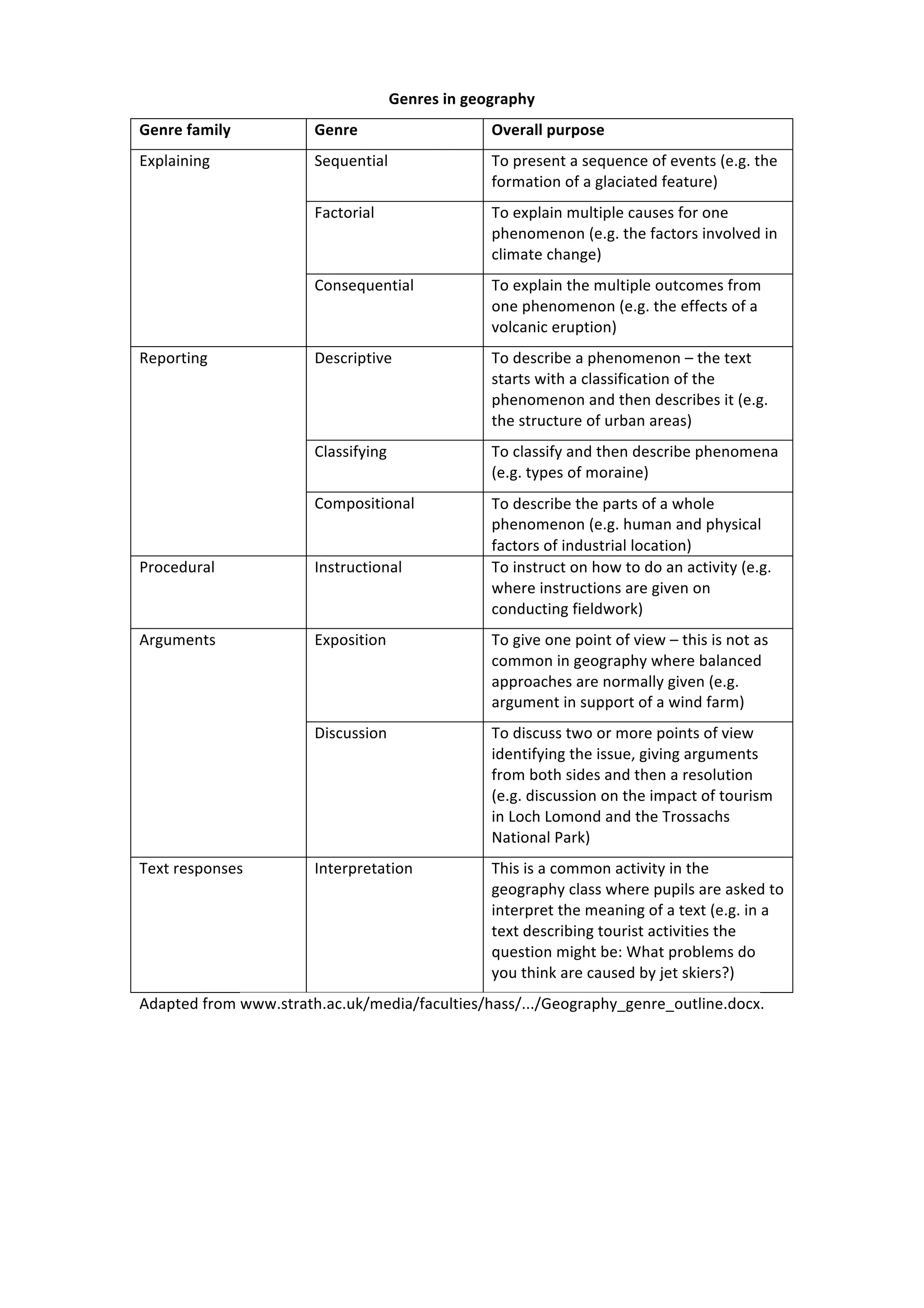
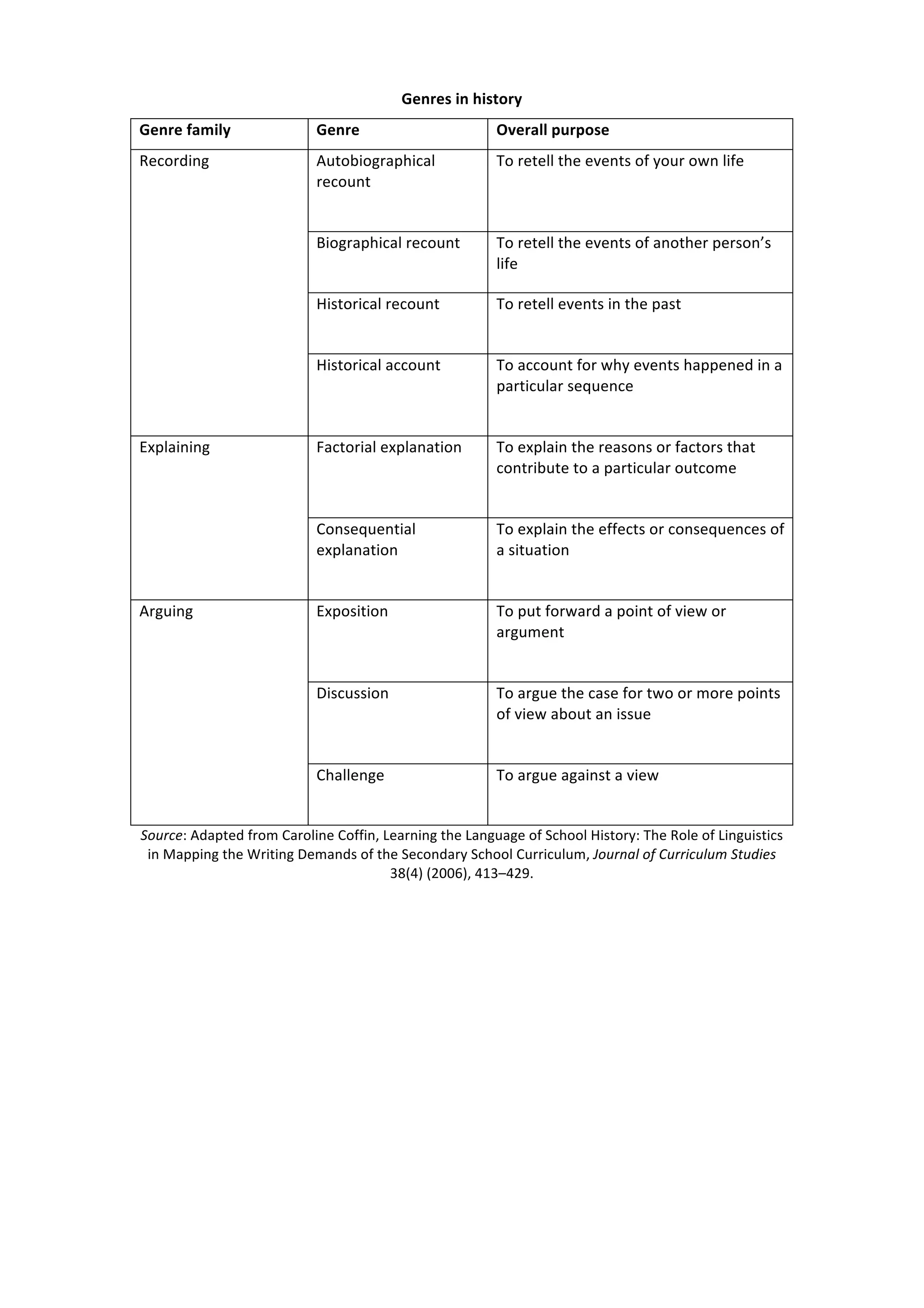
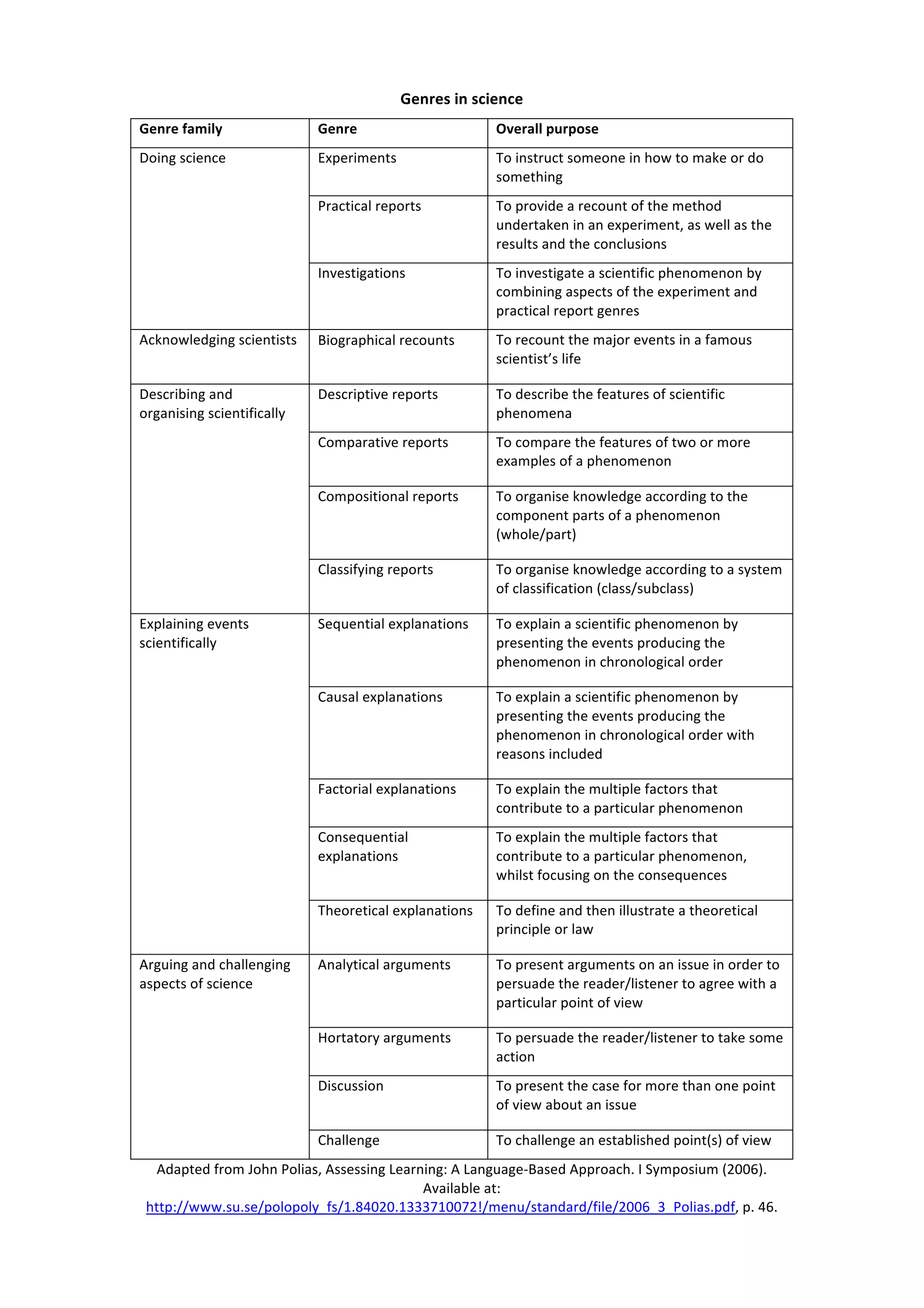
The document discusses different genres used in geography, history, and science. In geography, genres include sequential, factorial, and consequential explanations to present processes, causes, and effects. Descriptive genres provide classifications and descriptions of phenomena. In history, genres involve recording events through recounts and accounts, as well as explaining factors and consequences. Science genres encompass experimentation, descriptions, explanations through sequences, factors, and consequences, as well as arguments and challenges. The genres are used to organize and communicate information for different purposes.