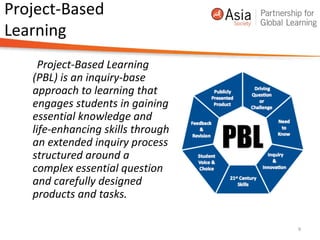
This document discusses instructional models that support graduation portfolio work, including project-based learning. It describes how instruction should backmap from graduate profiles and performance outcomes. Examples of supportive instruction include simulations, community engagement, projects, essential questions, and immersions. Project-based learning is highlighted as an inquiry-based approach involving essential questions, constructed artifacts, and collaboration over an extended time frame. The document provides examples of classroom practices and follow-up to communicate these instructional ideas.