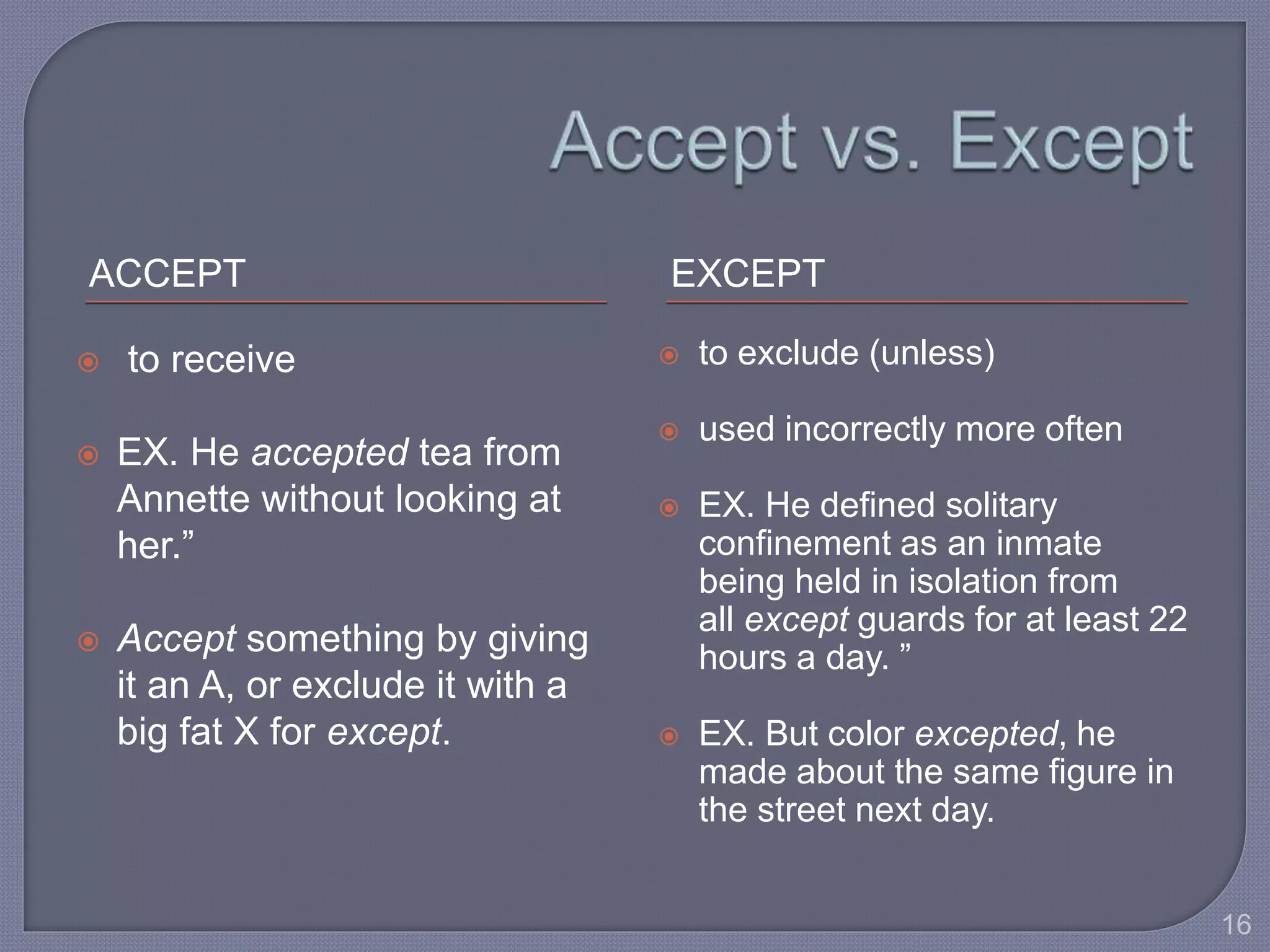
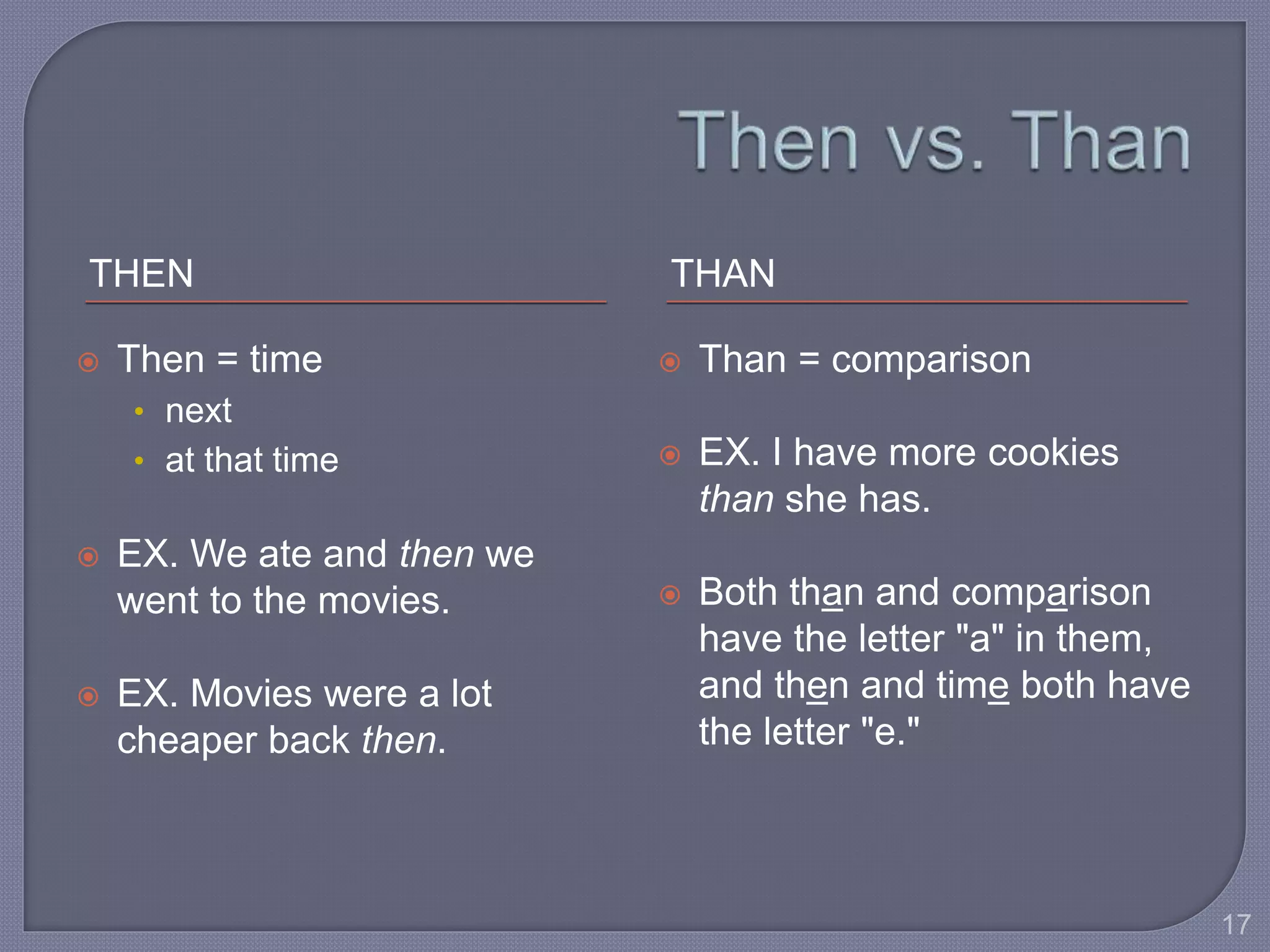
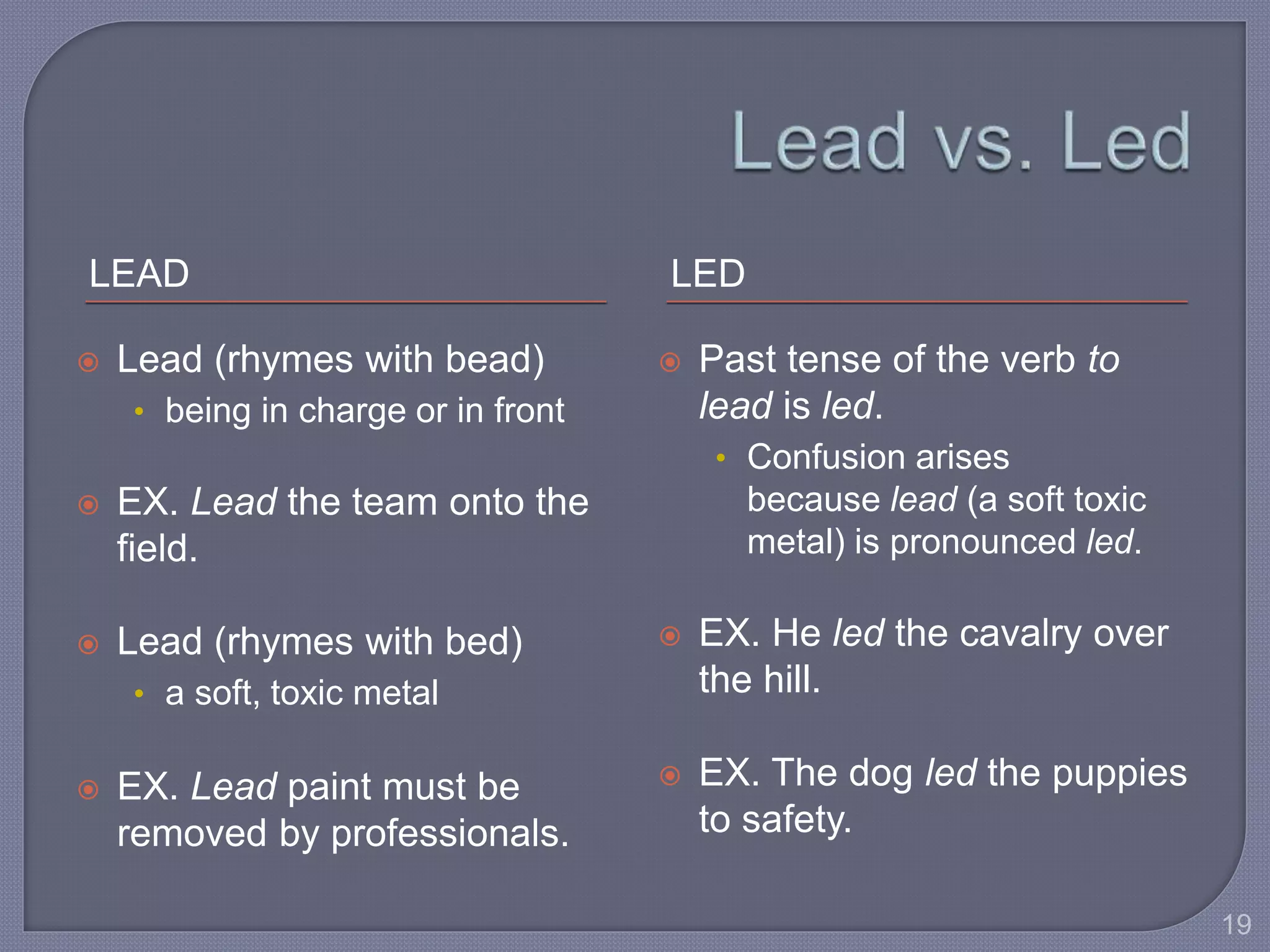
