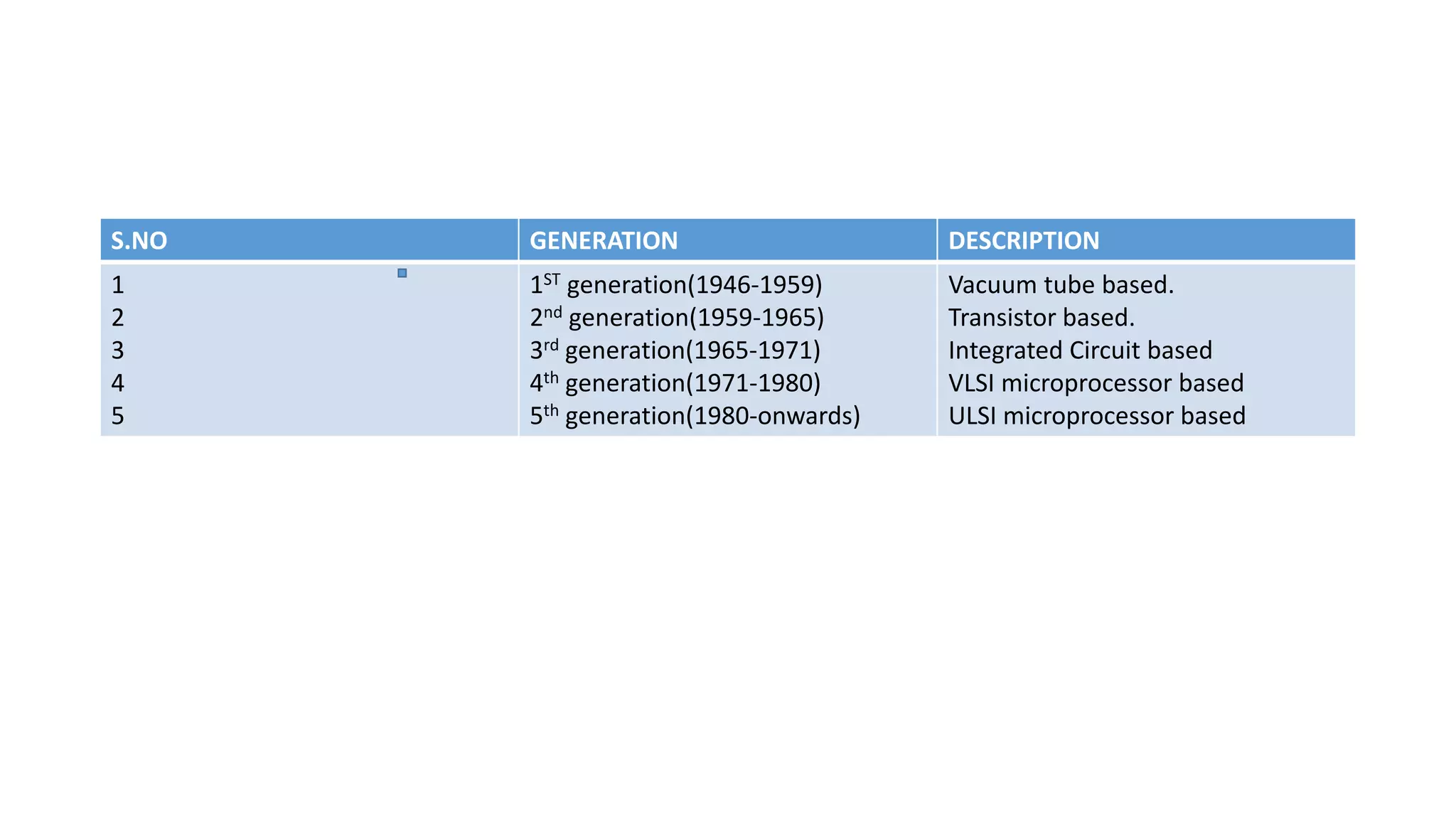
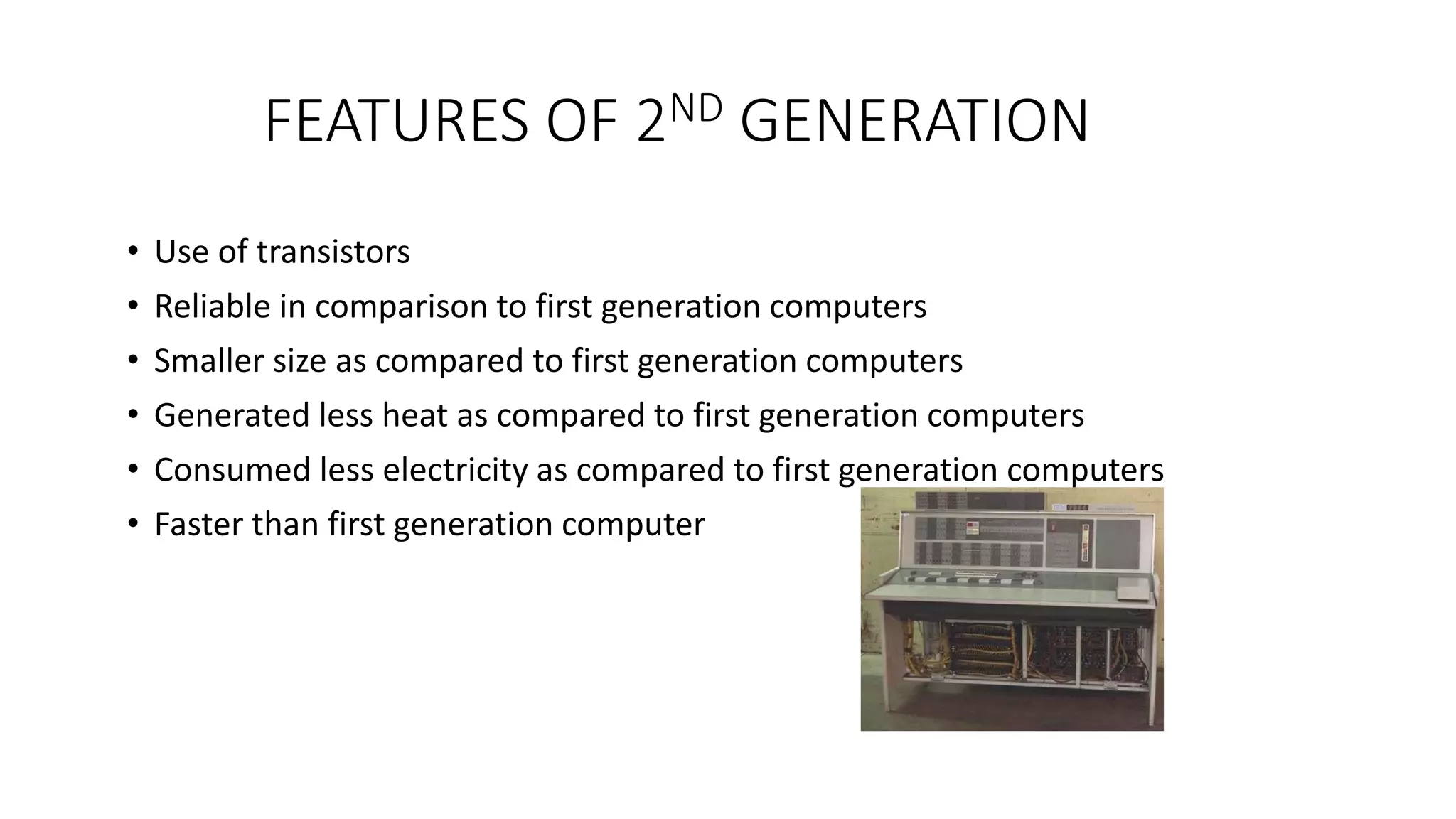
The document summarizes the five generations of computers from the first to the fifth generation. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were unreliable, costly, and generated a lot of heat. The second generation used transistors which were more reliable and smaller. The third generation used integrated circuits which were even more reliable and smaller. The fourth generation used microprocessors and were very small, portable, and reliable. The fifth generation uses ultra-large scale integration and is focused on parallel processing and artificial intelligence.