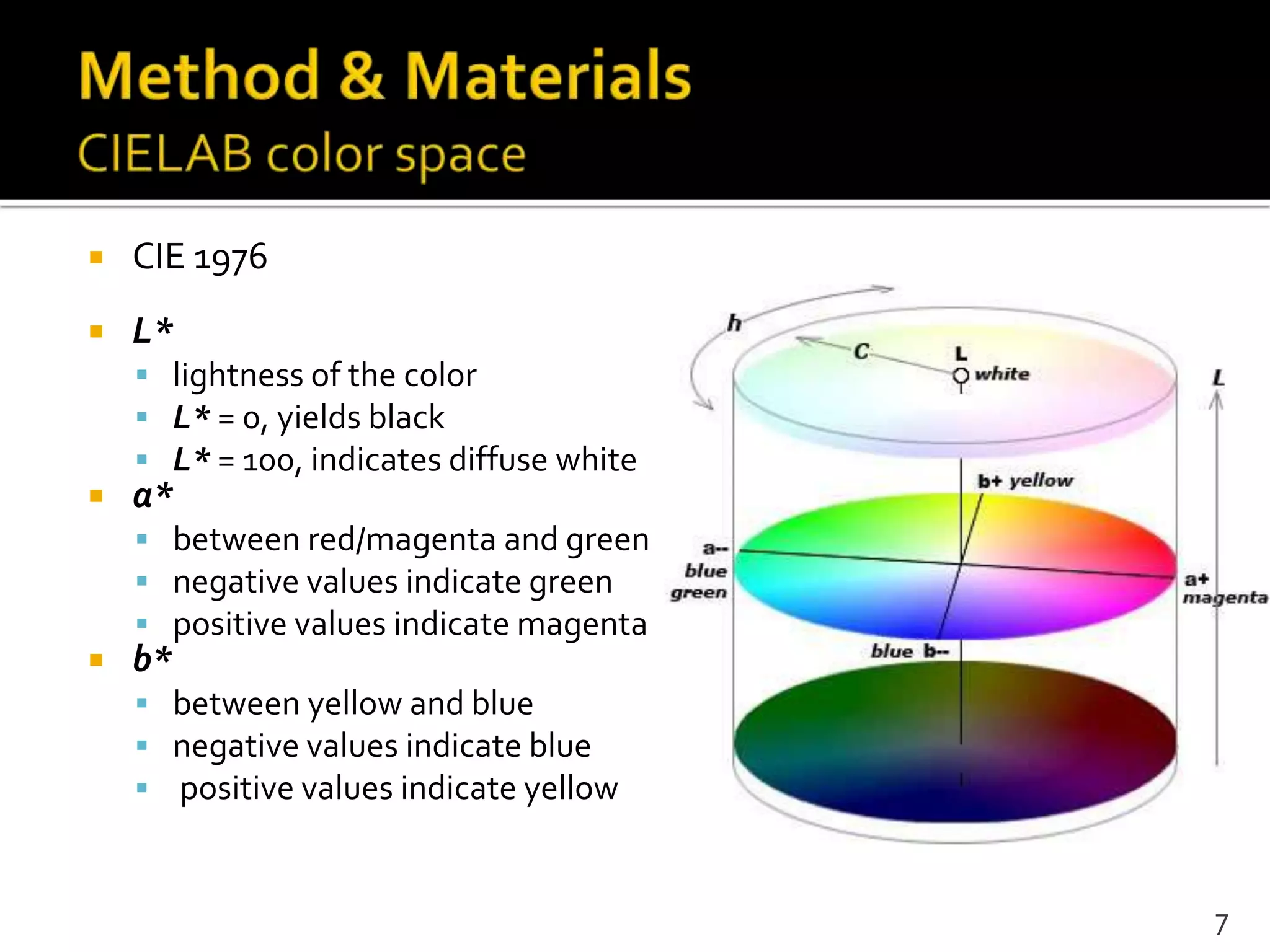
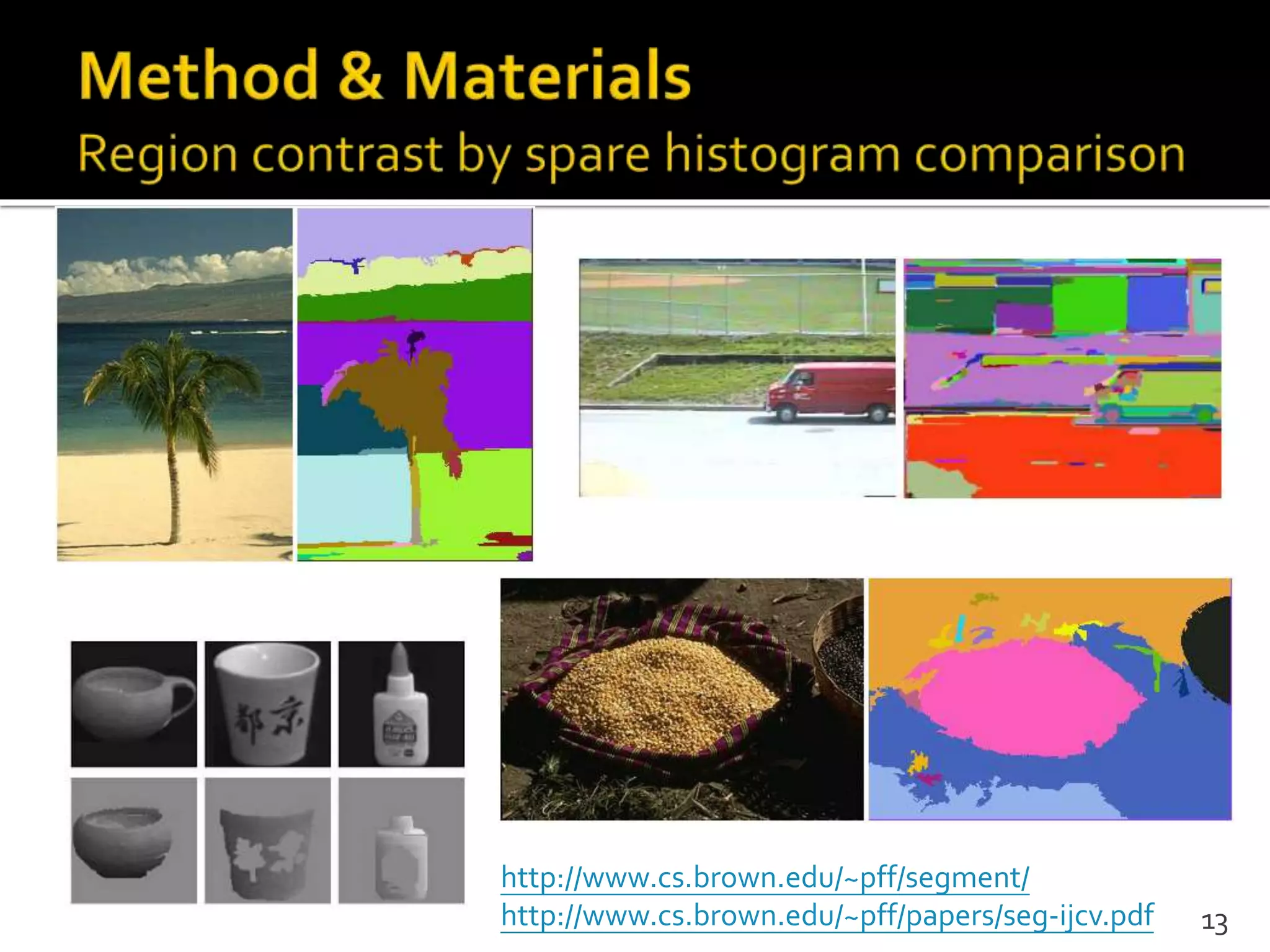
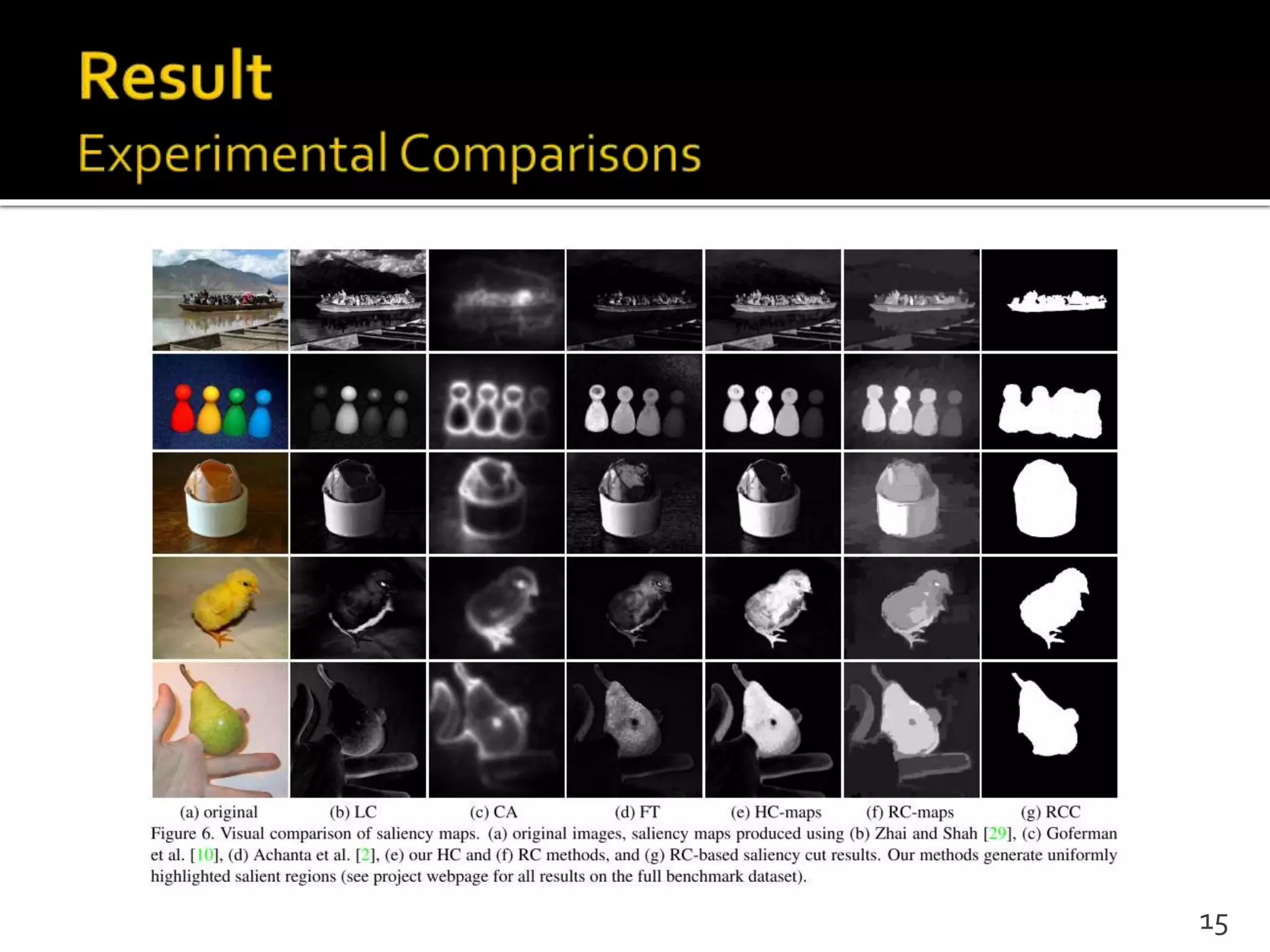
