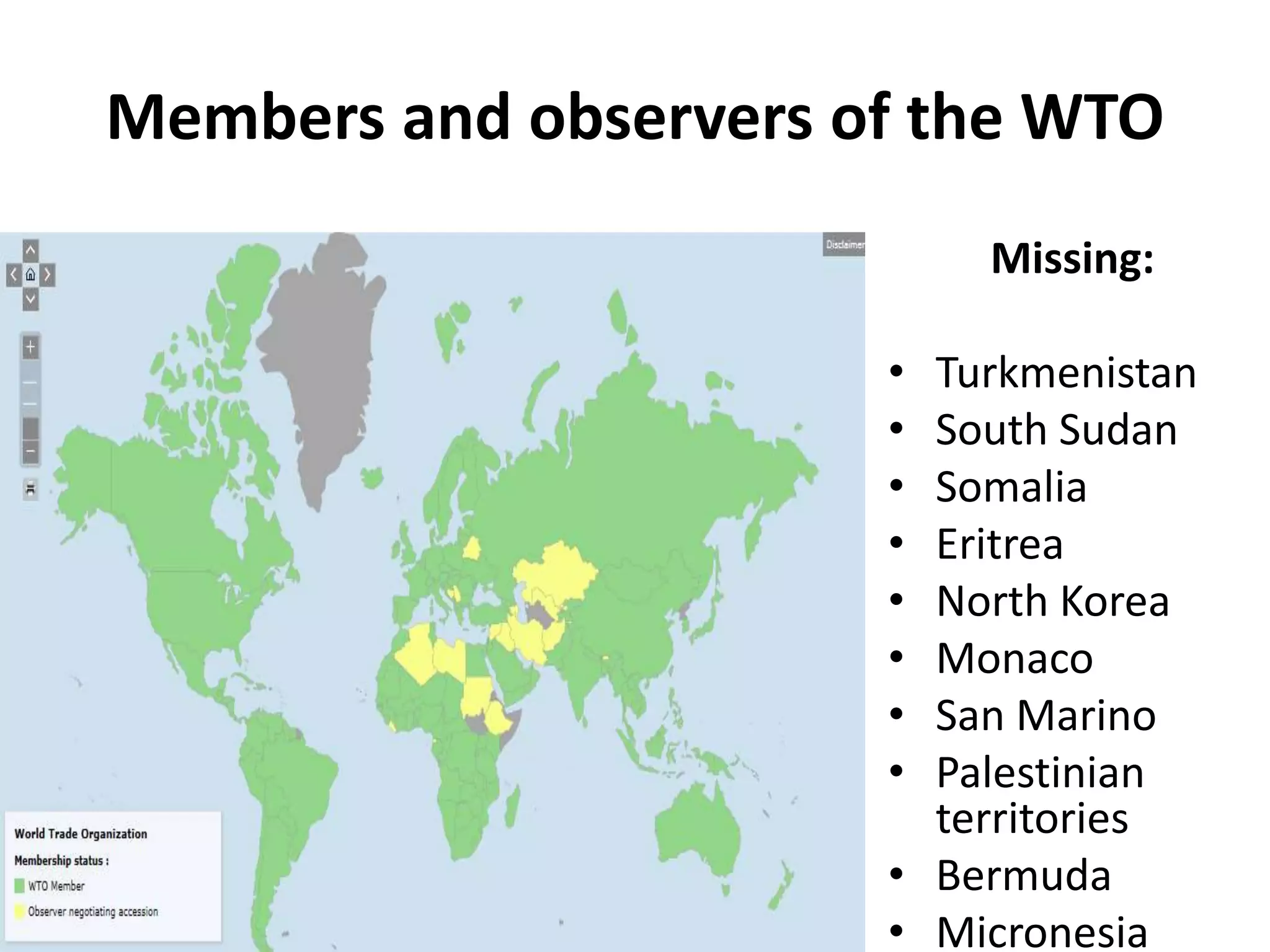
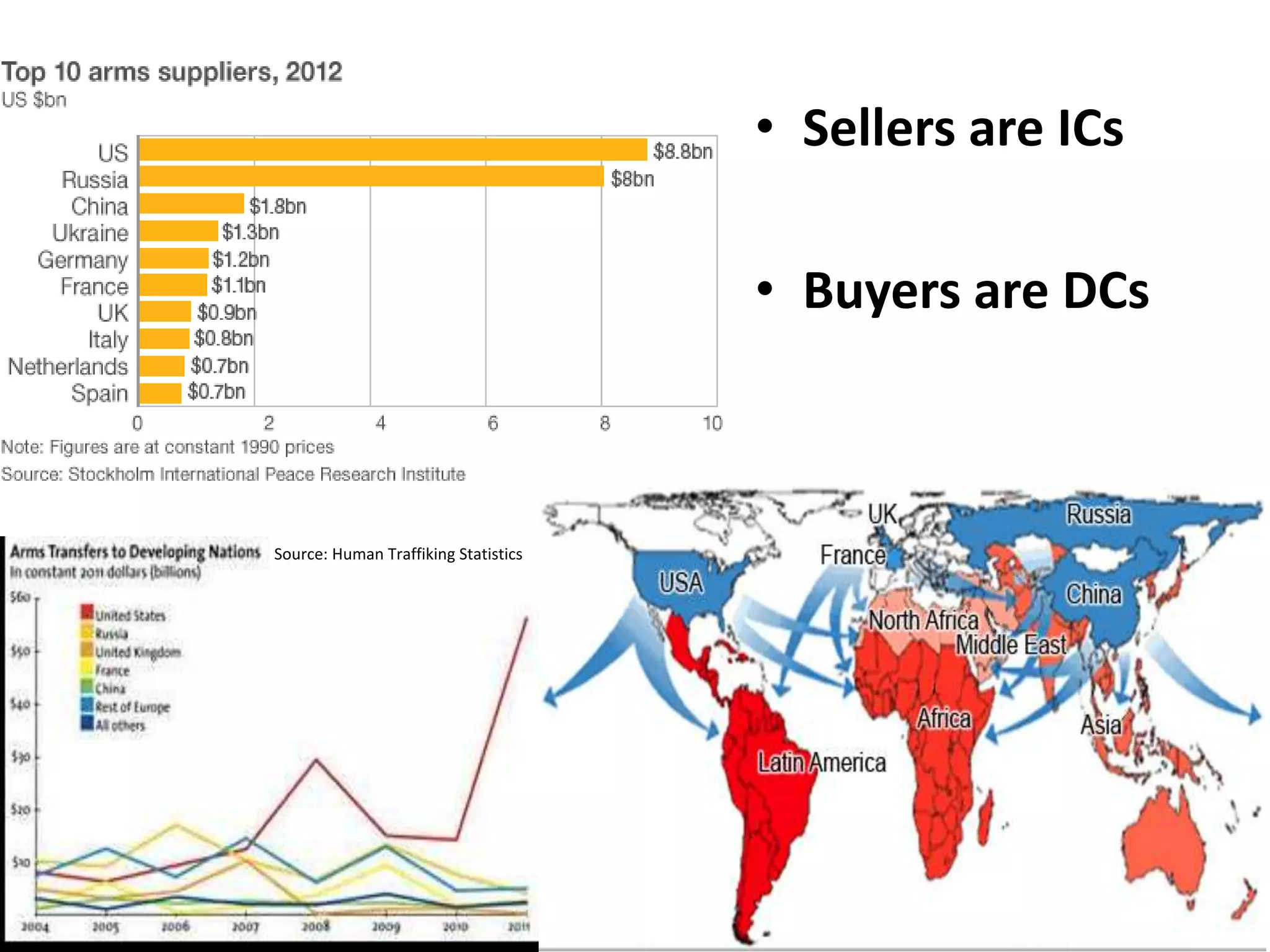
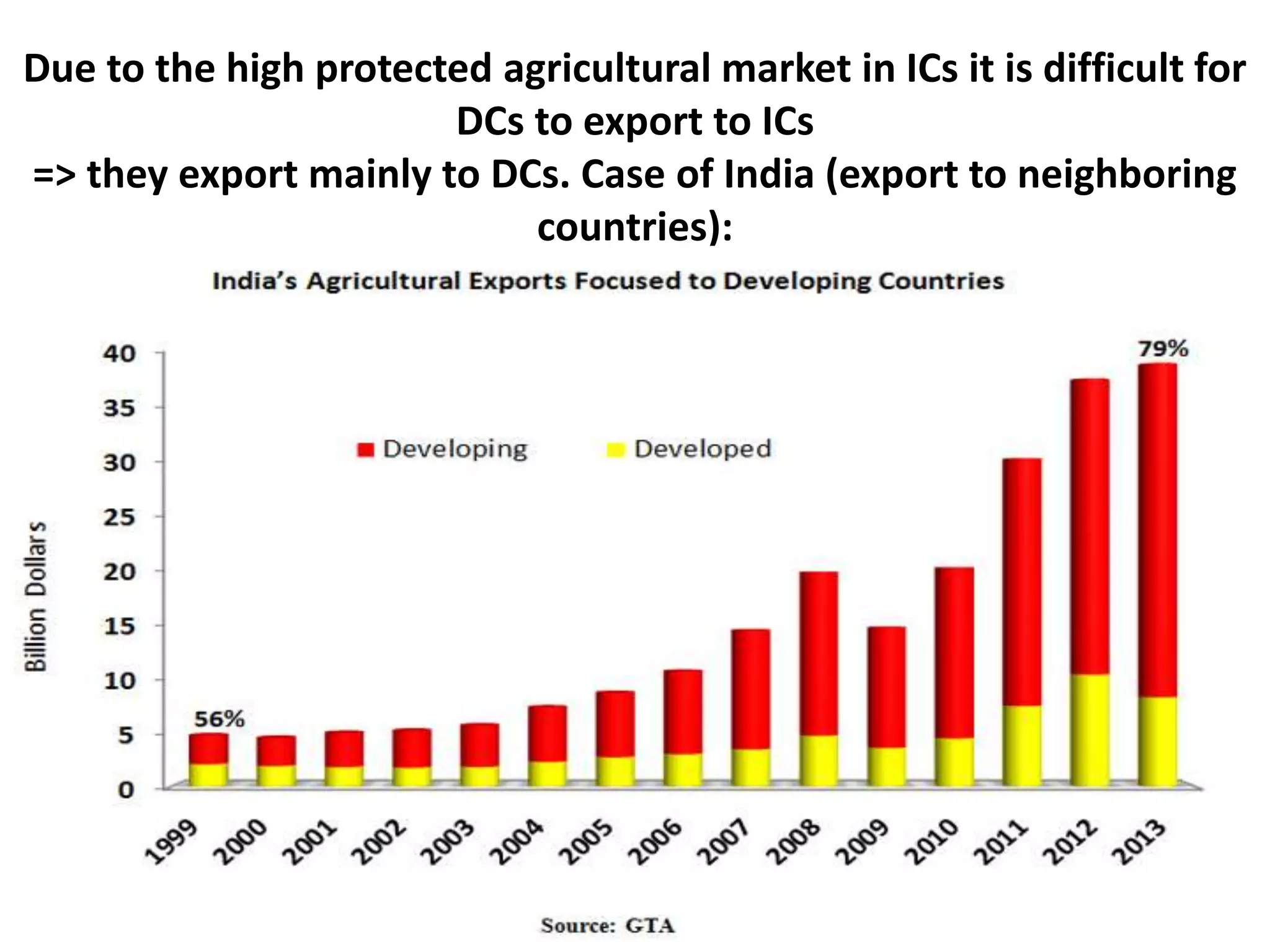
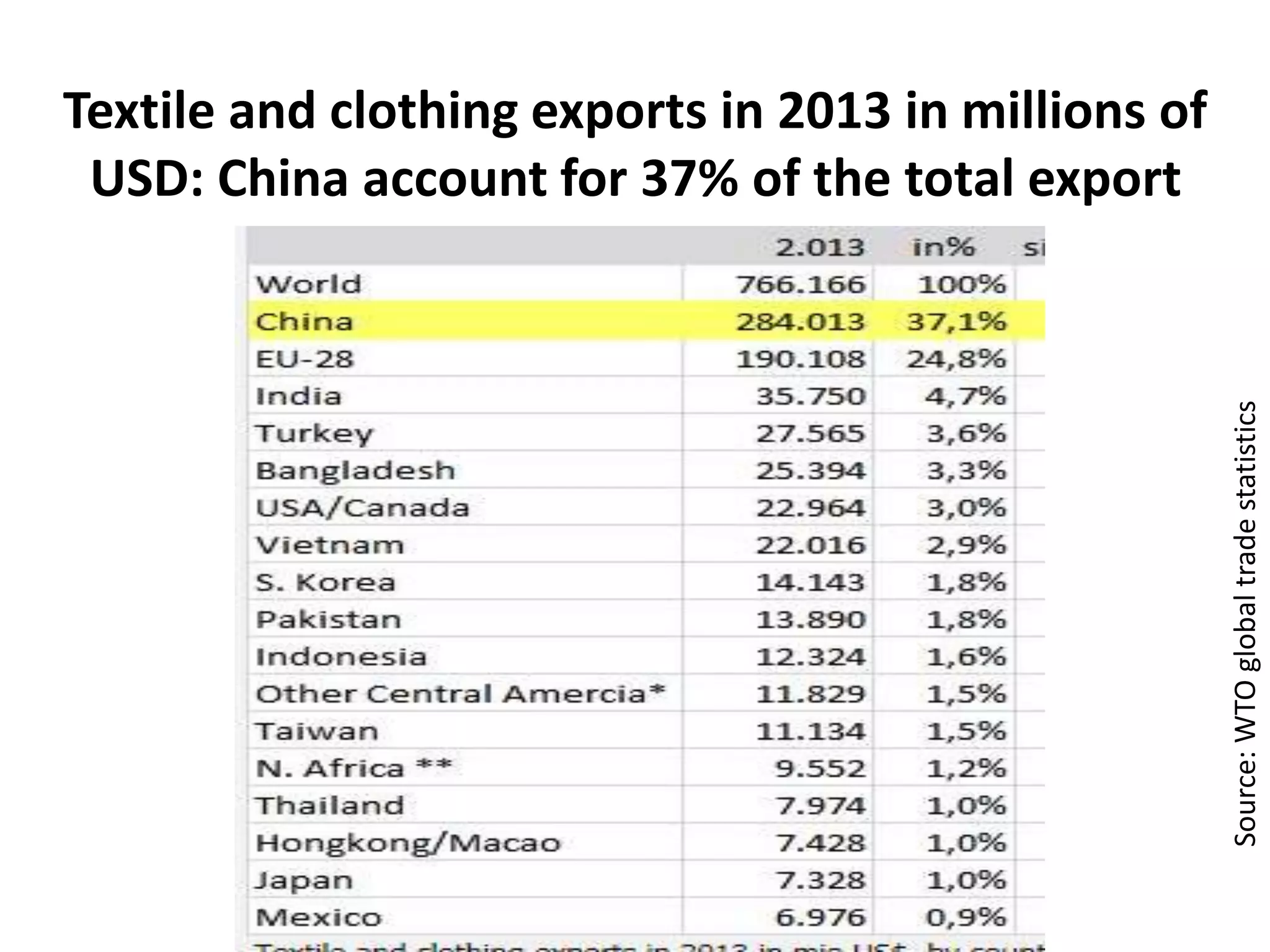
