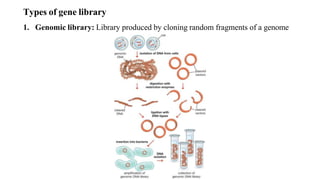
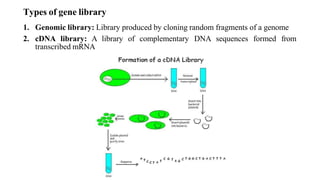
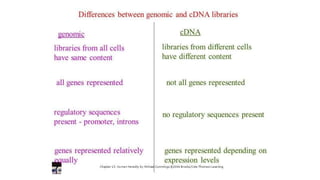
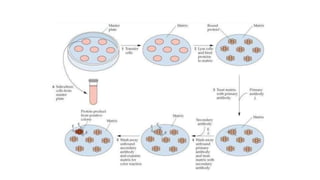
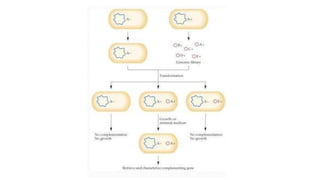
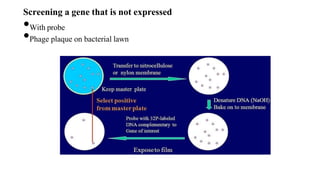
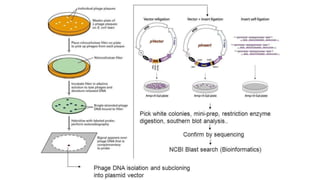
Gene libraries contain cloned DNA fragments from an organism that can represent the full genome. Genomic libraries contain random fragments of genomic DNA inserted into vectors, while cDNA libraries contain transcribed mRNA sequences. Genomic libraries require DNA fragmentation, appropriate vector selection based on genome size, and ligation into vectors. Screening identifies clones containing genes of interest using probes, phenotypic assays, antibiotic resistance, or complementation of mutant strains.