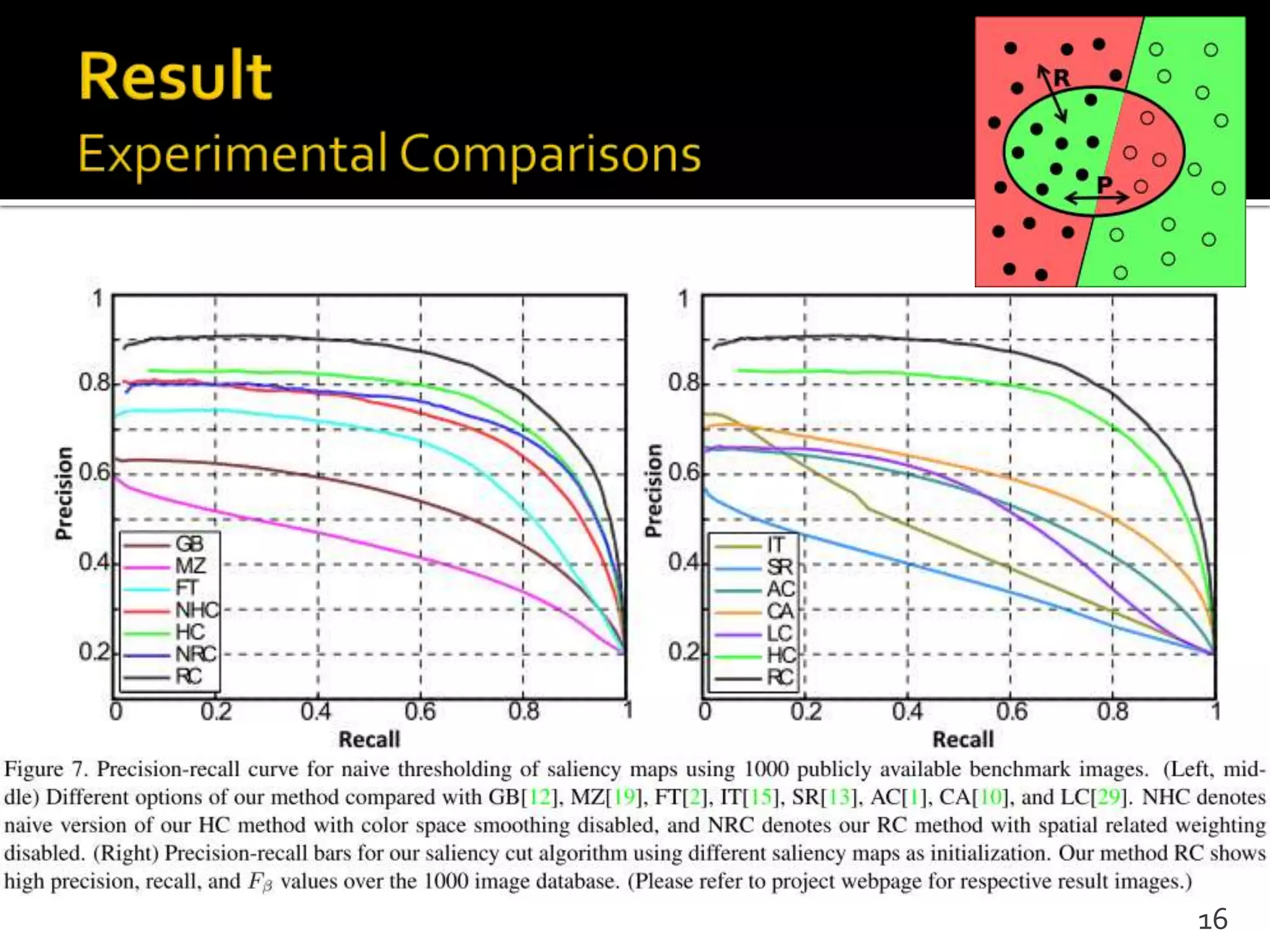
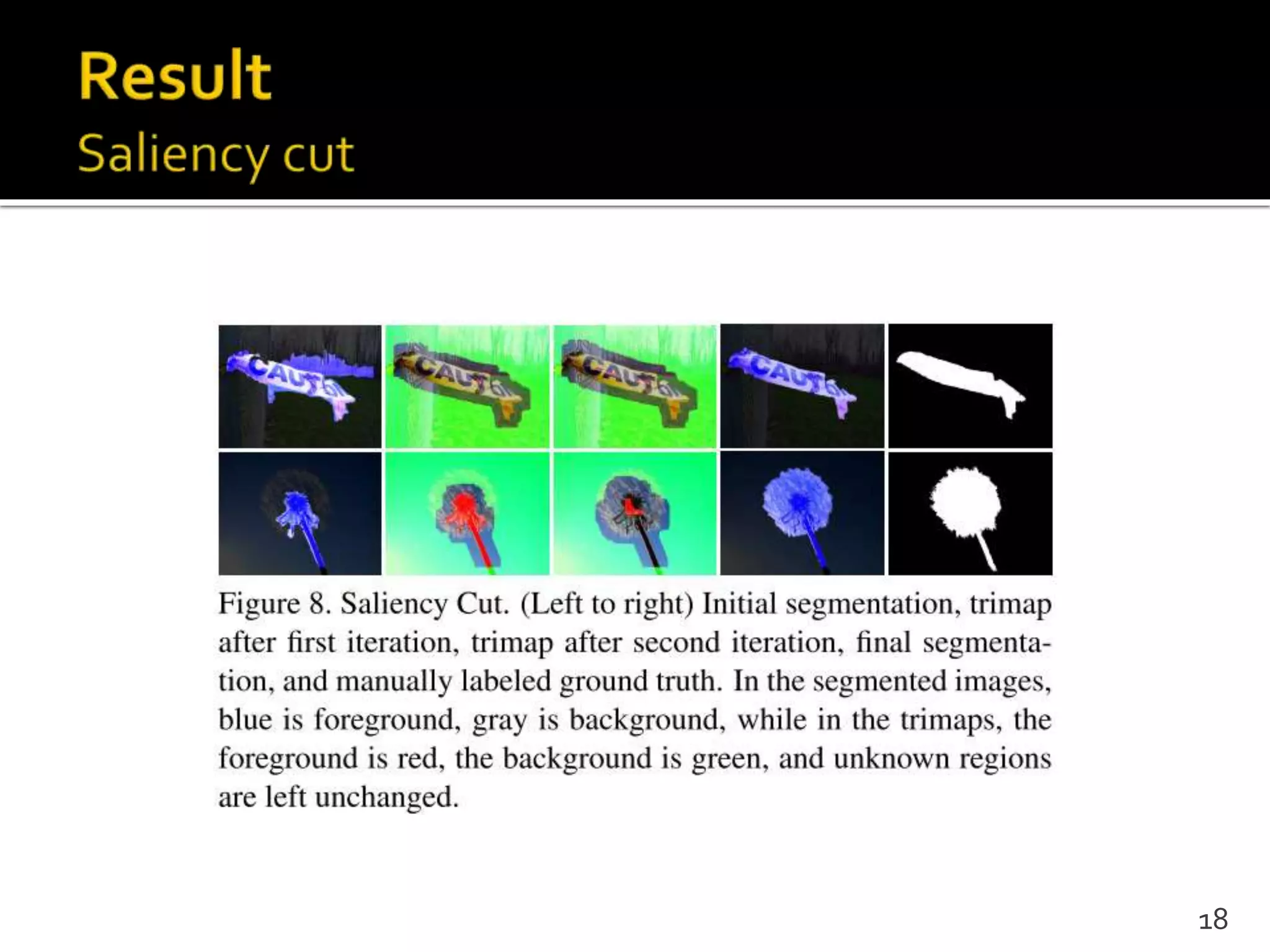