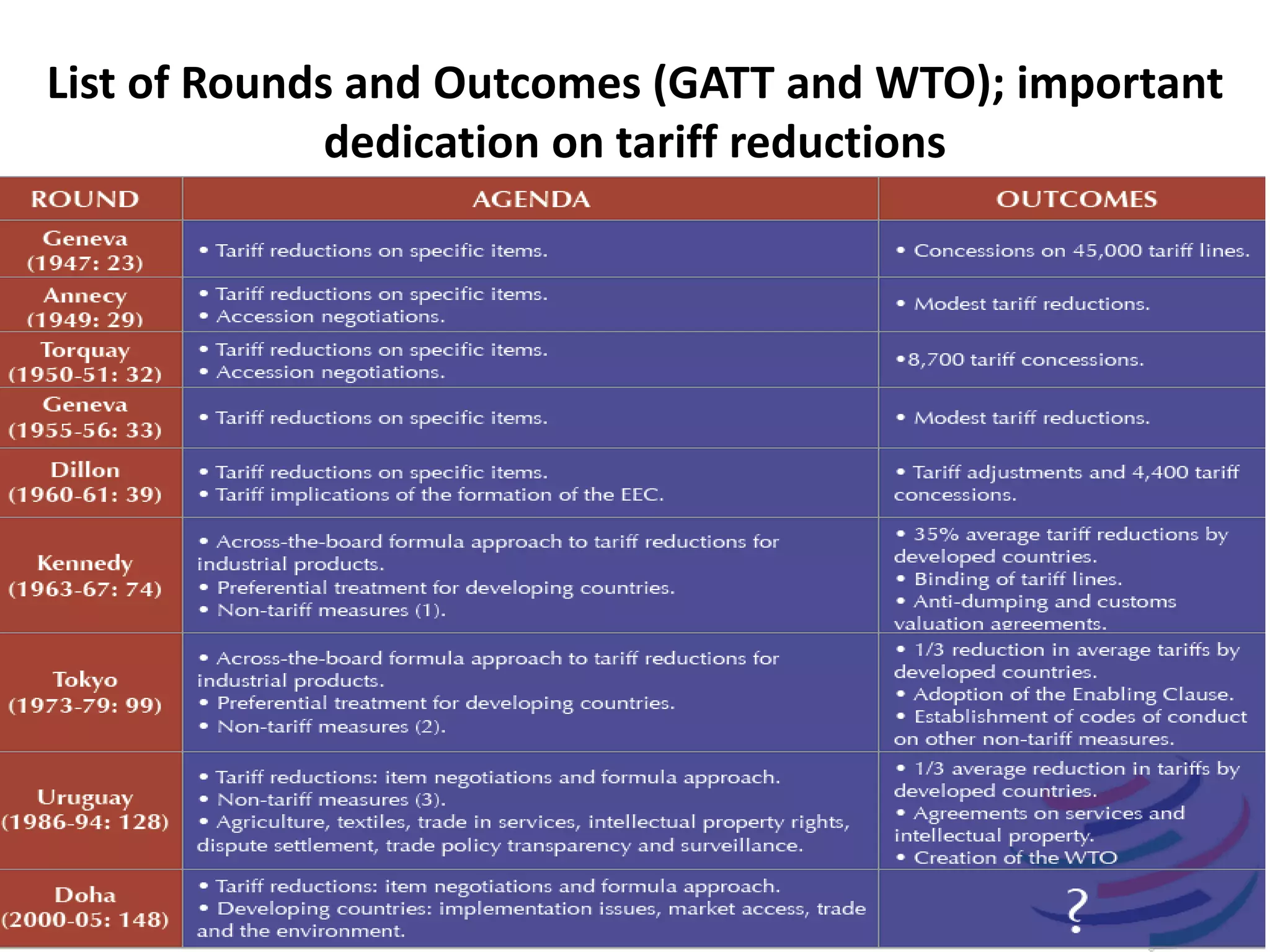
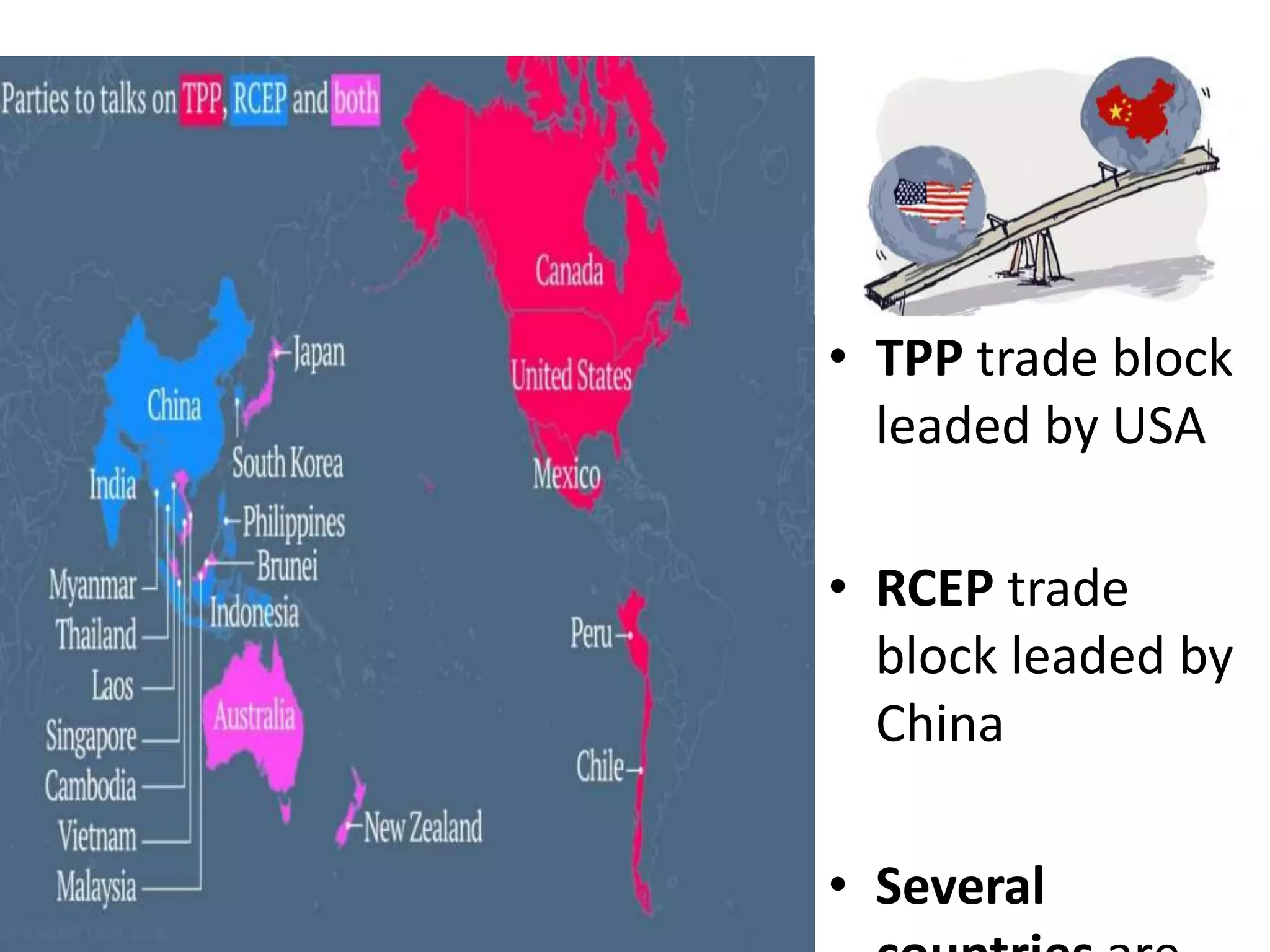
The document discusses concepts related to the current global economic order and institutions like the World Bank and IMF. It provides an overview of how these institutions work, their goals and activities, as well as concepts like poverty, inequality, and voting power within the IMF. Some key points include:
- The current economic order is centered around rules established by Bretton Woods institutions and aims to maintain Western power through the dominance of the US dollar.
