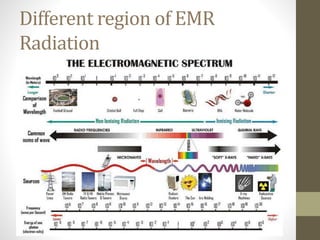
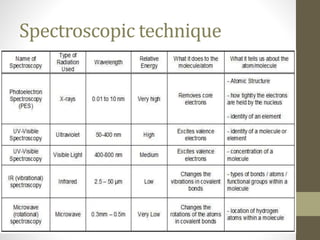
The document provides an overview of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) and its various regions, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and X-rays. It describes the instruments used in spectroscopy, including various light sources and detectors, as well as the materials for cell construction. Additionally, it outlines Beer’s Law and Lambert’s Law regarding light absorption in relation to the concentration of solutes and the path length.