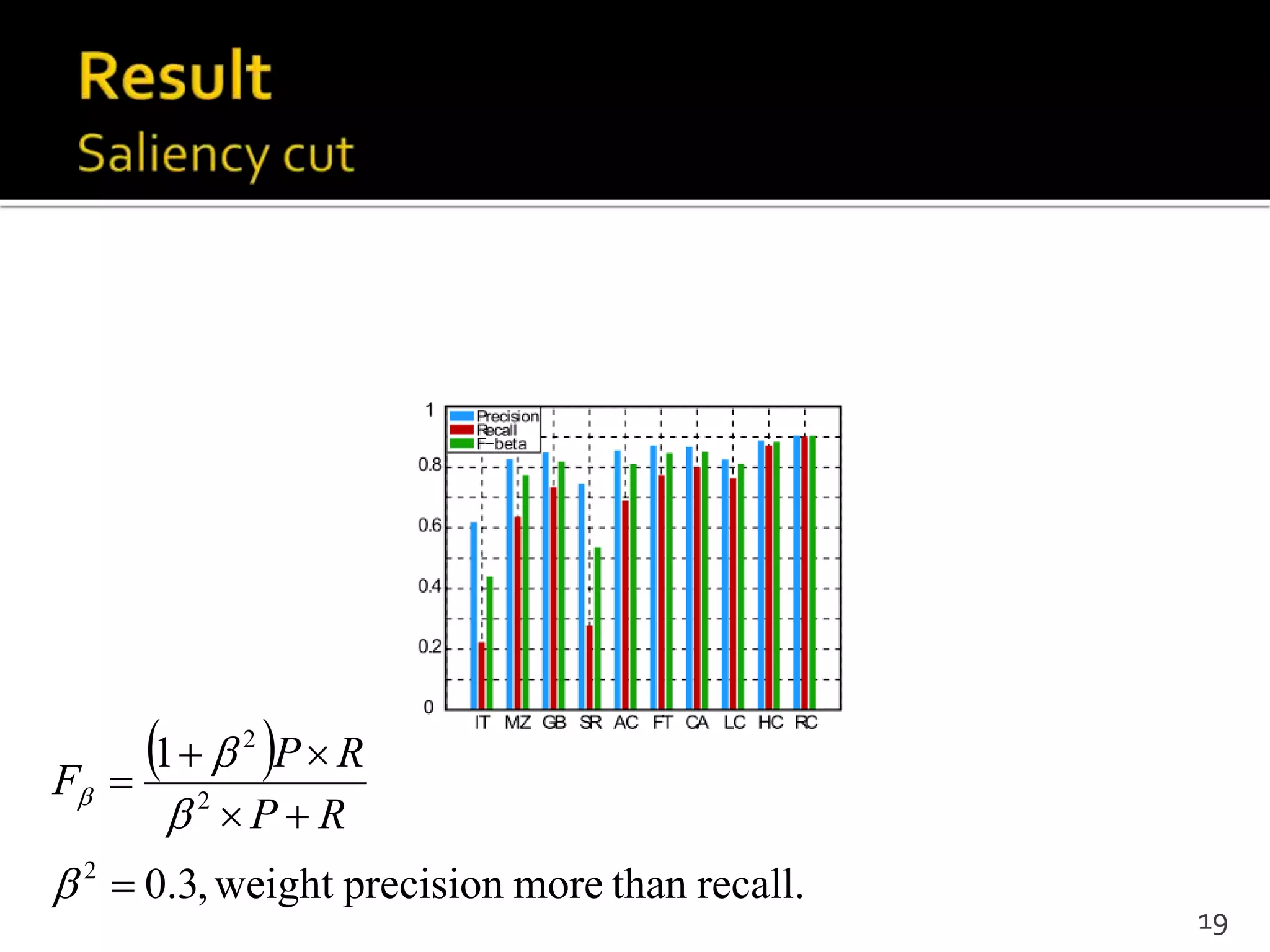
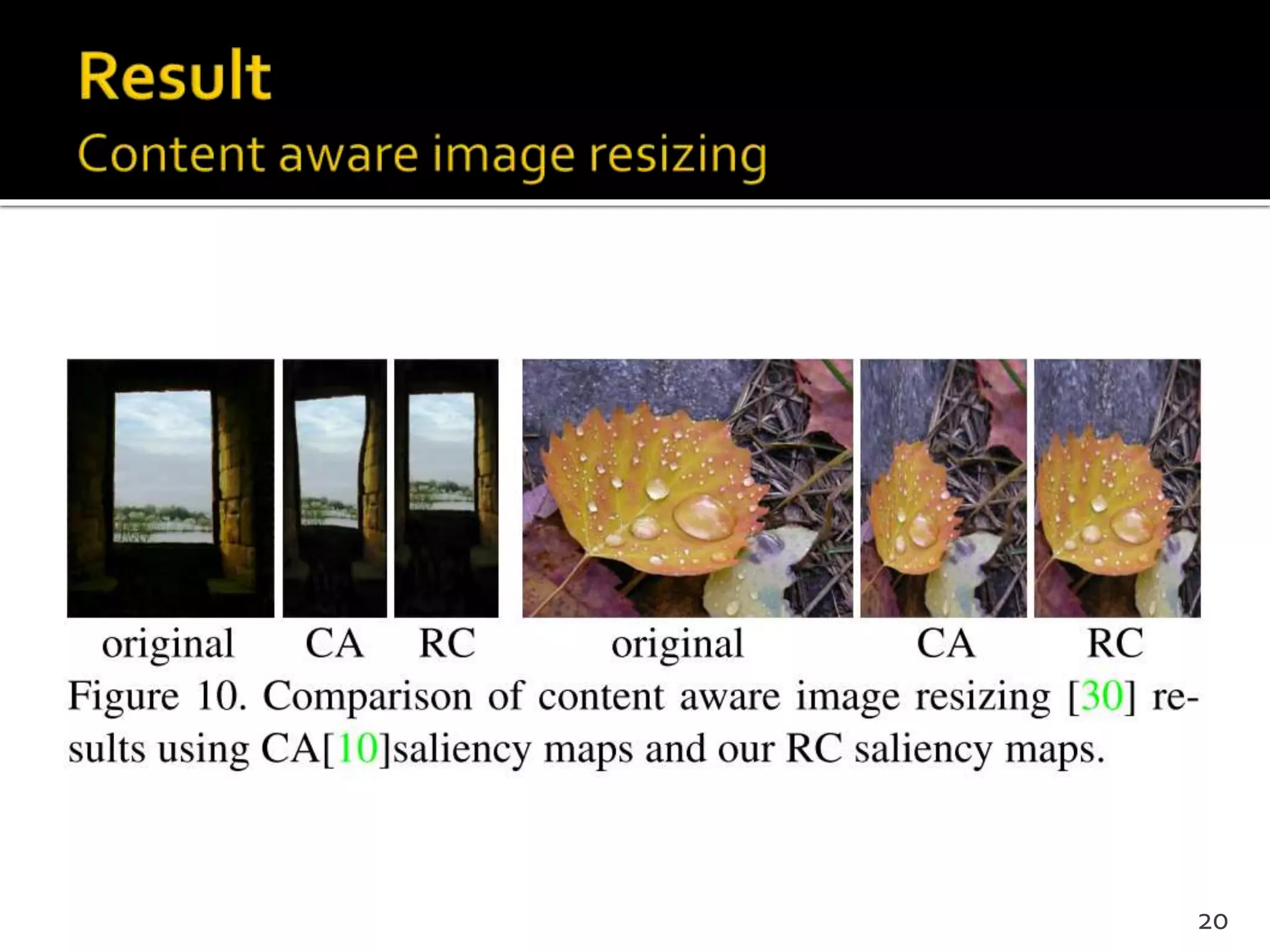
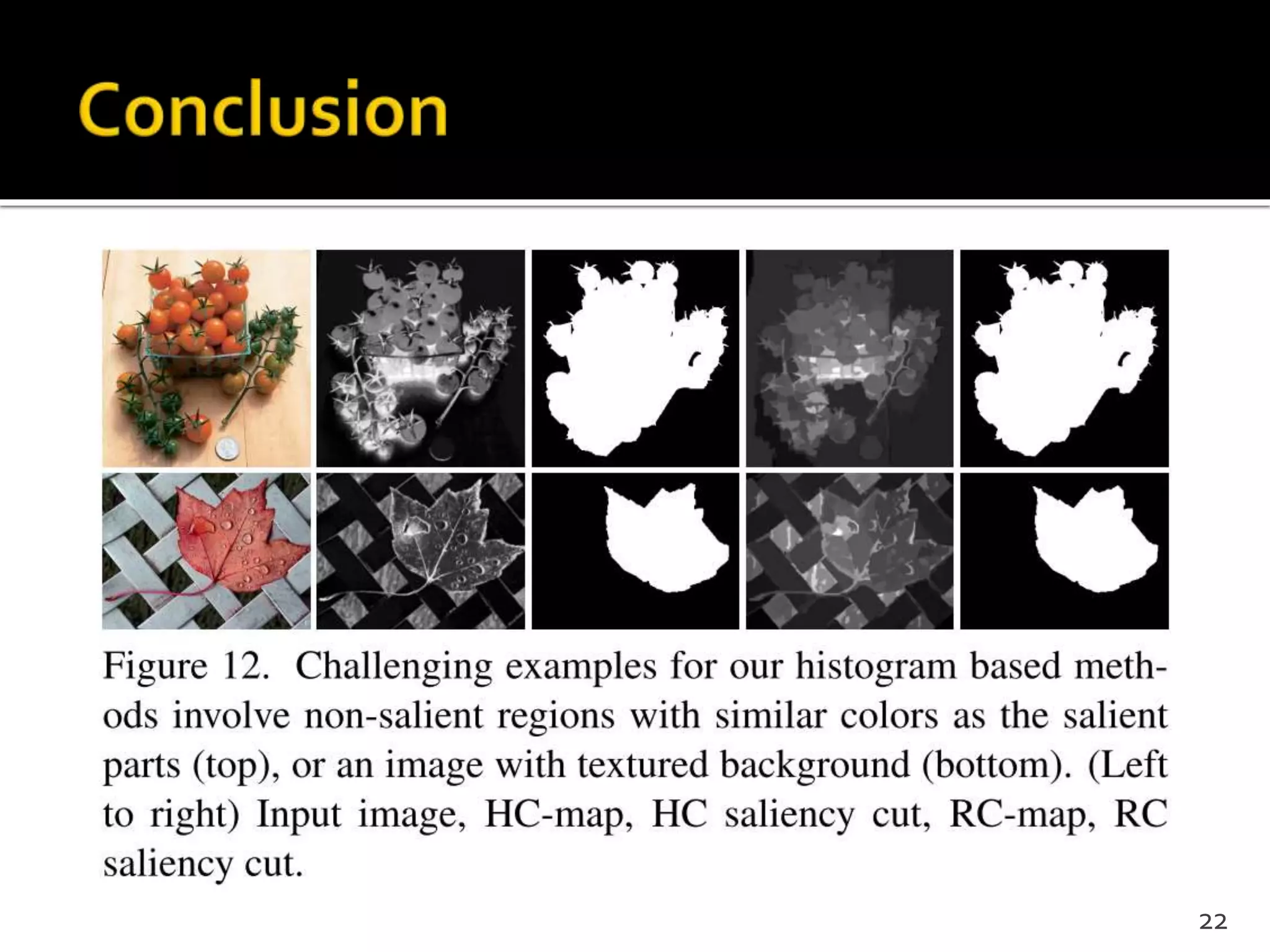
