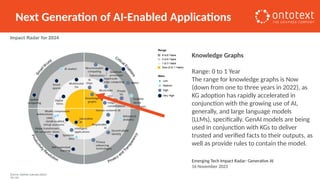
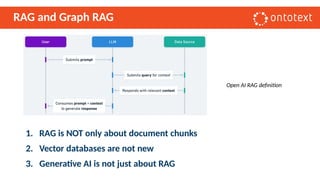
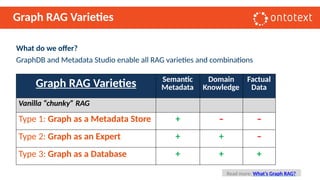
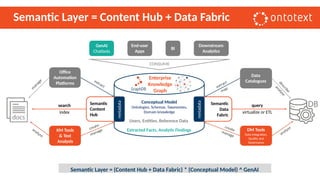
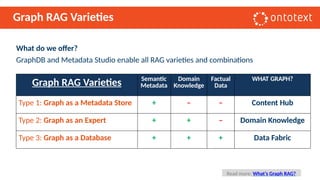
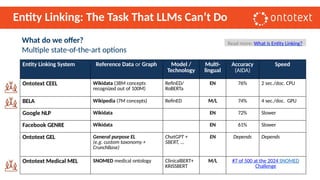
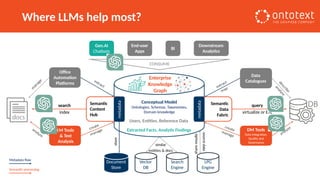
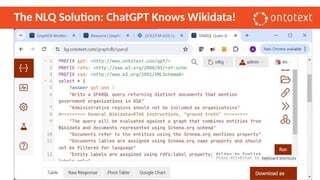
The document presents an overview of knowledge graphs and their integration with generative AI technologies, highlighting their role in transforming complex business data into competitive advantages. It discusses the capabilities of various graph data management systems, their use cases in entity linking, and the benefits of fine-tuning large language models with knowledge graphs. Additionally, it addresses challenges faced in applying retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and proposes solutions for enhancing data discoverability and effectiveness in managing and utilizing organizational data.