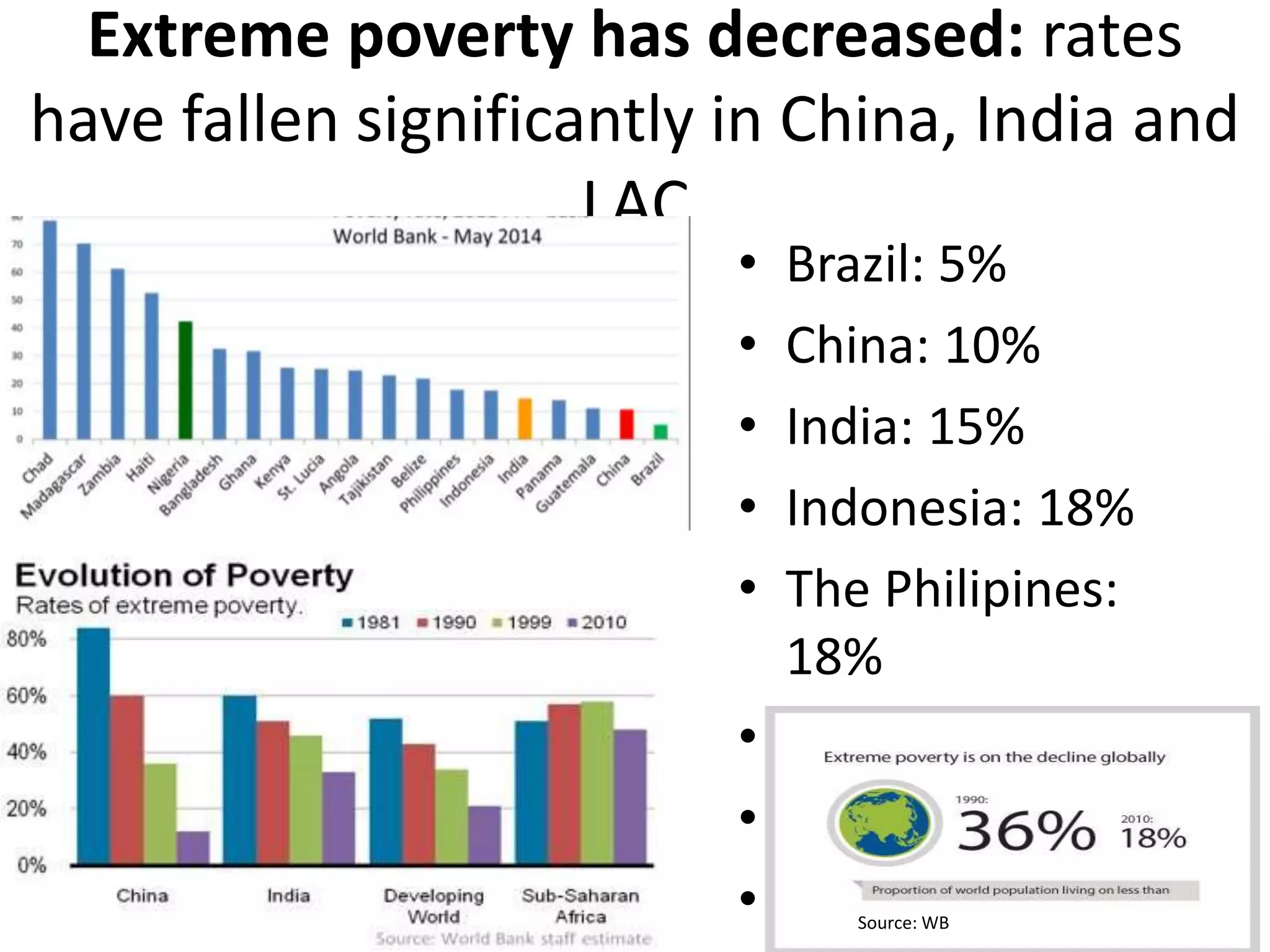
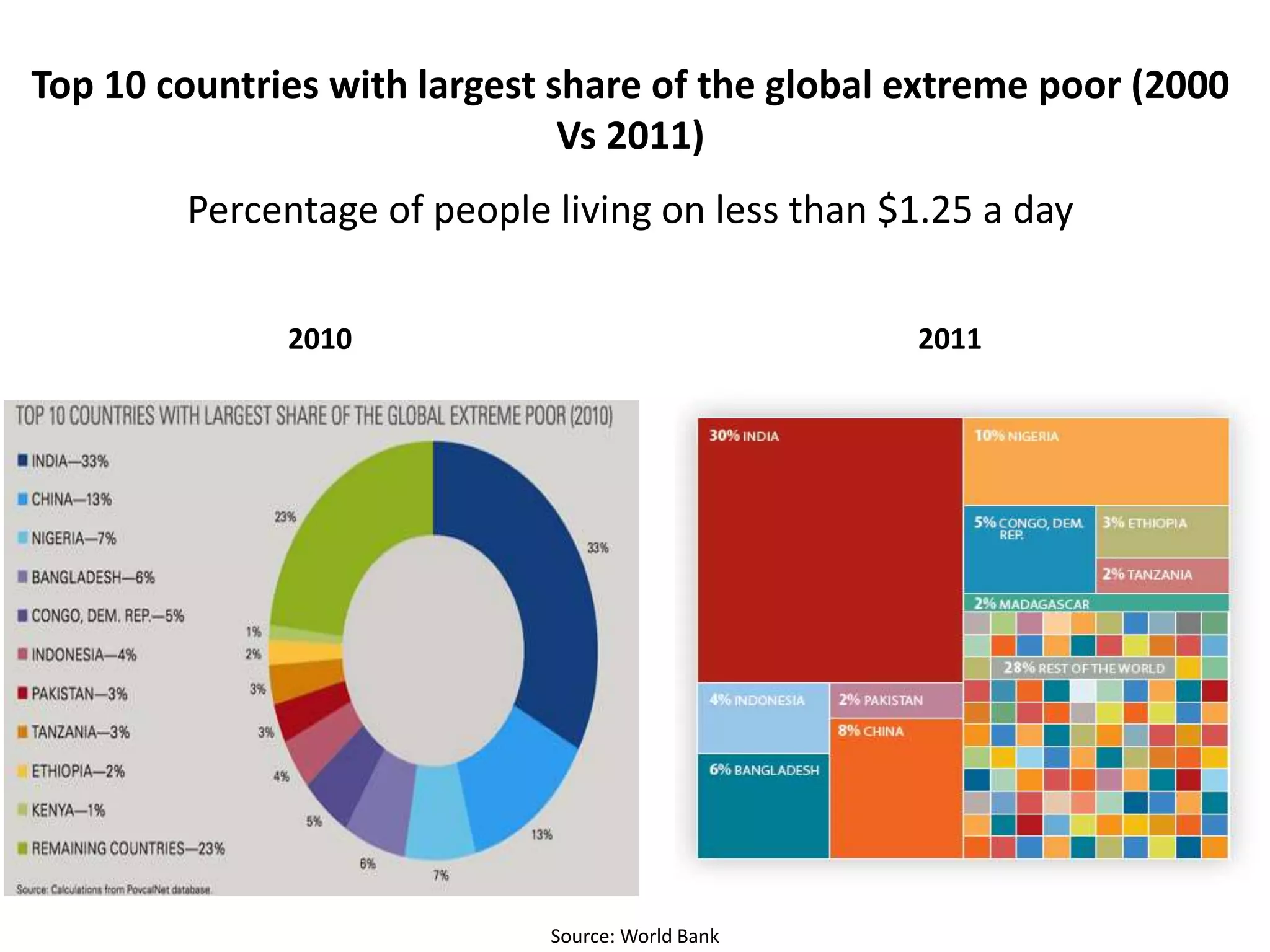
- The World Bank aims to promote development through projects, loans, and partnerships. It works to reduce poverty defined as living on less than $1.25 or $2 per day.
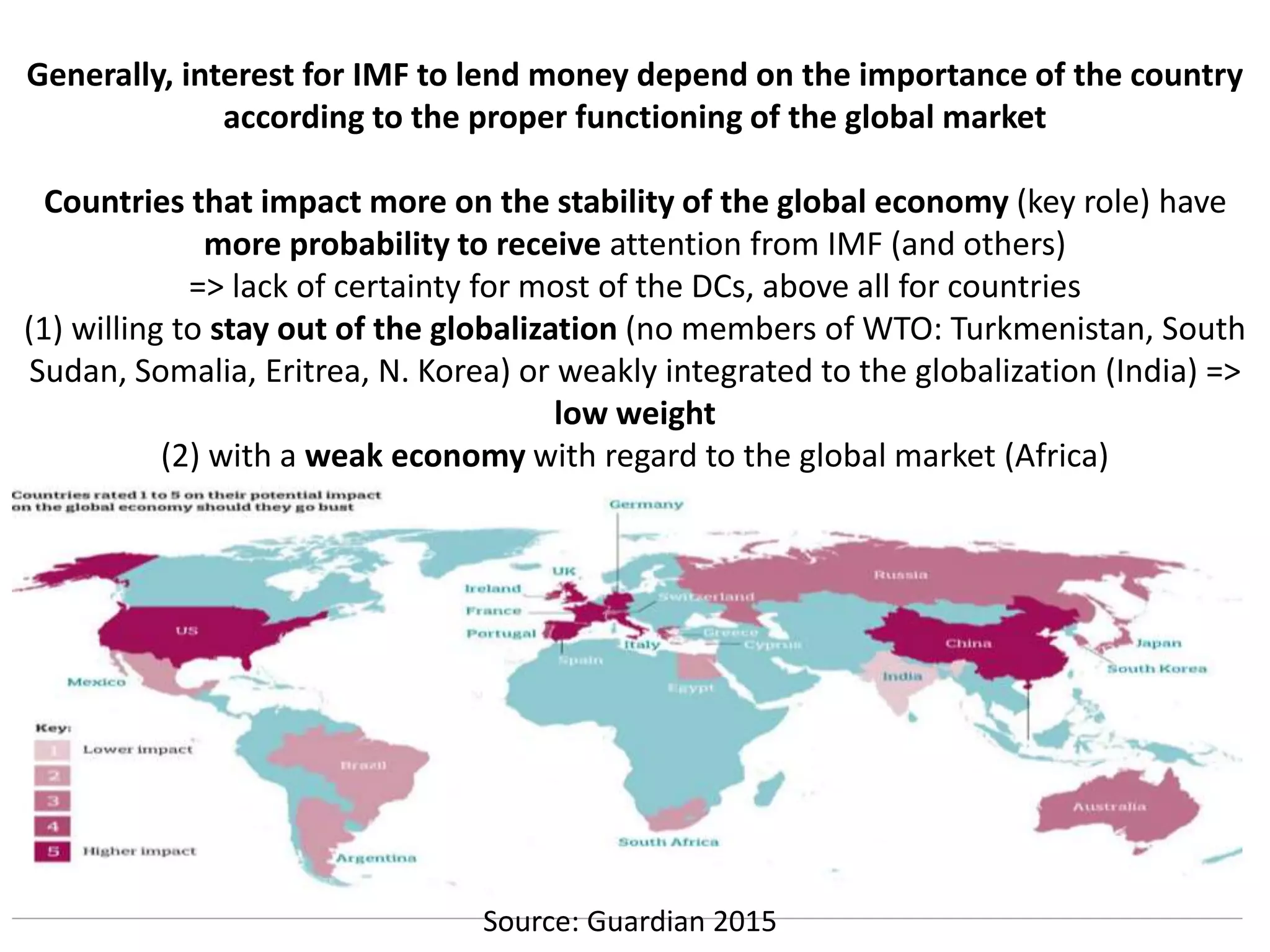
- The IMF aims to foster macroeconomic stability and