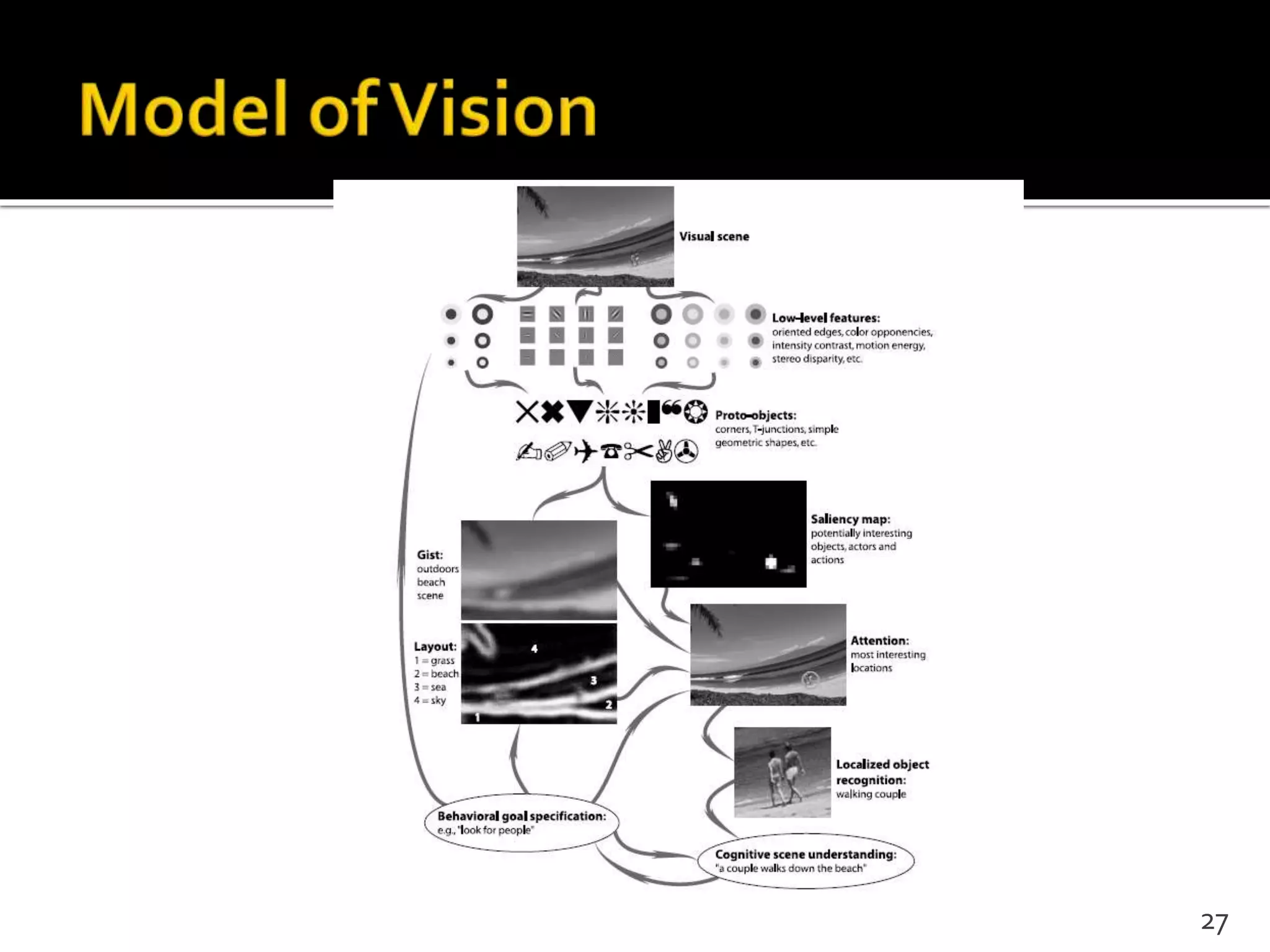
This document proposes a regional contrast based saliency extraction algorithm that separates objects from their surroundings and assigns comparable saliency values within objects. It quantizes color channels to reduce complexity while preserving most frequent colors. Segmentation is performed and saliency values are calculated based on regional color distances and spatial weights. The algorithm achieves state-of-the-art precision and recall rates for extracting salient objects from natural images.