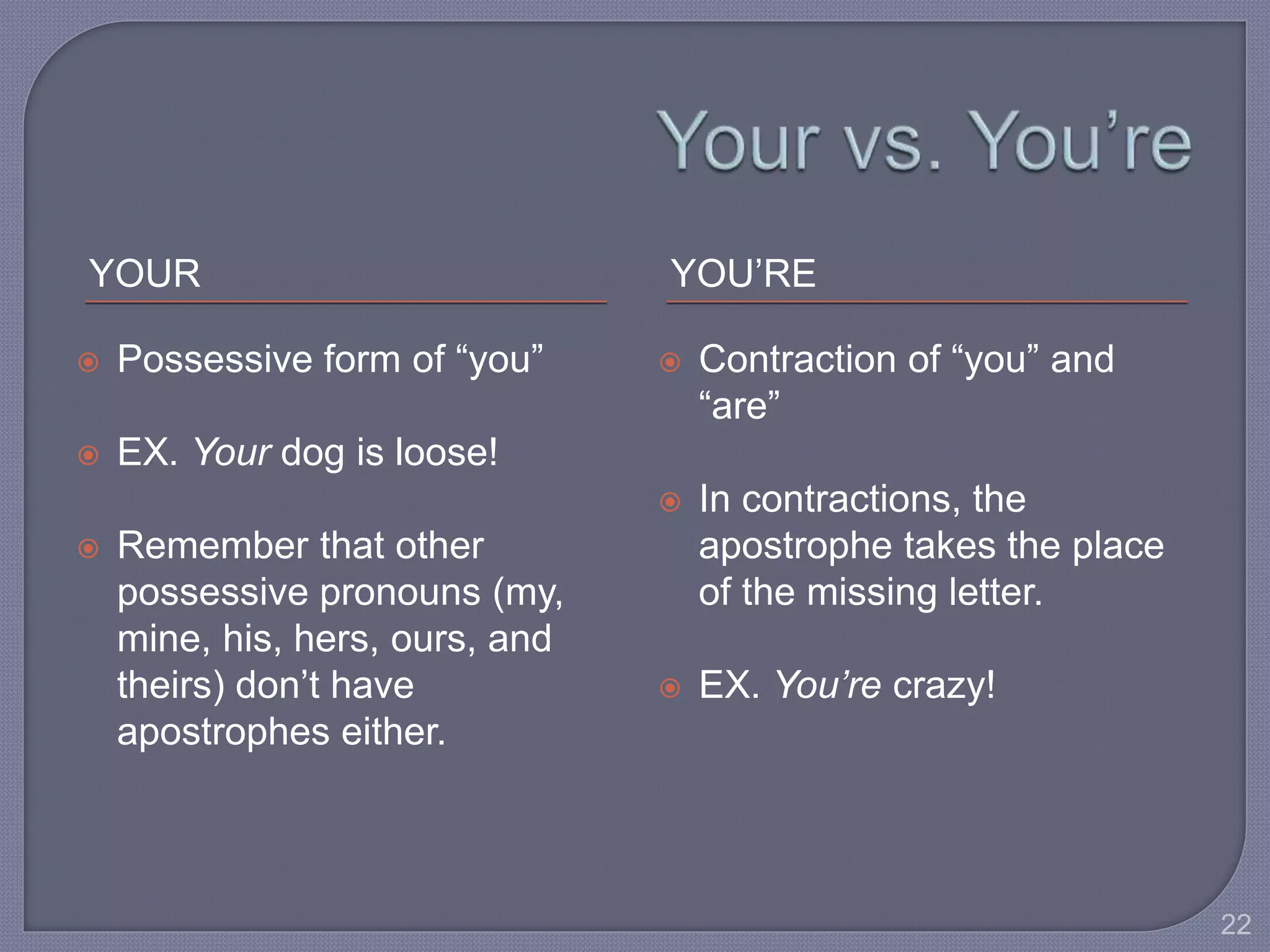
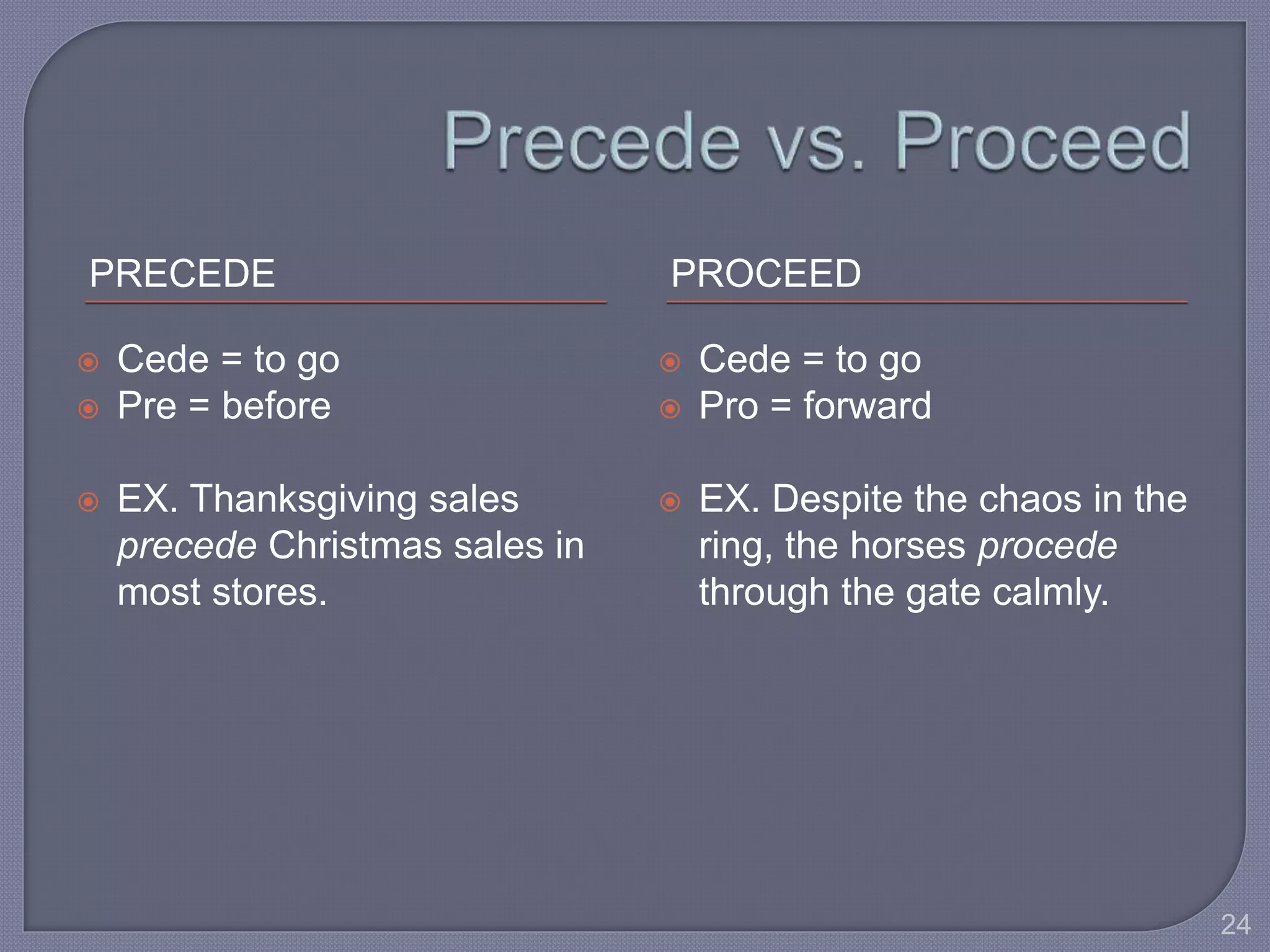
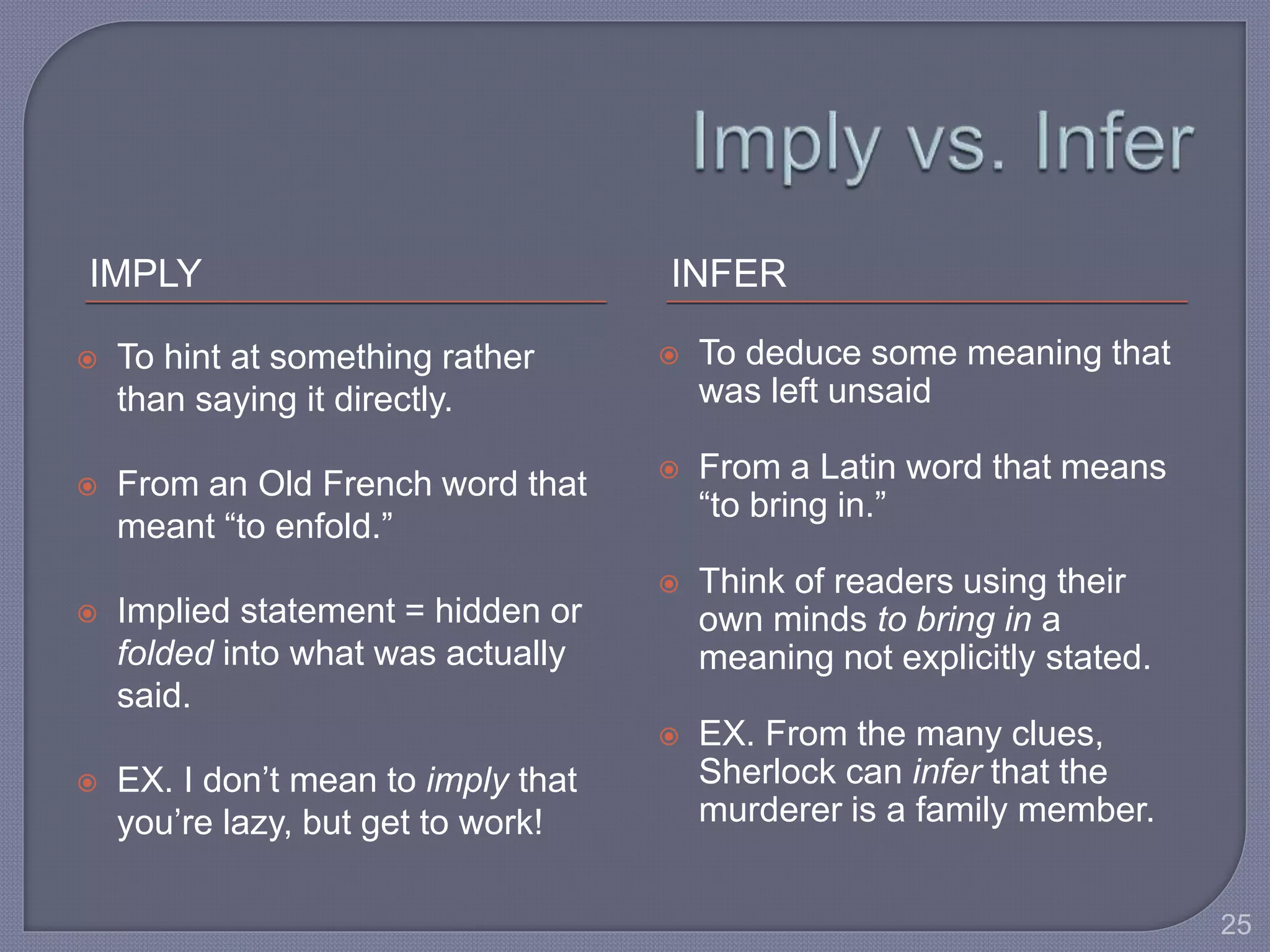
