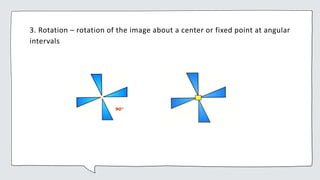
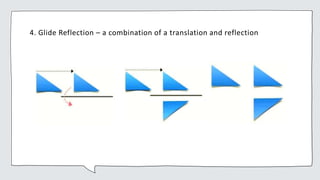
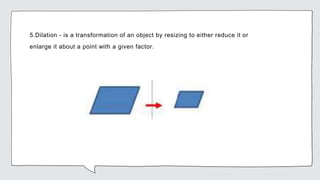
Geometry is the measurement of earth and involves measuring land and building structures. It is used in fields like physics, medicine, geology, mechanical drawing, and astronomy.
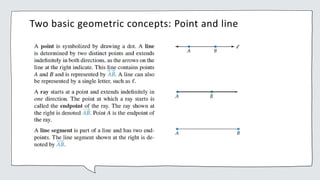
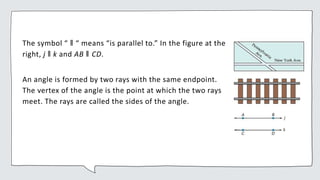
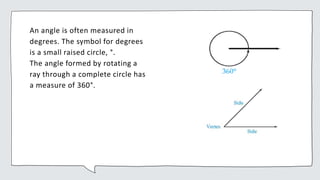
Two basic geometric concepts are points and lines. A plane is a flat surface that extends forever. Figures in a plane are called plane figures. Lines can intersect or be parallel. An angle is formed by two rays with the same endpoint. Angles are often measured in degrees.
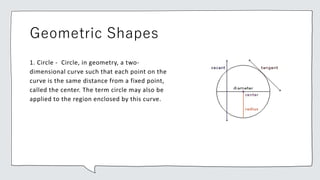
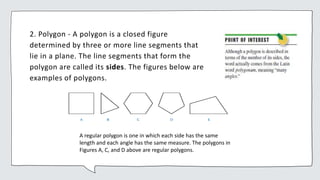
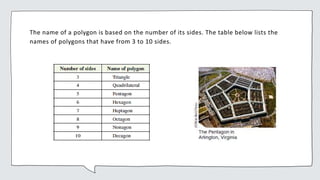
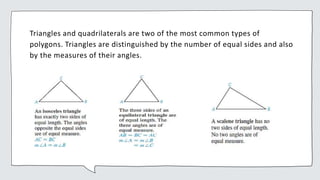
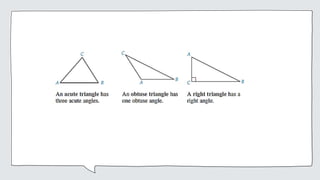
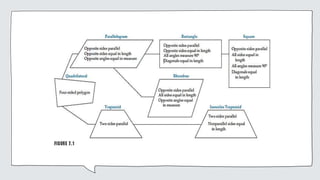
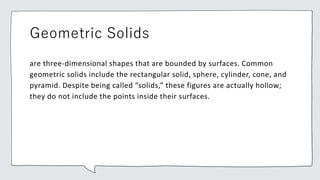
Common geometric shapes include circles, polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals, and geometric solids. Polygons are closed figures made of three or more line segments. Common solids are rectangular solids, spheres, cylinders, cones, and pyramids.