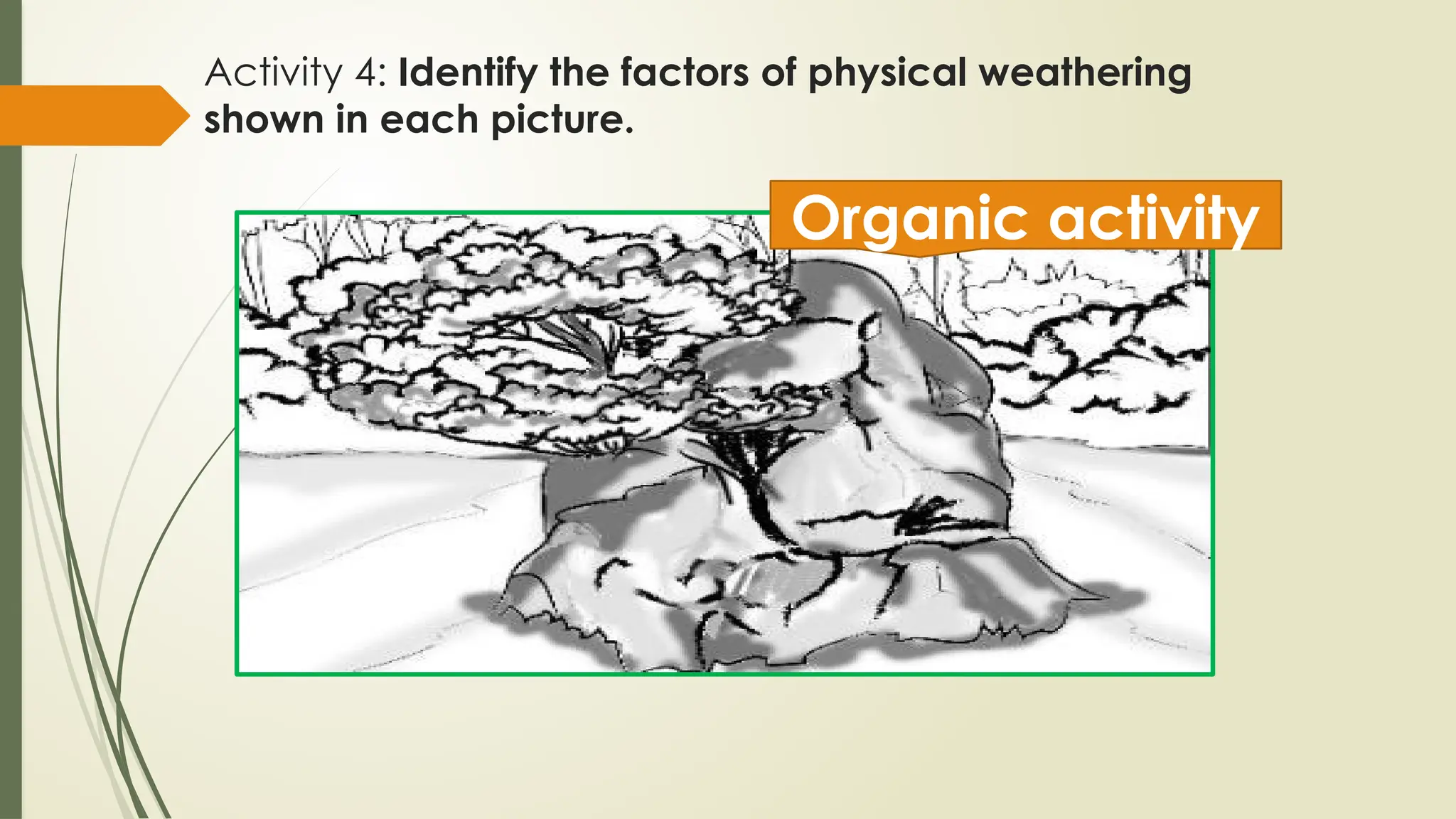
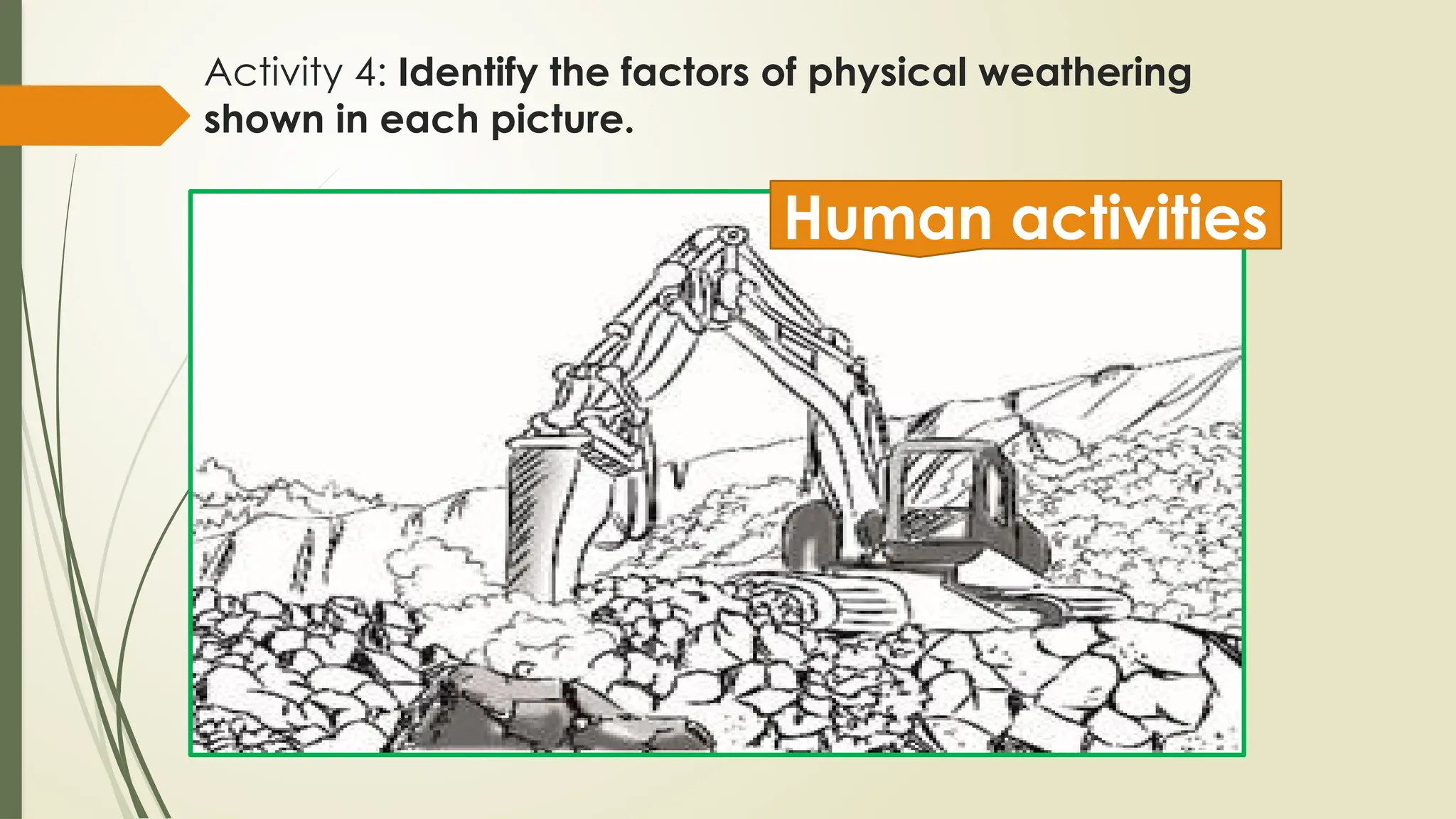
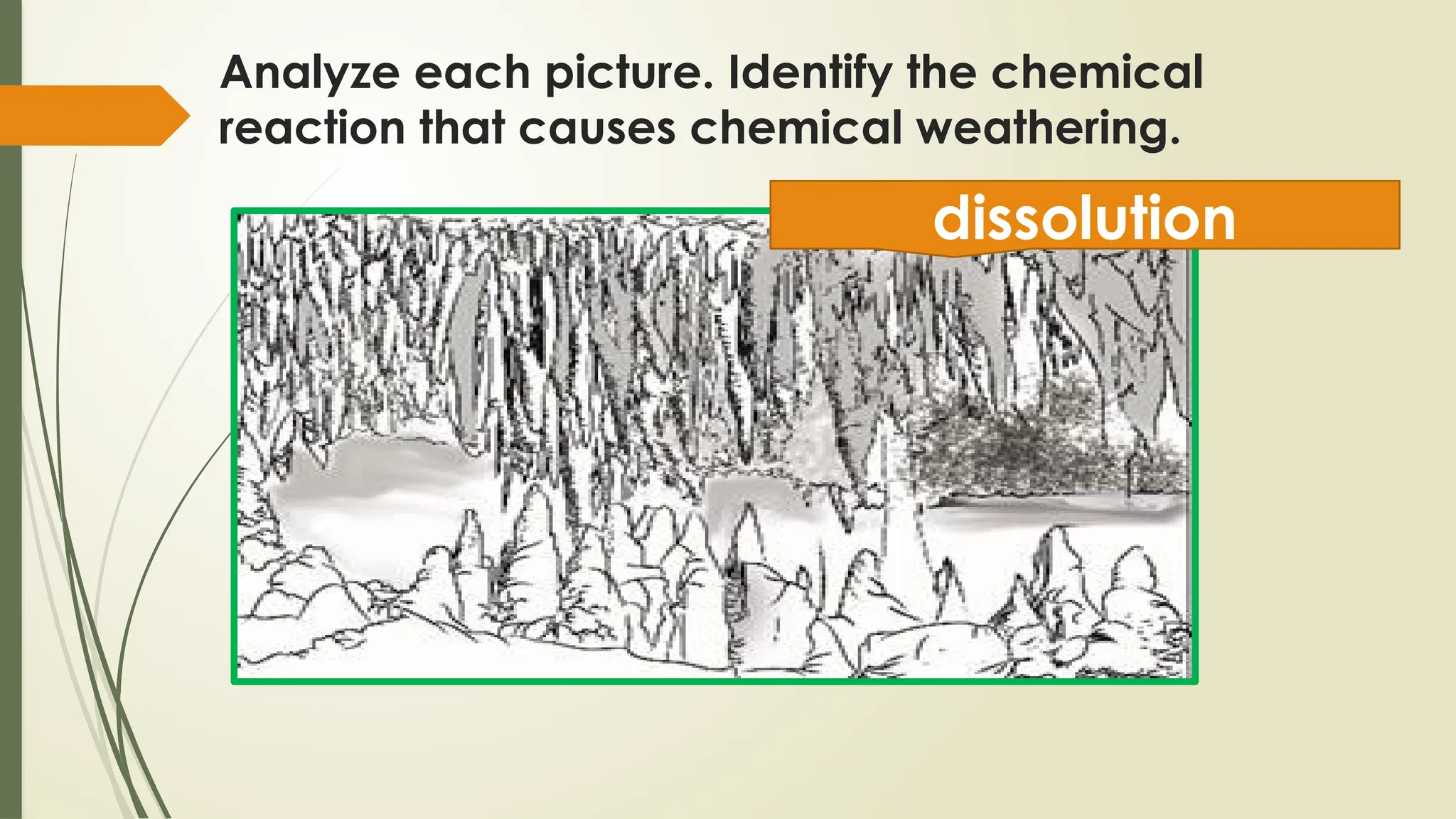
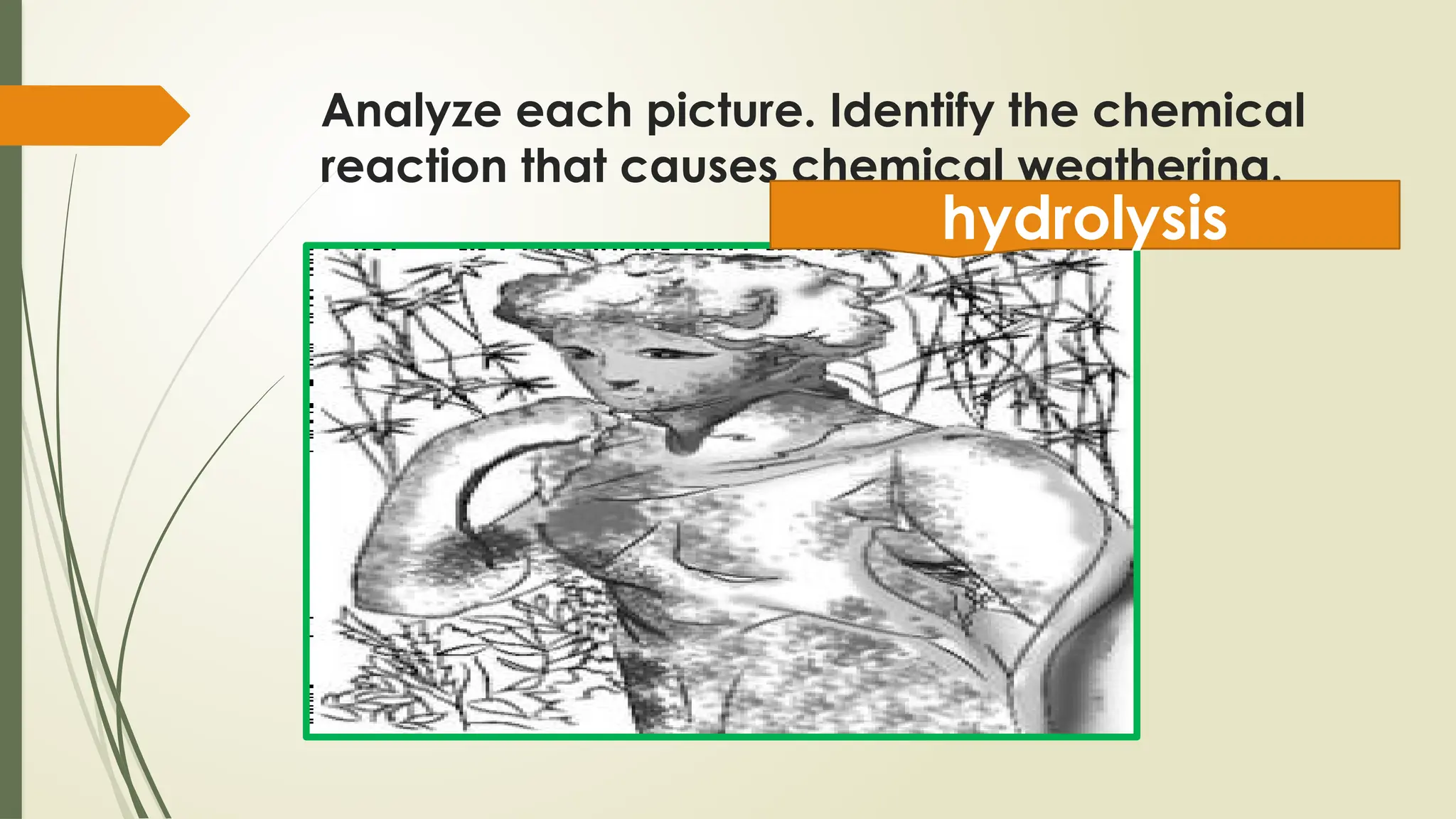
The document discusses exogenic processes that occur on the Earth's surface, including weathering and erosion, which are primarily driven by water, ice, and wind. It distinguishes between mechanical weathering, which breaks down rocks without changing their composition, and chemical weathering, which alters their composition through reactions. Additionally, the document covers factors influencing these processes, such as pressure, temperature, and human activities, as well as the processes of erosion and mass wasting.