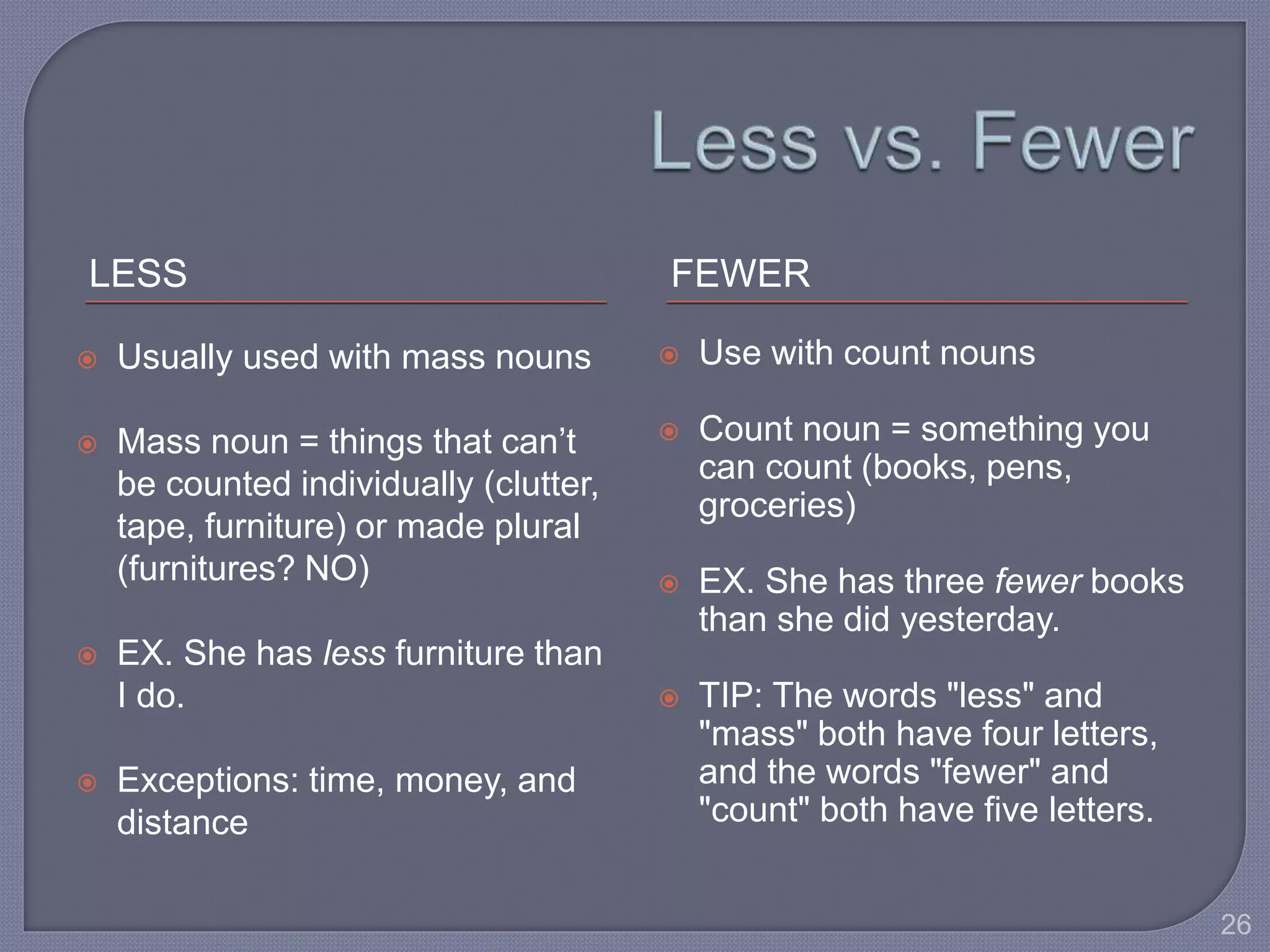
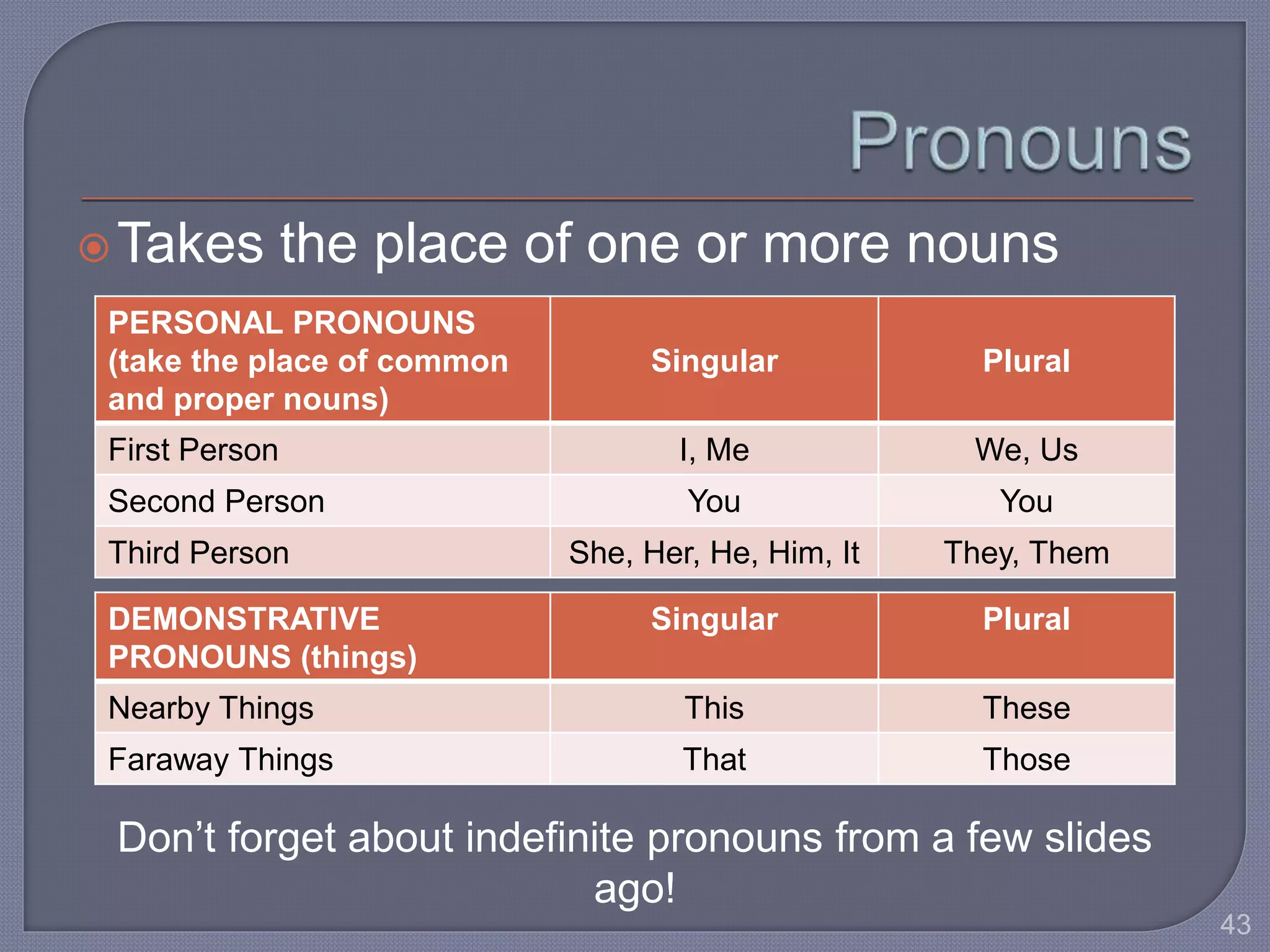
