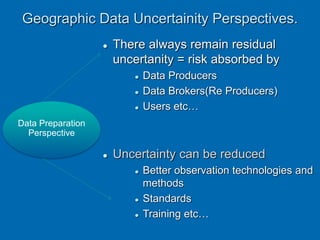
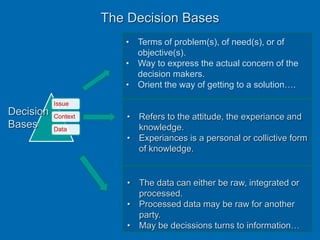
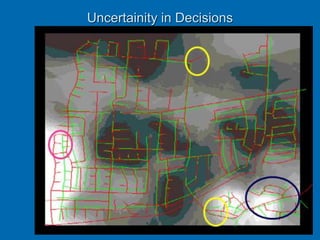
The document discusses geographic data uncertainty and its impact on decision-making processes, detailing various facets of uncertainty that arise from data quality and interpretation. It presents a model of decision-making that encompasses documentation, analysis, taking, implementation, and evaluation phases, highlighting the continuous presence of uncertainty throughout these steps. Additionally, it emphasizes the ethical responsibilities associated with data quality, advocating for the use of safeguards and adherence to professional codes of ethics to mitigate risks.