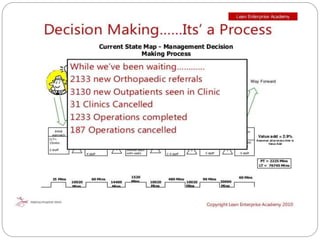
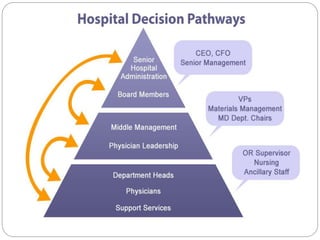
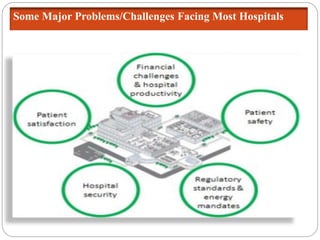
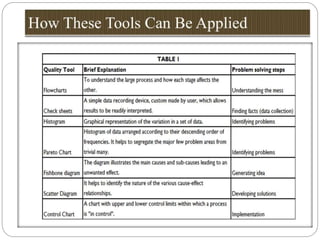
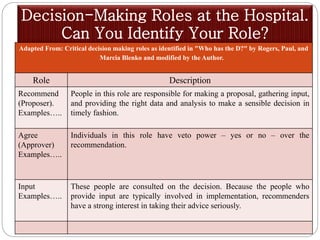
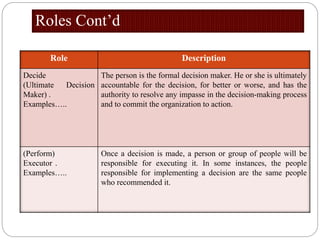
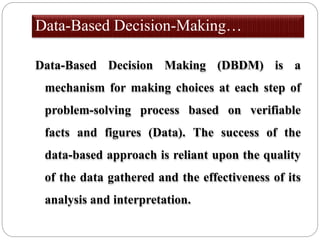
The document outlines a training session for healthcare professionals focused on data-driven problem solving and decision-making in hospital management. Participants will learn to identify healthcare challenges, apply various tools for problem solving, and enhance data collection and analysis to improve hospital outcomes. Key topics include the stages of problem solving, roles in decision-making, and the importance of data quality in supporting effective decisions.