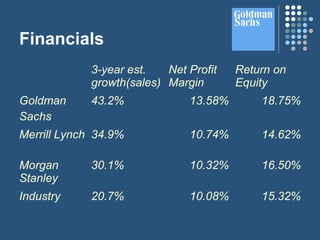
- Goldman Sachs is a global investment banking, securities and investment management firm founded in 1869. It offers a range of financial services including asset management, commercial banking, commodities, investment banking, investment management, mutual funds and prime brokerage.
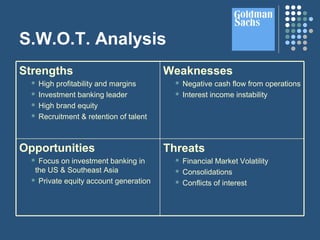
- A S.W.O.T. analysis identifies threats such as financial market volatility and consolidations, while opportunities include focusing on investment banking in Southeast Asia and private equity. Strengths are high profitability and brand equity, and weaknesses include negative cash flows and interest income instability.
- Goldman Sachs aims to be a global leader in investment banking, securities and investment management. It employs a decentralized, management-by-objective style without a clear mission statement.