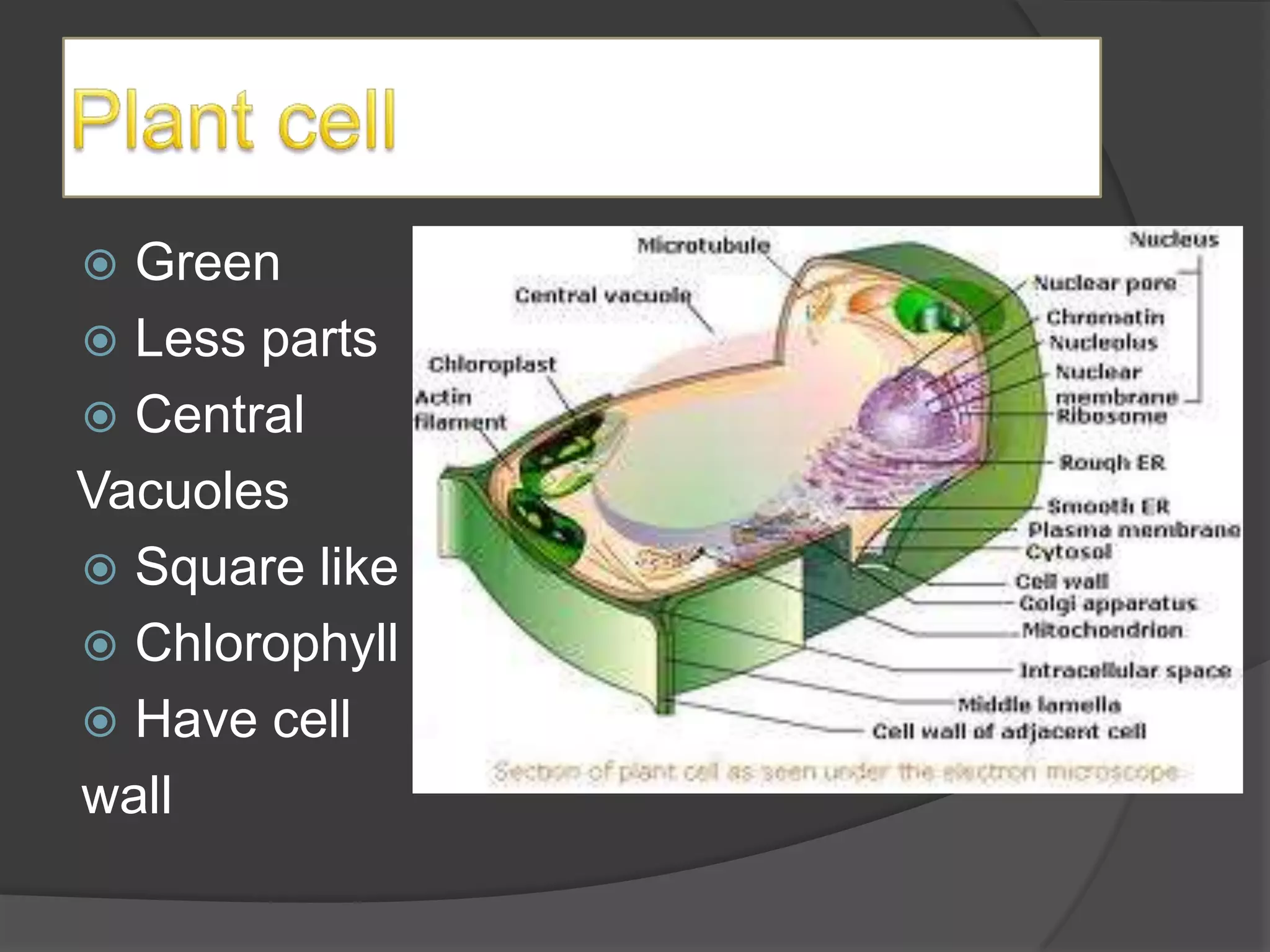
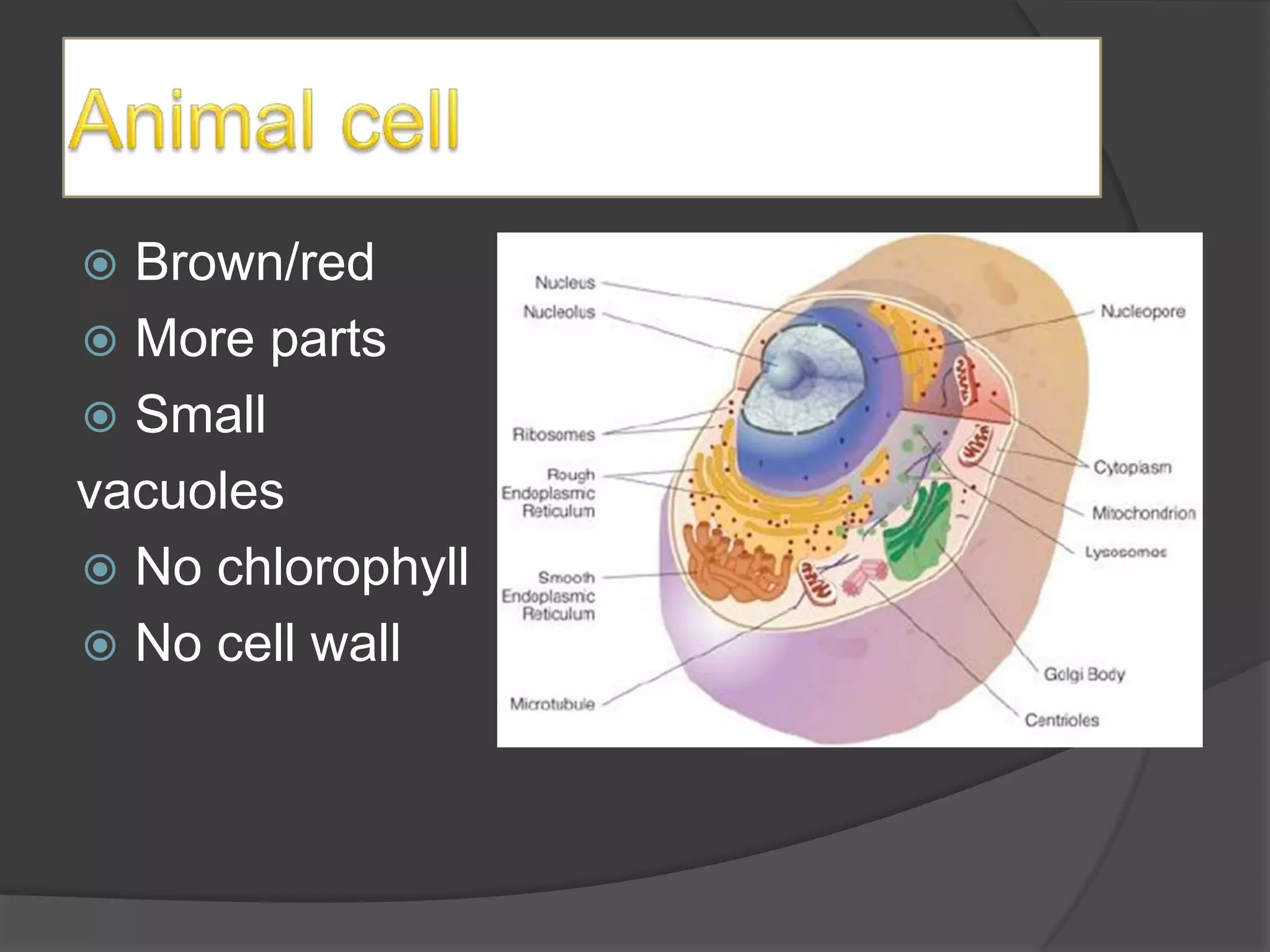
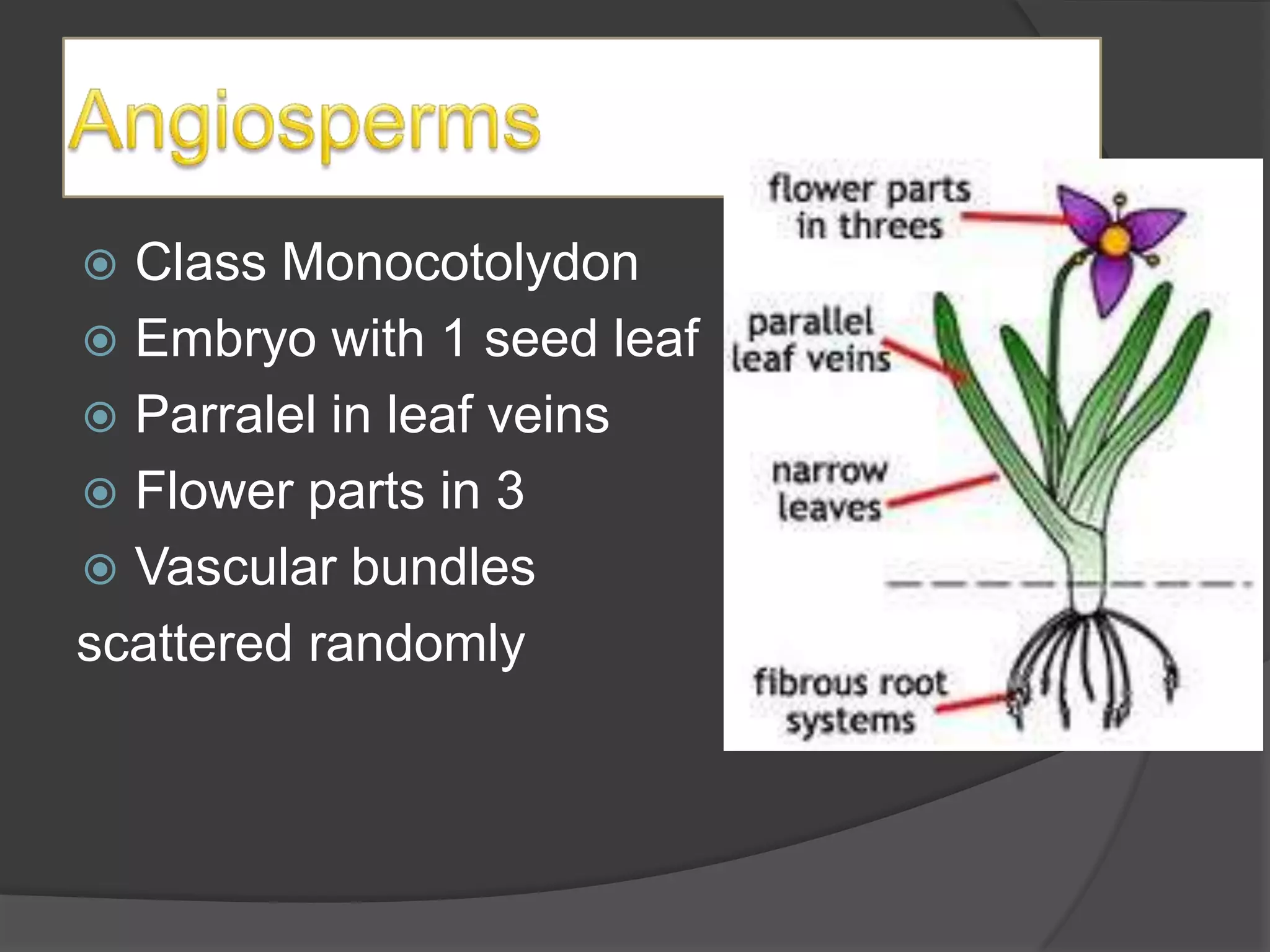
This document defines and provides examples of different types of organisms across kingdoms, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists. It also describes characteristics of species endangerment and describes plant structures and tropisms. Key points covered include the defining features of major kingdoms, examples of endangered and extinct species, and descriptions of plant tissues and responses to stimuli.