This document summarizes some of the key enhancements between Java 6 and Java 7, including improved type inference for generics, new syntax for number and string literals, expanded exception handling with multi-catch and try-with-resources, and new concurrency utilities like the Fork/Join framework and NIO watch service. It also covers miscellaneous features like symbolic file links and method handles.









![java.lang.invoke
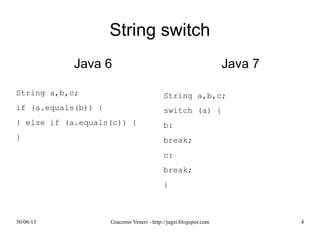
Java 6
class MyClass {
public void myMethod(int i, String j) {
...
}
}
...
Class<?>[] argTypes = new Class[] { int.class, String.class };
meth = MyClass.class. getDeclaredMethod("myMethod", argTypes);
meth.invoke(new MyClass(), 2, "EFG");
Java 7
class MyClass {
public void myMethod(int i, String j) {
...
}
}
...
MethodHandle mh;
MethodType desc = MethodType.methodType(v
mh = MethodHandles.lookup().findVirtual(M
mh.invokeExact(new MyClass(), 1, "ABCDE")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromj6toj7-130630054634-phpapp02/85/From-Java-6-to-Java-7-reference-11-320.jpg)