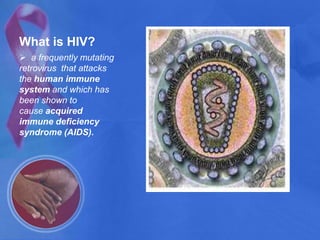
HIV originated in non-human primates in Africa and was transferred to humans in the late 19th/early 20th century. It attacks CD4+ T cells and can be spread through bodily fluids. There are two main types, HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV is not spread through air, water, insects, or casual contact. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the later stage of HIV when the immune system is severely damaged. Sub-Saharan Africa has been most heavily affected, with 68% of global cases. Women and children in Africa are especially vulnerable victims due to gender inequality, violence, lack of inheritance/property rights, and inability to negotiate condom use or number of partners