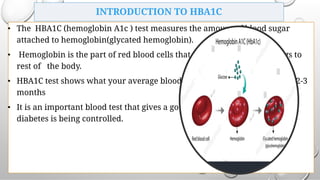
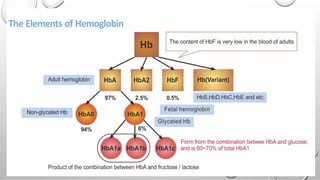
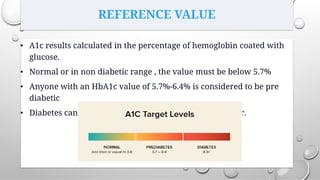
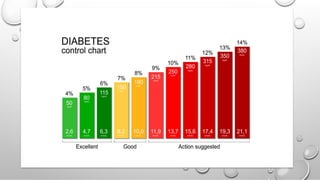
This document provides an overview of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) testing used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. HbA1c measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin over the past 2-3 months and provides an indication of average blood sugar control. Elevated HbA1c levels can diagnose diabetes, while levels between 5.7-6.4% indicate prediabetes. Several factors like recent blood transfusions or illnesses can impact HbA1c levels. Proper specimen collection and storage is important for accurate HbA1c testing results.











![REFERENCE
1. American diabetes association [internet]. Arlington (VA): American diabetes
association; c1995–2022. Understanding A1C: A1C does it all; [ cited 2022 may
17];
2. American diabetes association [internet]. Arlington (VA): American diabetes
association; c1995–2022. Common terms; [cited 2022 may 17]; [about 57 screens]
3. Centers for disease control and prevention [internet]. Atlanta: U.S. Department
of health and human services; all about your A1C; [reviewed 2021 Aug 10; cited
2022 may 17];
4. Centers for disease control and prevention [internet]. Atlanta: U.S. Department
of health and human services; diabetes risk factors; [reviewed 2022 Apr 5;cited
2022 may 17];
5. Mayo clinic [internet]. Mayo foundation for medical education and research;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalsandrappt-231222091342-381d03db/85/Glycalated-haemoglobin-and-analysisppt-pdf-18-320.jpg)

