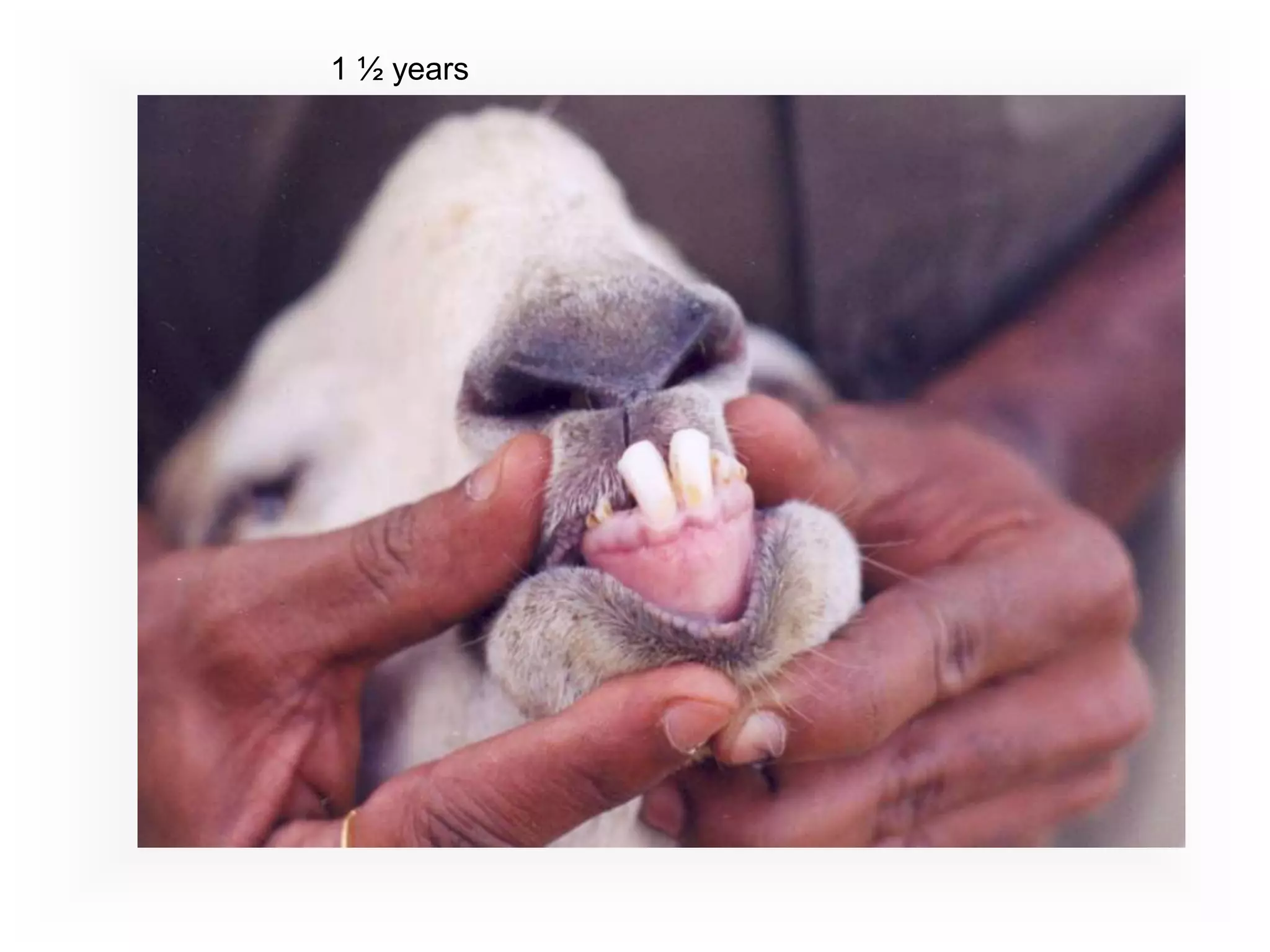
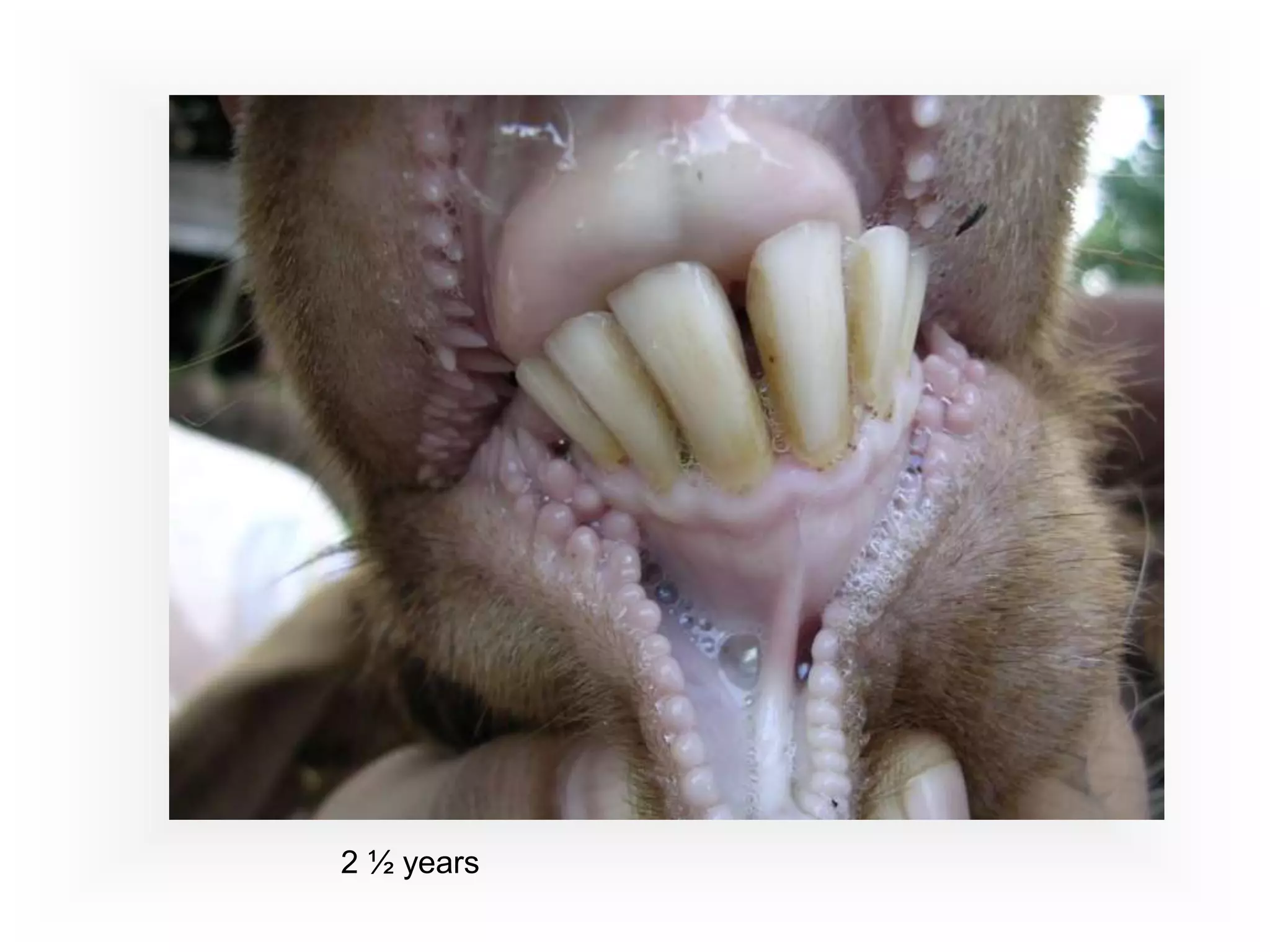
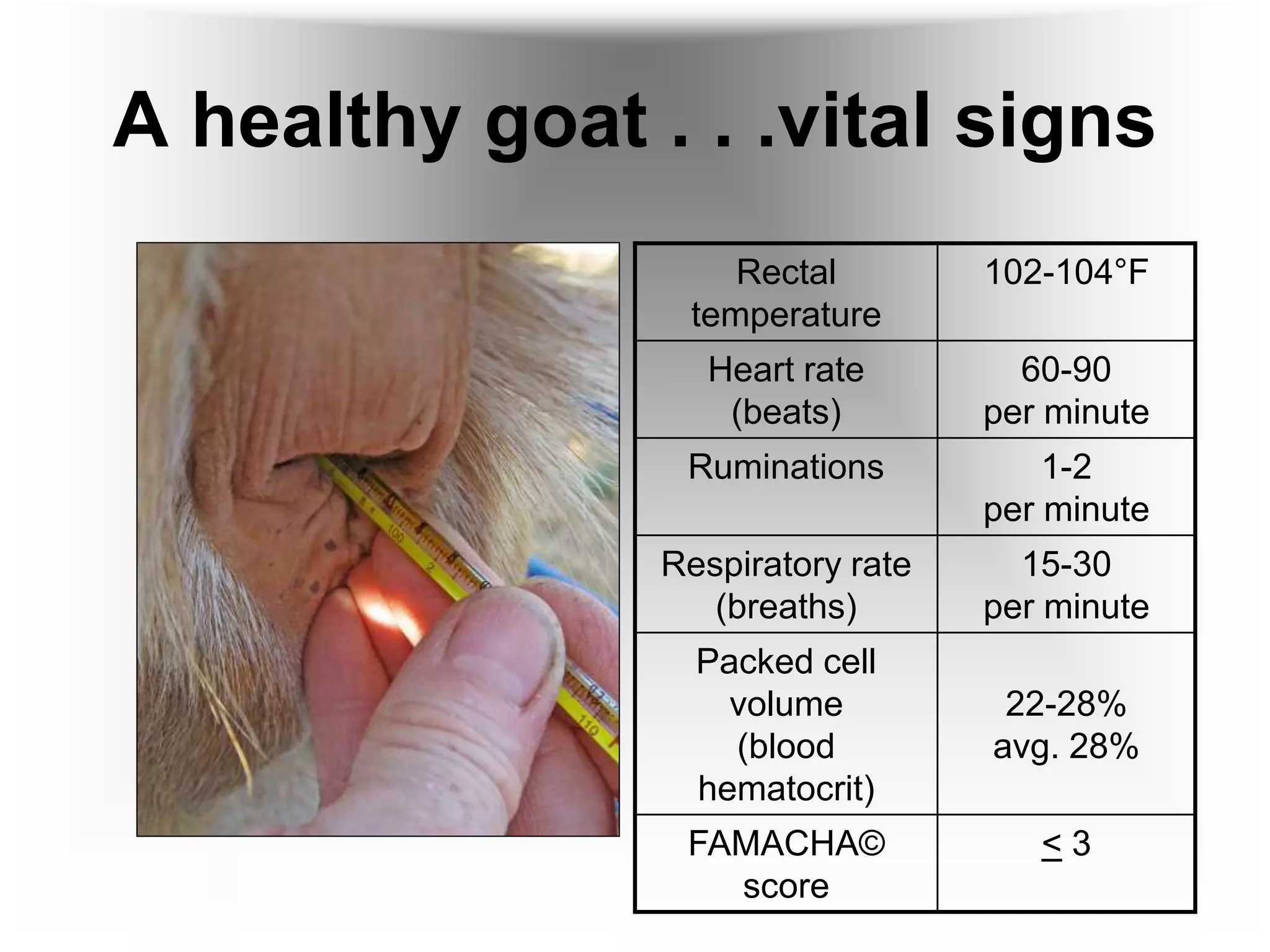
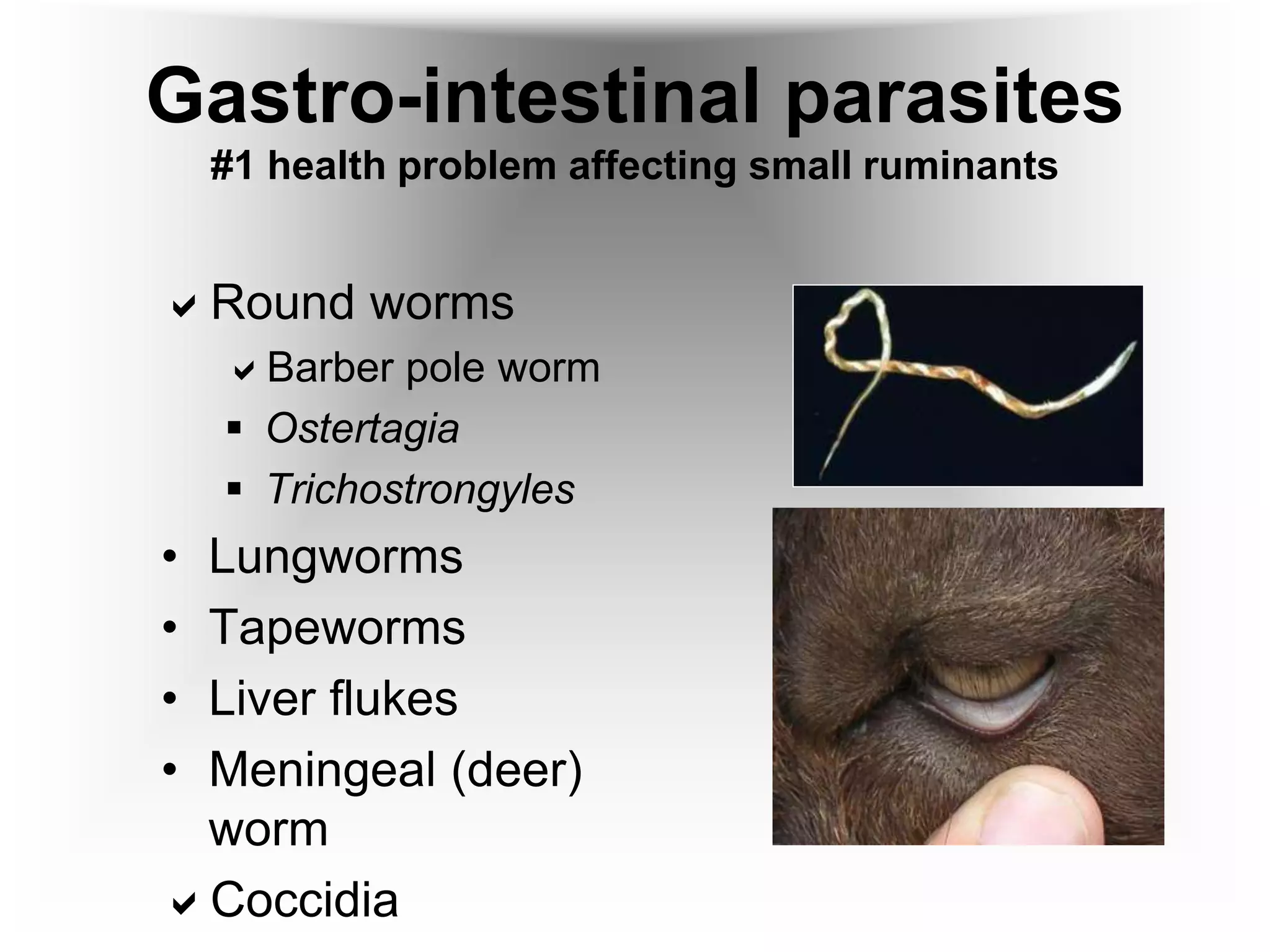
This document provides information on goat health and management. It discusses typical lifespans for goats of 1-2.5 years depending on their intended use. It covers breeding and reproduction details like estrus cycles, gestation period, litter sizes. Kidding details are provided like most does needing little assistance. Normal vital signs for goats are listed. Common health problems discussed include internal and external parasites, digestive/nutritional issues, respiratory diseases, reproductive problems, hoof issues, skin conditions, and chronic conditions. The FAMACHA system for assessing anemia and barber pole worm infection is described.