmarks for variants. Key topics include assembly basics, reference-grade human assemblies, and updates on GRCh38, including the addition of novel sequences and improved representation of genetic variation. It also discusses accessing data from various resources and highlights contributions from the assembly team and community collaborators.