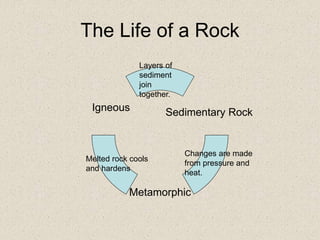
Rocks undergo changes through various natural processes. Sedimentary rock is formed through the compression of sediment layers, metamorphic rock is formed from changes caused by heat and pressure to other rock types, and igneous rock is formed by the cooling and hardening of melted rock. Rocks break down through weathering and erosion over time and the fragments can form new types of rock in a continuous cycle. Fossils preserved in sedimentary rock provide evidence of past life and the age of the earth.