provides loans to countries experiencing economic cri




















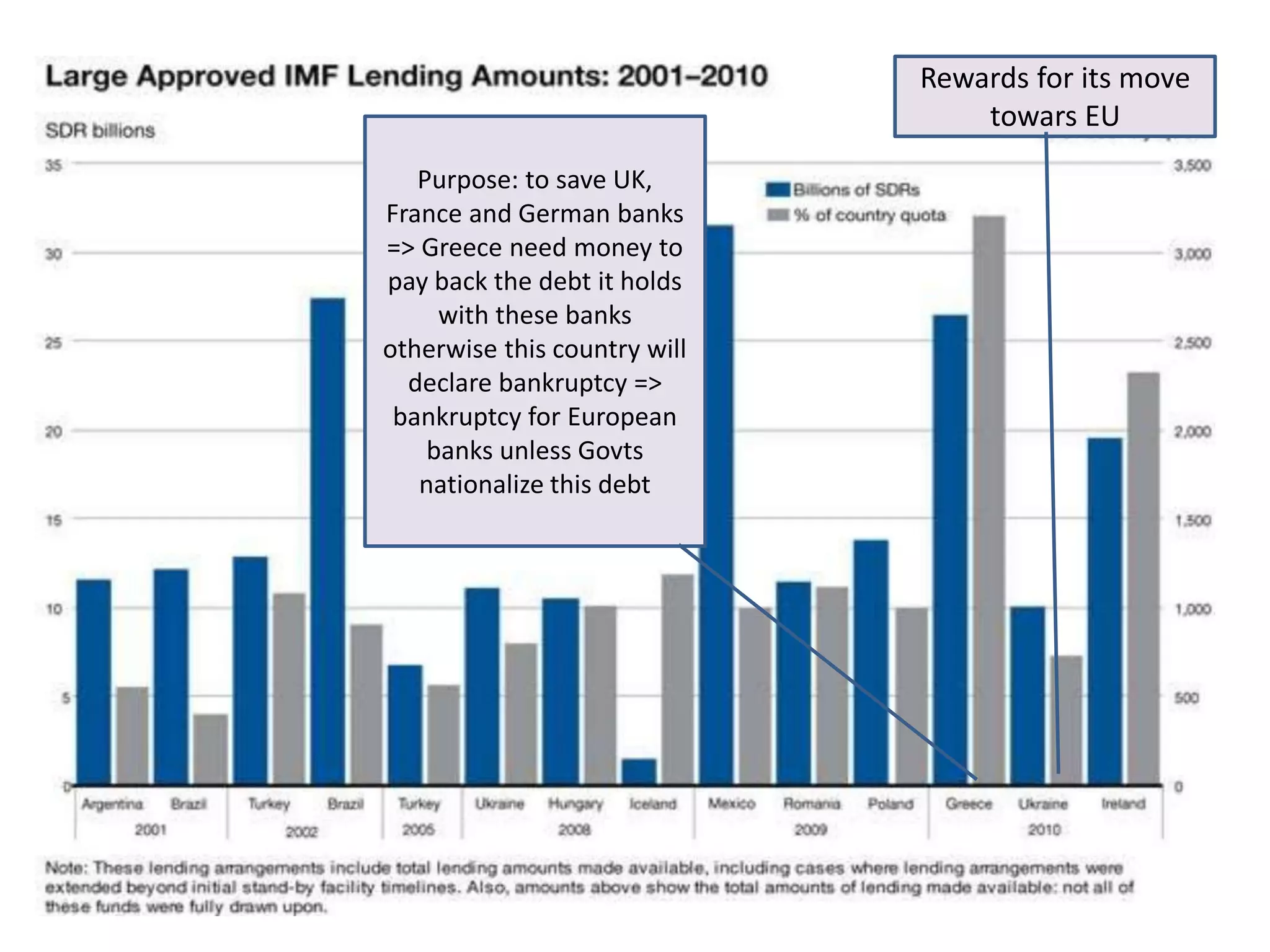
![IMF loans • At first: lending to ICs (UK and
France during 50s and 60s to
foster reconstruction)
• During 1980s and 1990s: strong
intervention in DCs (LAC, Asia,
Commonwealth of Independent
States[CIS]) to facilitate
integration and to face crisis
(1982, 1995, 1997, 1998, 1999,
2001)
• 2000s: Eastern Europe to ease its
integration process with EU
• 2010s: Southern Europe and
Ireland](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/globaleconomicorderanddevelopingcountries-150807191412-lva1-app6891/75/Global-economic-order-and-developing-countries-23-2048.jpg)