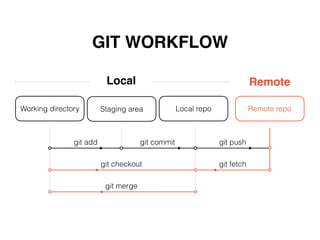
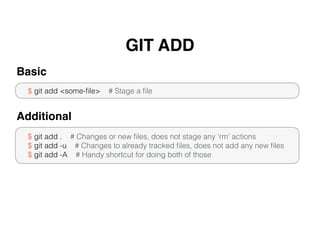
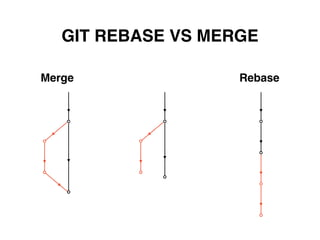
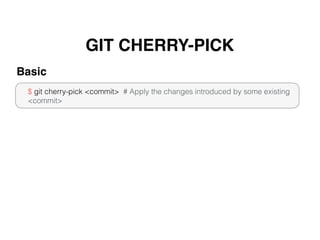
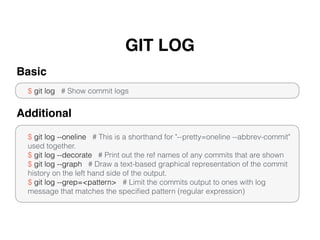
Git is a distributed version control system that doesn't delete files when changes are made. It uses a local repository and staging area to track changes that are committed. Basic configuration involves setting a user name and email. Common commands include git add to stage changes, git commit to commit staged changes, and git push to update a remote repository. Git pull fetches changes and merges them into the local repository. Git reset, checkout, merge, rebase and other commands help manage the commit history and work with remote repositories.