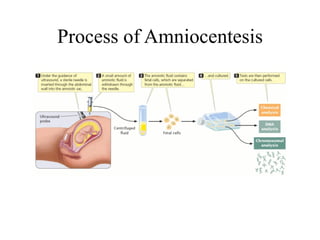
Genetic screening uses techniques like karyotyping, amniocentesis, and preimplantation genetic diagnosis to detect abnormalities or predict diseases. Karyotyping examines chromosomes for changes in number or structure. Amniocentesis analyzes amniotic fluid samples for fetal DNA, while chorionic villus sampling tests placental tissue. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis screens embryos before implantation. Genetic screening can prevent birth defects but also raises issues regarding which conditions to test for and the social impact of results.