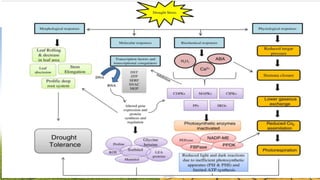
This document discusses using genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches to improve drought tolerance in opium poppy (Papaver somniferum.L). It identifies several genes involved in drought response pathways like signal perception, transcriptional control, and ion homeostasis. The document outlines a study to subject poppy plants to artificial drought, analyze relative water content and proline levels, perform transcriptomic and proteomic analyses to identify responsive genes and proteins, and validate targets using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. The overall goal is to identify mechanisms of drought tolerance at the gene and protein level to breed more drought-resistant poppy varieties.