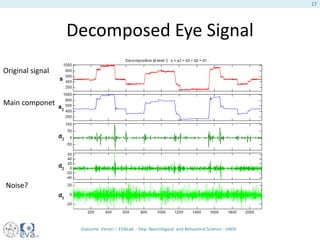
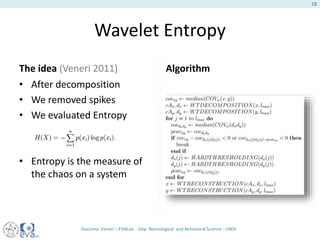
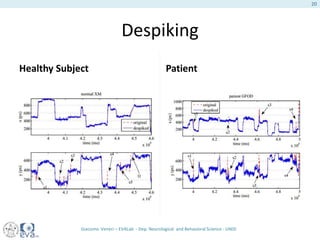
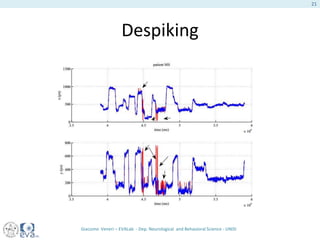
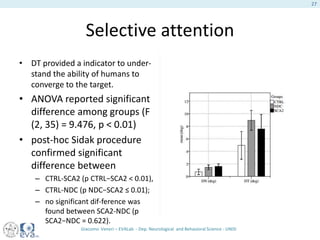
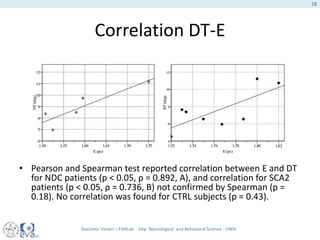
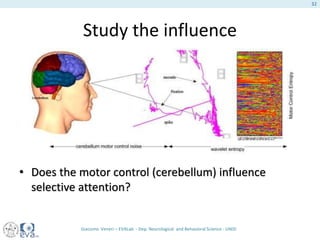
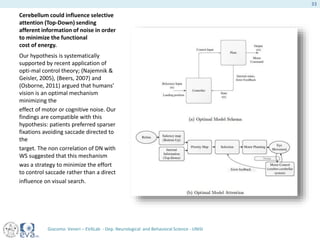
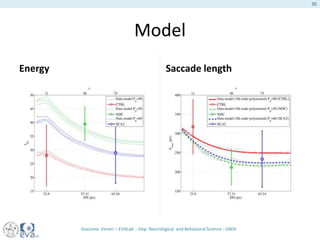
This document presents a study on the influence of motor control, particularly from the cerebellum, on selective attention through methods like entropy analysis and eye tracking. It developed two methodologies: evaluating selective attention and analyzing entropy using wavelet decomposition, aimed at understanding how subjects manage eye movements during visual tasks. The findings suggest that patients adapt their eye fixation strategies to reduce cognitive load, supporting the hypothesis that motor control affects visual search efficiency.


![Methods
1. Veneri, G., Federighi, P., Rosini, F., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2010). Influences of data filtering on human-computer interaction by gaze-contingent
display and eye-tracking applications. Computers in Human Behavior , 26 (6), 1555 - 1563. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2010.05.030 [SCOPUS, ACM]
2. Veneri, G., Federighi, P., Rosini, F., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2011, Mar). Spike removal through multiscale wavelet and entropy
analysis of ocular motor noise: A case study in patients with cerebellar disease. Journal of Neuroscience Methods , 196 (2), 318–326.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.01.006 [MEDLINE, SCOPUS]
3. Veneri, G., Piu, P., Rosini, F., Federighi, P., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2011). Automatic eye fixations identification based on analysis of variance and
covariance. Pattern Recognition Letters , 32 (13), 1588 - 1593. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.06.012 [SCOPUS]
4. Veneri, G., Pretegiani, E., Rosini, F., Federighi, P., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2011, Mar). Evaluating the human ongoing visual search performance by
eye tracking application and se-quencing tests. Comput Methods Programs Biomed . Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2011.02.006
doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2011.02.006 [SCOPUS. MEDLINE, ACM]
5. Veneri, G., Rosini, F., Federighi, P., Federico, A., & Rufa, A.(2012, Feb). Evaluating gaze control on a multi-target sequenc-ing task:
The distribution of fixations is evidence of exploration optimisation. Comput Biol Med , 42 (2), 235–244. Retrieved from
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2011.11.013 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2011.11.013 [SCOPUS. MEDLINE, ACM]
InProceedings
1. Veneri, G., Federighi, P., Pretegiani, E., Rosini, F., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2009). Eye tracking - stimulus integrated semi automatic case base system.
In Proceeding of the 13th world multi-conference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics.
2. Veneri, G., Pretegiani, E., Federighi, P., Rosini, F., & Rufa, A. (2010). Evaluating human visual search performance by monte carlo methods and
heuristic model. In IEEE (Ed.), 10th ieee international conference on information technology and applications in biomedicine (itab 2010). [SCOPUS,
IEEE]
3. Veneri, G., Piu, P., Federighi, P., Rosini, F., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2010, jun.). Eye fixations identification based on statistical analysis - case study. In
Cognitive information processing (cip), 2010 2nd international workshop on (p. 446 -451). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/CIP.2010.5604221 [SCOPUS, IEEE]
Others (posters)
1. Veneri, G., Federighi, P., Rosini, F., Pretegiani, E., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2009). The role of latest fixations on ongoing visual search: a model to
evaluate the selection mechanism. In Rovereto workshop of attention.
2. Veneri, G., Olivetti, E., Avesani, P., Federico, A., & Rufa, A. (2011). Bayesian hypothesis on selective attention. In Rovereto visual attention congress.
Giacomo Veneri – EVALab - Dep. Neurological and Behavioral Science - UNISI
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gveneri2012phddissertation-121210162136-phpapp01-210323200518/85/Giacomo-Veneri-PHD-Dissertation-6-320.jpg)