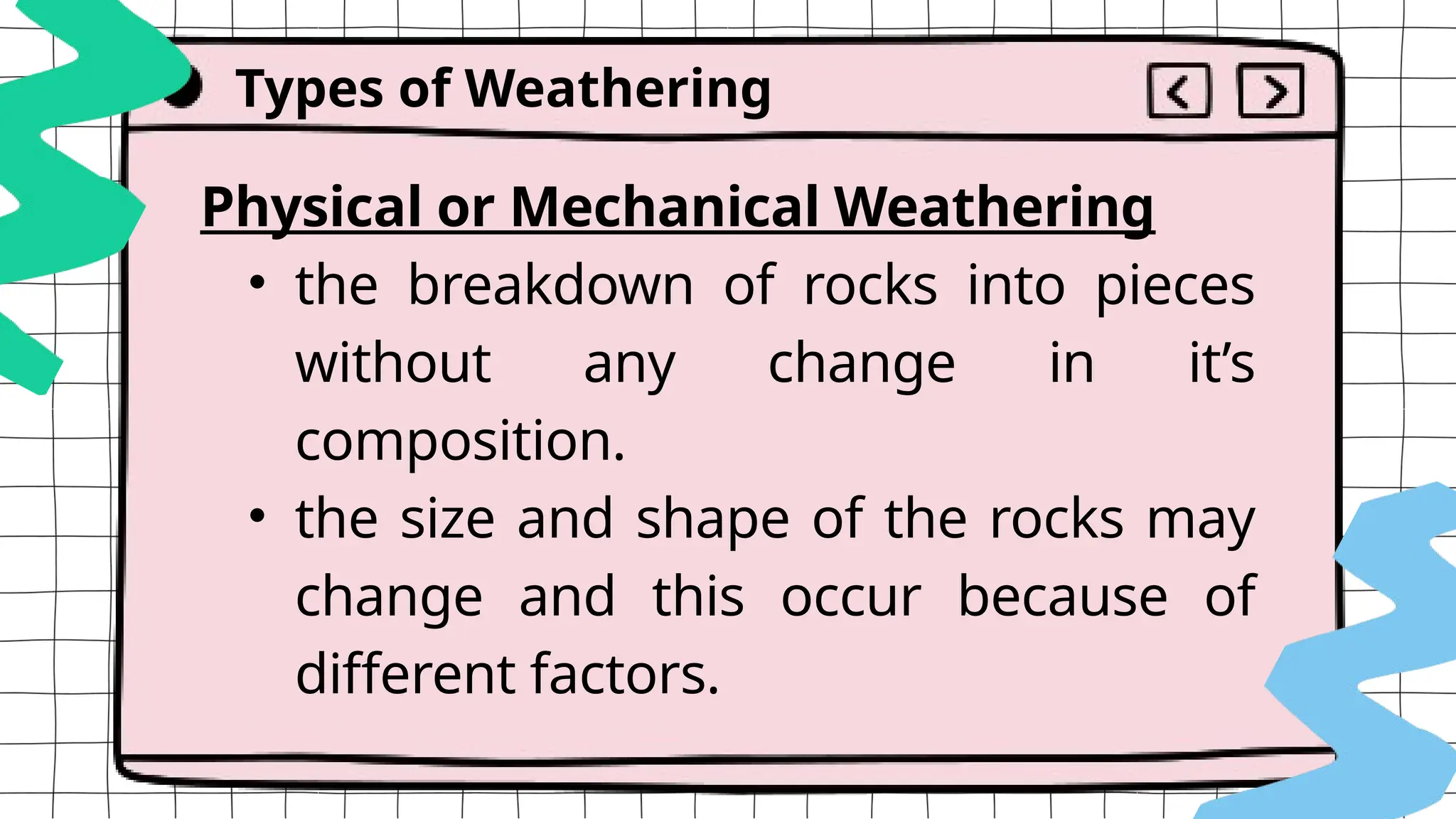
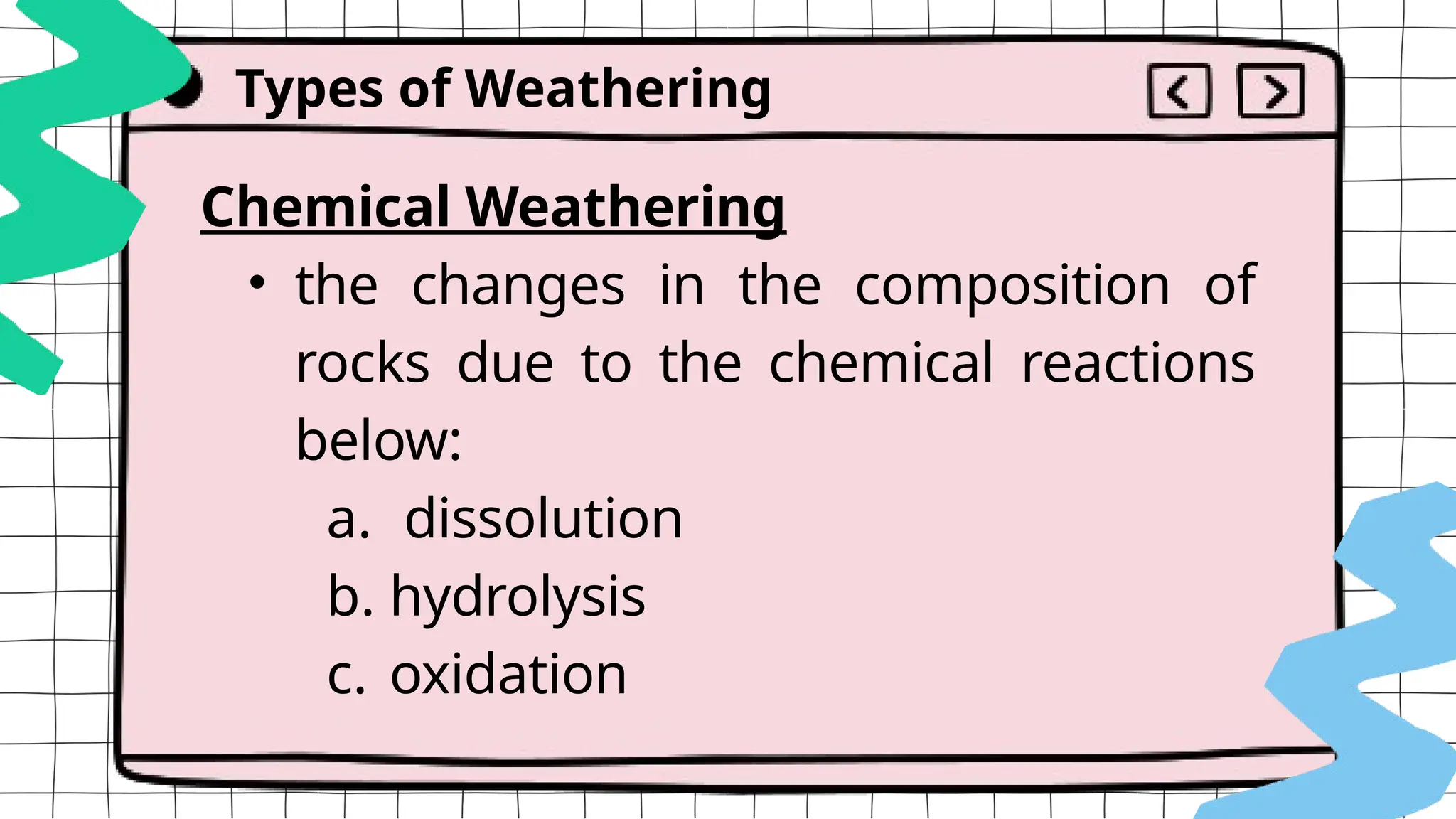
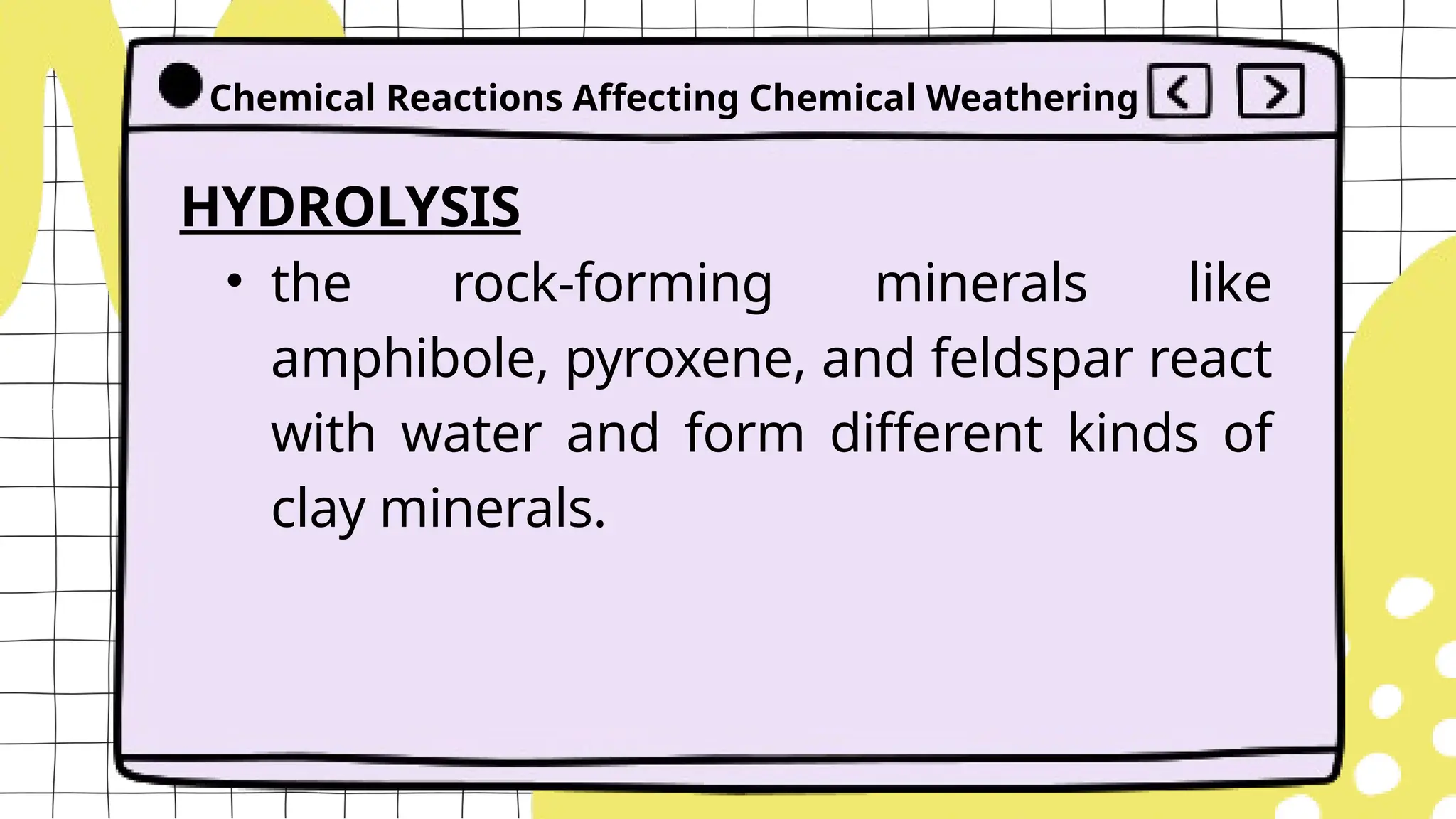
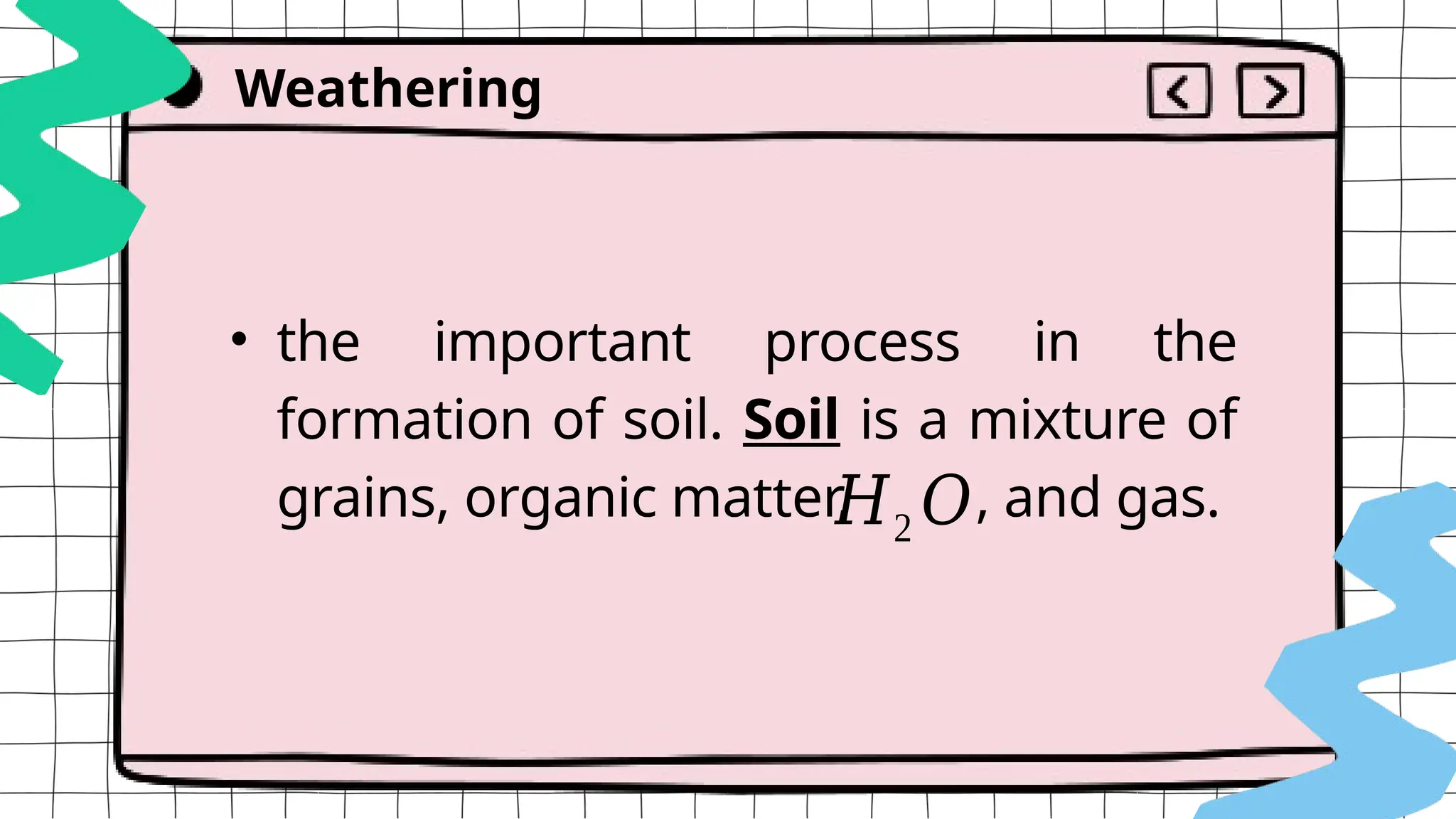
The document discusses geologic processes on Earth, categorizing them into exogenic and endogenic processes. It details exogenic processes, including weathering (physical, chemical, and biological), erosion and sedimentation, as well as factors affecting these processes such as temperature and human activity. Additionally, it explains mass wasting, which involves the settling of weathered materials due to erosion.