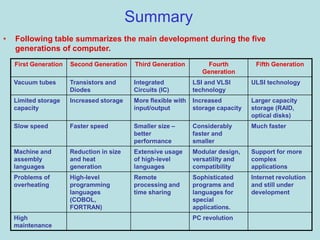
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. Each generation saw improvements in technology, from vacuum tubes in first generation computers to integrated circuits and microprocessors today. Key developments included increased processing speed and memory capacity, smaller size and power consumption, multi-user systems, high-level programming languages, personal computers, and networking capabilities like the internet.