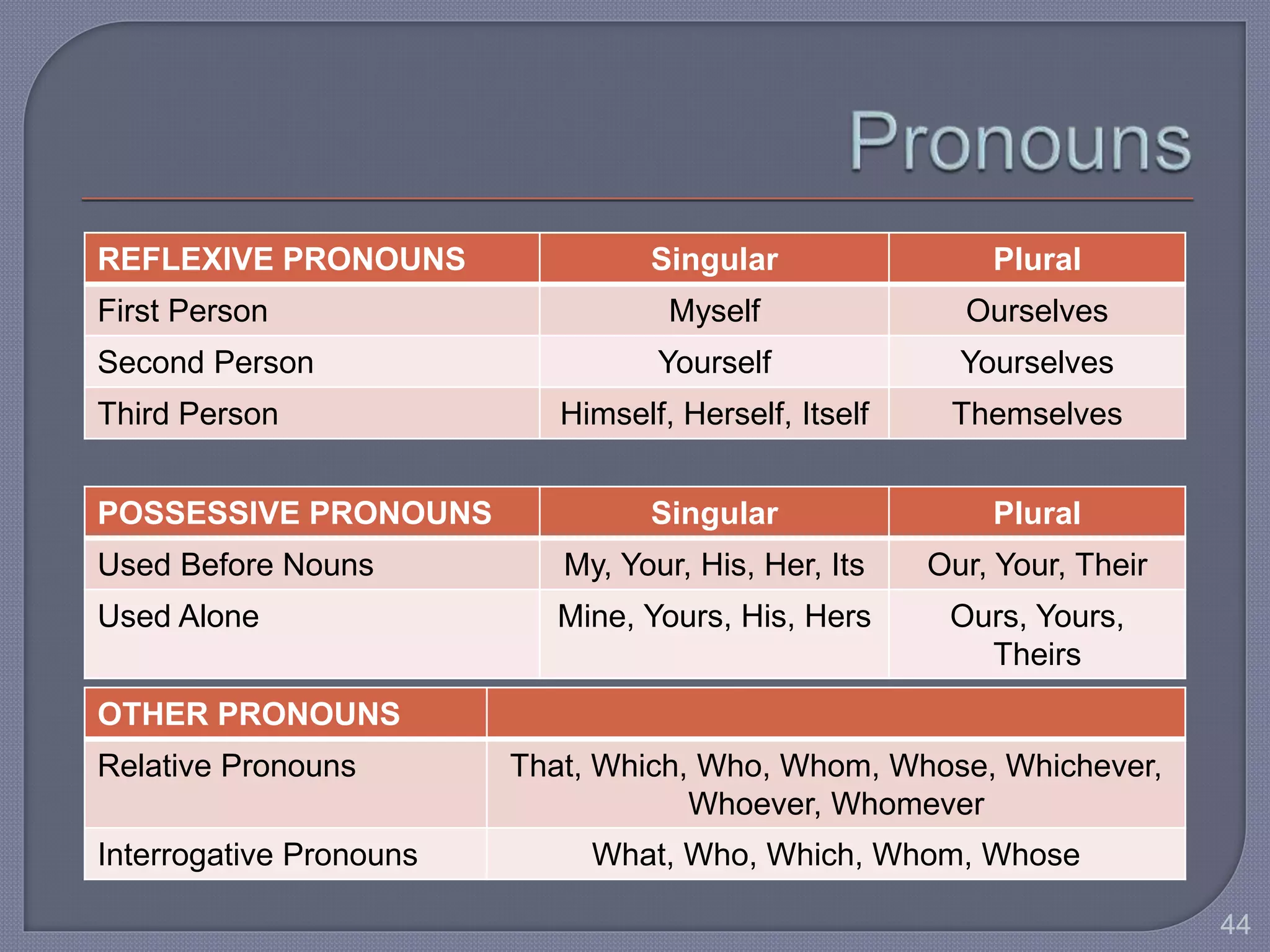
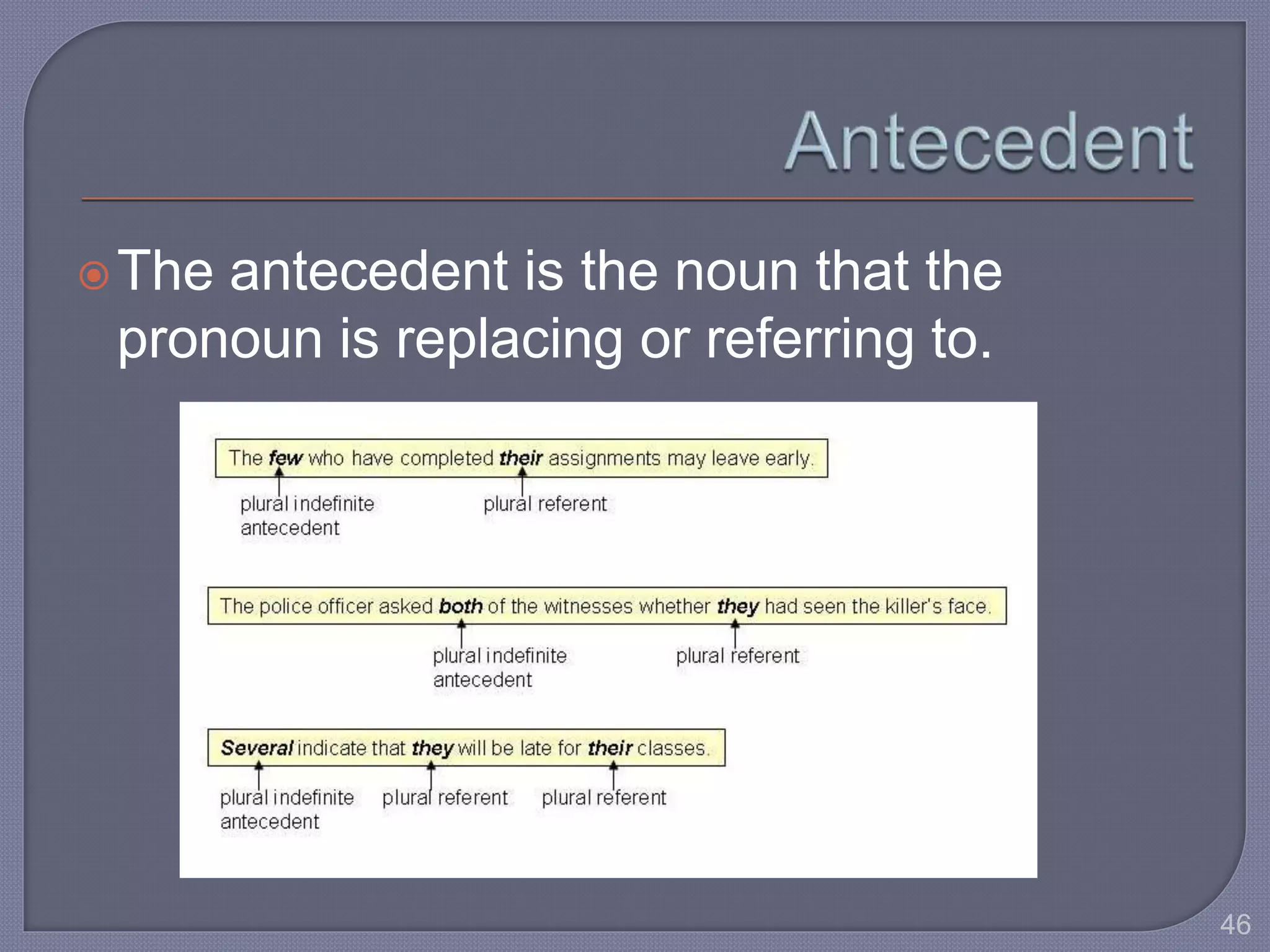
This document provides guidance for improving grammar skills in the workplace. It discusses commonly confused words and their definitions, as well as subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement. Examples are given of homophones, indefinite pronouns, and other grammar topics. Attendees are instructed to participate respectfully and focus on self-improvement. The goal is to help writers enhance credibility, avoid mistakes, and communicate clearly for different audiences and purposes.